Abstract
Objectives
This study was designed to investigate the intrapsychic factors affecting the quality of life of patients with chronic schizophrenia.
Methods
Quality of life was measured using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Scale-Brief (WHOQOL-BREF) in 72 community-dwelling patients with schizophrenia. Demographic status, psychopathology, independent living skill, and insight were examined. Based on this, correlation analysis between each scale and multiple regression analysis was performed to examine the factors that can predict the quality of life.
Results
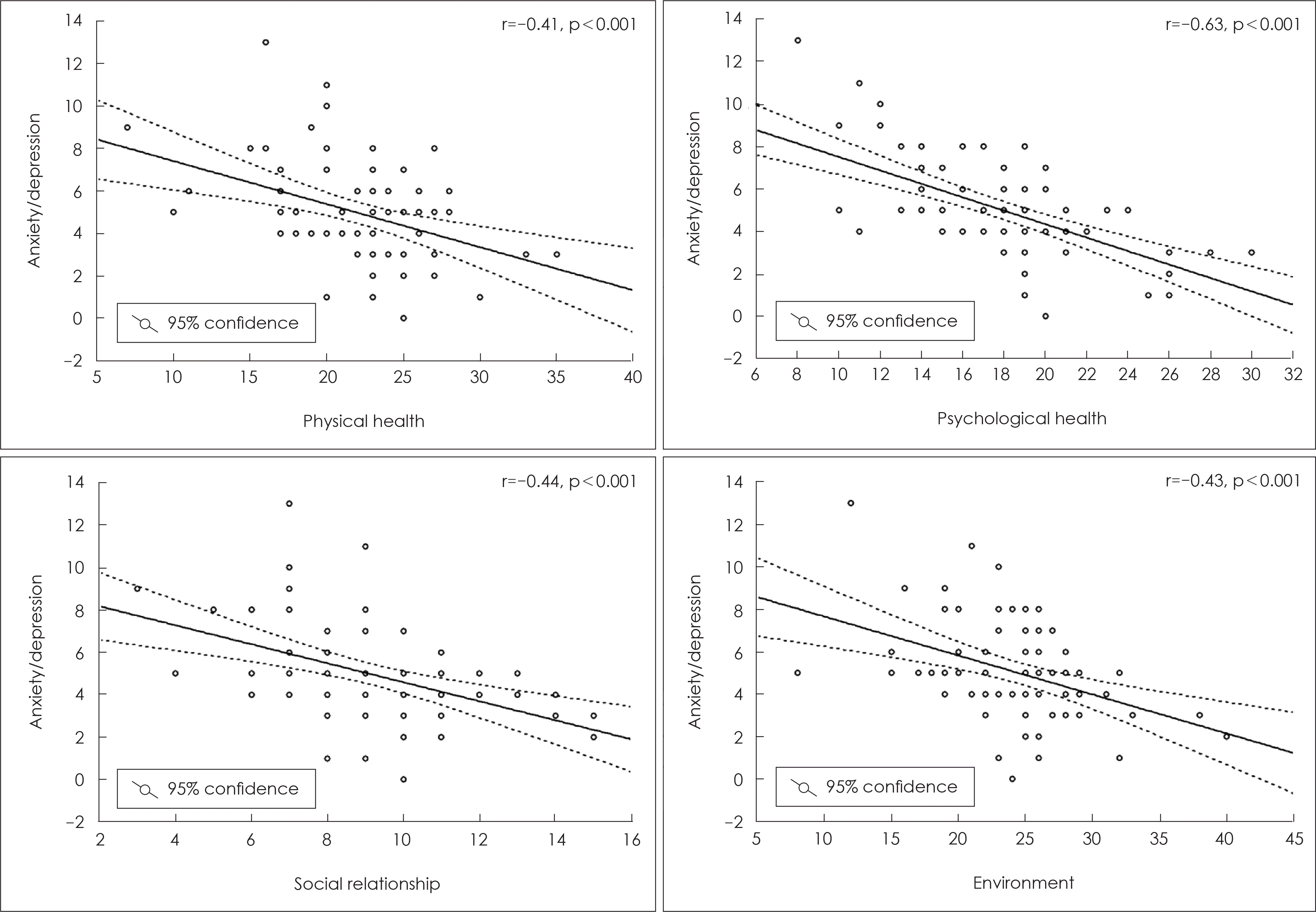
: The illness duration was over 10 years in 79.2% of patients. The patients with 10–20 years of illness duration showed lower scores of quality of life than those with less than 10 years or more than 20 years. Anxiety/depressive symptom, hostile/suspi-ciousness were associated with quality of life scores. Among those, anxiety/depressive symptom was the strongest predictor of quality of life in patients with chronic schizophrenia.
Go to : 
References
1. Davies LM, Drummond MF. Economics and schizophrenia: the real cost. Br J Psychiatry. 1994; Suppl:18–21.

