Abstract
Purpose
This study was performed to compare macular retinal thickness measured by four different optical coherence tomography (OCT) devices.
Methods
Macular retinal thicknesses were measured in 32 healthy eyes of 32 subjects by using Cirrus HD-OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec, Inc., Dublin, CA, USA), Spectralis OCT (Heidelberg engineering, Heidelberg, Germany), Topcon DRI OCT (Topcon Corp., Tokyo, Japan), and RS-3000 Advance OCT (Nidek, Co., Ltd., Gamagori, Japan). Macular retinal thickness measurements were compared among the devices.
Results
Average macular retinal thickness ranged 288.7 to 313.3 µm (p < 0.01). Differences in average macular retinal thickness among the devices ranged from 0.7 to 27.3 µm; the limit of agreement (LoA) ranged from 9.7 to 24.4 µm. Among the devices, comparison between Spectralis OCT and RS-3000 Advance OCT showed the smallest difference in average macular retinal thickness (mean, 0.7 µm) and the narrowest LoA (−6.4 to 3.3 µm).
Figures and Tables
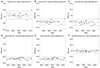 | Figure 1Bland-Altman plots for agreement of macular retinal thickness as measured by different optical coherence tomography (OCT) devices. Upper and lower dashed lines indicate limit of agreement and middle dashed lines present mean difference between the devices (A, Cirrus HD-OCT versus Topcon DRI OCT; B, Cirrus HD-OCT versus RS-3000 Advance OCT; C, Cirrus HD-OCT versus Spectralis OCT; D, Topcon DRI OCT versus RS-3000 Advance OCT; E, Topcon DRI OCT versus Spectralis OCT; F, RS-3000 Advance OCT versus Spectralis OCT). |
References
1. Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, et al. Comparison of macular thickness measurements between time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:4893–4897.

2. Kiernan DF, Hariprasad SM, Chin EK, et al. Prospective comparison of cirrus and stratus optical coherence tomography for quantifying retinal thickness. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:267–275.

3. Forooghian F, Cukras C, Meyerle CB, et al. Evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in the measurement of diabetic macular edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:4290–4296.

4. Kakinoki M, Sawada O, Sawada T, et al. Comparison of macular thickness between cirrus HD-OCT and stratus OCT. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2009; 40:135–140.

5. Legarreta JE, Gregori G, Punjabi OS, et al. Macular thickness measurements in normal eyes using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2008; 39:S43–S49.

6. Wolf-Schnurrbusch UE, Ceklic L, Brinkmann CK, et al. Macular thickness measurements in healthy eyes using six different optical coherence tomography instruments. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50:3432–3437.

7. Giani A, Cigada M, Choudhry N, et al. Reproducibility of retinal thickness measurements on normal and pathologic eyes by different optical coherence tomography instruments. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 150:815–824.

8. Lammer J, Scholda C, Prünte C, et al. Retinal thickness and volume measurements in diabetic macular edema: a comparison of four optical coherence tomography systems. Retina. 2011; 31:48–55.
9. Mylonas G, Ahlers C, Malamos P, et al. Comparison of retinal thickness measurements and segmentation performance of four different spectral and time domain OCT devices in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:1453–1460.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download