2. Eack SM, Newhill CE. Psychiatric Symptoms and Quality of Life in Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis. Schizophr Bull. 2007; 33:1225–1237.

3. Lee KU, Bahk WM. A New Goal of Treatment for Schizophrenia: Quality of Life. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2006; 17:13–23.
4. The WHOQOL group, WHO, Div of Mental Health, Geneva. The World Health Organization Quality of Life assessment (WHOQOL): position paper from the World Health Organization. Soc Sci Med. 1995; 41:1403–1409.
6. Sainfort F, Becker M, Diamond R. Judgments of quality of life of individuals with severe mental disorders: Patient self-report versus provider perspectives. Am J Psychiatry Apr. 1996; 153:497–502.
7. Kook SH, Son CN. The Development of Happy-QoL Scale for Assessing the Quality of Life in Patients with Schizophrenic Disorder. Kor J Clin Psychol. 2002; 21:665–691.
8. Kim JH, Yim SJ, Min SK, Kim SE, Son SJ, Diane JW, et al. The Korean Version of 4th Revision of Schizophrenia Quality of Life Scale: Validation Study nad Relationship with PANSS. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2006; 45:401–410.
9. Yoon JS, Kook SH, Lee HY, Lee C, Paik IH. The Development of a Korean Modification of the Scale to Measure Subjective Well-Being under Neuroleptic Treament (KmSWN). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000; 39:987–998.
10. McNary SW, Lehman AF, O'grady KE. Measuring subjective life satisfaction in persons with severe and persistent mental illness: A measurement quality and structural model analysis. Psychol Assess.
11. Ha HS, Won SD, Choi H, Kim EJ, Lee JH. The Effect of Depressive Symptoms and Emotional Awareness on the Quality of Life in Schizophrenic Patients. J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry. 2012; 18:55–62.
12. 오진승. 조현병 환자의 주관적 안녕감에 영향을 미치는 변인. 서 울: 고려대학교 대학원;. 2013.
13. 장창현. 지역 정신보건센터에 등록된 조현병 환자의 삶의 질 및 관련 정신사회적 요인. 서울: 한양대학교 대학원;2014.
14. Kokacya MH, Virit O, Çöpoğlu ÜS, Savaş H, Ari M, Bahçeci B. Symptomatic remission determines functional improvement and quality of life in Schizophrenia. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2016; 53:328–333.

15. Fontanil Gómez Y, Alcedo Rodríguez MÁ, Gutiérrez López MI. Personal and macro-systemic factors as predictors of quality of life in chronic schizophrenia. Psicothema. 2017; 29:160–165.
16. Savill M, Orfanos S, Reininghaus U, Wykes T, Bentall R, Priebe S. The relationship between experiential deficits of negative symptoms and subjective quality of life in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2016; 176:387–391.

17. Voruganti L, Heslegrave R, Awad AG, Seeman MV. Quality of life measurement in schizophrenia: reconciling the quest for subjectivity with the question of reliability. Psychol Med. 1998; 28:165–172.

18. 최지혜. 만성조현병 환자의 자아존중감과 우울 및 삶의 질. 서울: 성신여자대학교 일반대학원;. 2016.
19. 진정애. 만성정신질환의 삶의 질에 영향을 미치는 요인. 서울: 서울 시립대학교 도시과학대학원;. 2014.
20. Berlim MT, Pavanello DP, Caldieraro MA, Fleck MP. Reliability and validity of the WHOQOL BREF in a sample of Brazilian outpatients with major depression. Qual Life Res. 2005; 14:561–564.

21. Melo-Neto VLd. Valença AM, Nascimento I, Lopes FL, Nardi AE. Quality of life assessment by WHOQOL-BREF in panic disorder patients during treatment. Rev Psiquatr Clin. 2008; 35:49–54.
22. Hwang SK, Kim HC, Lee MJ, Cho HJ, Jun TY, Lee MS, et al. The Effect of Antidepressant Treatment on Quality of Life in Parients with Depressive Disorder. J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry. 2011; 17:112–120.
23. Kim SJ, Kim YS, Yoo SW. The Quality of Life in Patients with Panic Disorder. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2001; 40:407–415.
24. Gomes E, Bastos T, Probst M, Ribeiro JC, Silva G, Corredeira R. Quality of life and physical activity levels in outpatients with schizophrenia. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2016; 38:157–160.

25. Hofer A, Kemmler G, Eder U, Edlinger M, Hummer M, Fleischhacker WW. Quality of life in schizophrenia: the impact of psychopathology, attitude toward medication, and side effects. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004; 65:932–939.
26. Hofer A, Mizuno Y, Wartelsteiner F, Wolfgang Fleischhacker W, Frajo-Apor B, Kemmler G, et al. Quality of life in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: The impact of symptomatic remission and resilience. Eur Psychiatry. 2017; 46:42–47.

27. Maat A, Fett AK, Derks E, Investigators G. Social cognition and quality of life in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2012; 137:212–218.

28. Makara-Studzinska M, Wolyniak M, Krys K. Influence of anxiety and depression on quality of life of people with schizophrenia in the eastern region of poland. ISRN Psychiatry. 2012; 2012:839324.

29. Munikanan T, Midin M, Daud TIM, Rahim RA, Bakar AKA, Jaafar NRN, et al. Association of social support and quality of life among people with schizophrenia receiving community psychiatric service: A cross-sectional study. Compr Psychiatry. 2017; 75:94–102.

30. Kim MH, Kong BG, Jung DU, Kang JW, Moon JJ, Kim JE, et al. Effects of Antipsychotics-Induced Amenorrhea on Attitudes Toward Treatment and Quality of Life in Women with Schizophrenia. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2011; 22:199–207.
31. Kim YH, Yun KW, Kim MK, Lee HJ. A Study on Depression, Anxiety and Quality of Life in Amenorrhea Schizophrenics Treated with Risperidone. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2004; 43:537–545.
32. Min SK, Park JK, Seo SY, Kim DK. Effects of Haloreridol and Risperidone on the Subjective Quality of Life in Stable Chronic Schizophrenic Patients. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2002; 41:76–83.
33. Ko H, Han JH, Kim EJ, Lim J, Sim M, Lee WH. The Relationship between Cognitive Function and Psychosocial Function in Chronic Schizophrenia Patients. Kor J Clin Psychol. 2017; 36:10–19.
34. Min SK, Lee CI, Kim KI, Shin YS, Kim DK. Development of Korean Version of WHO Quality of Life Scale Abbreviated Version (WHOQOL-BREF). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000; 39:571–579.
36. Wallace CJ, Liberman RP, Tauber R, Wallace J. The Independent Living Skills Survey: A comprehensive measure of the community functioning of severely and persistently mentally ill individuals. Schizophr Bull. 2000; 26:631–658.

37. 정명훈. 한국어판 총괄기능평가척도(Global Assessment of Functioning Scale)의 신뢰도와 타당도. 춘천: 한림대학교 대학원;2003.
38. Amador XF, Strauss DH, Yale SA, Flaum MM, Endicott J, Gorman JM. Assessment of insight in psychosis. Am J Psychiatry. 1993; 150:873–879.
39. Song JY, Kim KT, Lee SK, Kim YH, Noh JH, Kim JW, et al. Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Scale to Assessment Unawareness of Mental Disorder (SUMD-K). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2006; 45:307–315.
40. Leucht S, Engel RR, Davis JM, Kissling W, zur Capellen KM, Schmauß M, et al. Equipercentile linking of the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale and the Clinical Global Impression Scale in a catchment area. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012; 22:501–505.

41. Galuppi A, Turola MC, Nanni MG, Mazzoni P, Grassi L. Schizophrenia and quality of life: how important are symptoms and functioning? Int J Ment Health Syst. 2010; 4:31.

42. Ruud T, Aarre TF, Boeskov B, le Husevag PS, Klepp R, Kristiansen SA, et al. Satisfaction with primary care and mental health care among individuals with severe mental illness in a rural area: a seven-year follow-up study of a clinical cohort. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2016; 10:33.

43. Zhou Y, Zhou R, Li W, Lin Y, Yao J, Chen J, et al. Controlled trial of the effectiveness of community rehabilitation for patients with schizophrenia in Shanghai, China. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2015; 27:167–174.
44. Norman RM, Malla AK, McLean T, Voruganti LP, Cortese L, McIntosh E, et al. The relationship of symptoms and level of functioning in schizophrenia to general wellbeing and the Quality of Life Scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000; 102:303–309.

45. Browne S, Roe M, Lane A, Gervin M, Morris M, Kinsella A, et al. Quality of life in schizophrenia: relationship to sociodemographic factors, symptomatology and tardive dyskinesia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996; 94:118–124.

46. An der Heiden W, Leber A, Hafner H. Negative symptoms and their association with depressive symptoms in the longterm course of schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016; 266:387–396.

47. Bottlender R, Sato T, Groll C, Jager M, Kunze I, Moller HJ. Negative symptoms in depressed and schizophrenic patients: how do they differ? J Clin Psychiatry. 2003; 64:954–958.
48. Charzynska K, Kucharska K, Mortimer A. Does employment promote the process of recovery from schizophrenia? A review of the existing evidence. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2015; 28:407–418.

49. Tomotake M. Quality of life and its predictors in people with schizophrenia. J Med Invest. 2011; 58:167–174.

Go to : 
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with schizophrenia (n=72)
Table 2.
Total and categorical mean scores of the WHOQOL BREF, BPRS, ILSS, GAF, and SUMD-K
Table 3.
General linear regression analysis of the predictive factors to overall quality of life scores




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download