INTRODUCTION
Red scrotum syndrome (RSS), also known as male genital dysesthesia, was first described by Fisher in 1997
123. It is a rarely recognized and under reported entity characterized by scrotal erythema, a burning sensation, pain, dysesthesia, increased temperature and sometimes pruritus and the absence of topical treatment response. Important features to distinguish it are sharp demarcation of the erythema and no scaling. The symptoms affect the anterior scrotum and occasionally the proximal penile shaft
45. Men older than 50 years are the most frequently affected. Despite its unknown etiology, in recent years most reports have linked this condition to chronic, topical corticosteroid use in the region
1.
RSS is a diagnosis of exclusion. Common differential diagnoses include tinea cruris, bacterial infections, contact dermatitis, and atopic dermatitis. Histopathological analysis is unremarkable. Clinical diagnostic criteria have been postulated and include persistent scrotal erythema, pain and burning in the area, and the absence of topical treatment response
14. While these criteria have not been validated, scarce literature information on this syndrome render them valuable for classification. Subdiagnosis make treatment information limited.
No standardized RSS treatment is currently available. Current evidence relies on case reports and small case series. Reported treatments with variable response include amitriptyline, doxycycline, carvedilol, gabapentin, and pregabalin
1246789.
The aim of this study is to describe the therapeutic response to pregabalin in patients diagnosed with RSS treated in an outpatient dermatologic clinic in a tertiary-care hospital. A case series was performed. Patients were identified by medical charts review. We received the patient's consent form about publishing all photographic materials. All subjects were evaluated between January 2016 and August 2017 in the dermatology department of the “Dr. José E. González” University Hospital in Monterrey, Mexico. Patients with a diagnosis of RSS, ≥18 years of age, with pregabalin treatment at diagnosis, and at least 1 follow-up consultation were included. Patients with initial treatment with medications other than pregabalin and under 18 years of age were excluded. Seven patients were identified for inclusion. Two were excluded due to initial treatment other than pregabalin and lack of follow-up (
Table 1). Wood's lamp examination was unremarkable in all cases. Potassium hydroxide test (KOH) and fungus culture was performed in all cases with negative result.
CASE REPORT
Case 1
A 28-year-old male patient presented with persistent scrotal erythema and inguinal striae of 6 months duration. He had a previous diagnosis of onychomycosis and tinea cruris treated with itraconazole. He had employed a topical combination cream of betamethasone, gentamicin, and clotrimazole for 14 months in the inguinal region with suspension 6 months before evaluation. He referred erythema, warmth, and dysesthesia. On examination, the patient had scrotal involvement and atrophic inguinal striae. The patient was treated with pregabalin 150 mg at night for 3 months with complete remission.
Case 2
A 53-year-old male patient presented with scrotal erythema of 2 months duration. He had a previous diagnosis in another institution of contact dermatitis in the area. He had employed topical hydrocortisone and other non-specified topical treatments for 2 months. He referred erythema, a burning sensation, and pain in the scrotum. Clinical examination revealed bright-red erythema in the scrotum. No clinical signs or suggestive symptoms of contact dermatitis were noted. The patient had suspended topical treatment 2 months before evaluation. Because of the low-suspicion of contact dermatitis, patch test was considered not appropriate at the time. The patient was treated with pregabalin 150 mg at night for 2 months with complete remission.
Case 3
A 63-year-old male patient presented with scrotal erythema of 3 months duration. He had a previous diagnosis of tinea cruris and had employed a combination cream of betamethasone, gentamicin, and clotrimazole for 1 month. He referred erythema, a burning sensation, and warmth. Clinical examination revealed scrotal erythema. Treatment with pregabalin 150 mg at night for 1 month resulted in complete remission.
Case 4
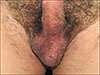
A 57-year-old male patient presented with scrotal and penile erythema of 3 months duration. He had a history of combination cream (betamethasone, gentamicin, and clotrimazole) used for 2 months (
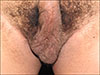
Fig. 1). He referred a 3-month symptomatology of erythema, dysesthesia, pain and warmth. Pregabalin 150 mg nightly and doxycycline 100 mg every 24-hour resulted in complete resolution after 1-month of treatment (
Fig. 2).
Case 5
A 53-year-old male patient presented with scrotal erythema of 3 months duration. He had a previous diagnosis of tinea cruris and had employed desonide and a combination cream of betamethasone/gentamicin/clotrimazole for 2 months. He referred a 3-month symptomatology of erythema, warmth, pain, a burning sensation, pruritus and dysesthesia. Pregabalin 150 mg nightly was prescribed. At 1-month follow-up the patient referred 70% symptomatology improvement with slight drowsiness. After 3 months of therapy, the patient referred complete remission.
DISCUSSION
RSS is an infrequently reported and diagnosed condition. Scarce evidence makes first-line therapy recommendations not currently possible. Furthermore, different etiological theories make therapy approach diverse. RSS has been considered a localized expression of erythromelalgia sharing some clinical characteristics such as erythema and burning pain
18. Rapaport and Rapaport
10 postulated the “steroid addiction” theory linking it to other chronic topical steroid abuse entities like red face syndrome. This steroid abuse may be secondary to previous inflammatory dermatological conditions such as atopic dermatitis or contact dermatitis. Abuse of over-the-counter products with corticosteroids may sometimes resolve the preceding dermatoses with posterior presentation of RSS. Nonetheless, confirmation of use because of other conditions rather than primary RSS symptoms is often not possible. Vasodilatation via nitric oxide secondary to steroid-use may play a fundamental role in RSS pathogenesis
10. Steroid suspension may lighten symptoms although cessation may follow flares and rebound and last months to years or persist chronically
11. Neurogenic inflammation in RSS may explain why predominant symptoms are a burning sensation and dysesthesia/hyperesthesia, and the plausibility of gabapentin and pregabalin treatment success
49.
Diagnosis of RSS is one of exclusion. A myriad of other dermatoses must be considered in the differential diagnosis. Direct mycological examination should be carried out in the presence of tinea suspicion. Tinea incognito is a dermatophytic infection with a modified clinical presentation secondary to topical steroid use. Tinea incognito does not respond to RSS treatment. Additionally, KOH and culture tend to be positive at diagnosis or after steroid discontinuation. When contact dermatitis is suspected, patch-testing should be performed. Contact dermatitis presentation is usually accompanied by erythema, scaling, excoriations, intense inflammation and topography may involve non-scrotal area
19. Although patch testing was not performed in our cases, the clinical symptoms, the erythema distribution and response to pregabalin make this diagnosis unlikely. Atopic dermatitis should be considered when extragenital involvement and additional atopy signs are present
9. While scrotodynia is characterized by a burning sensation or hyperesthesia, it lacks any clinical signs like erythema
9. Other entities such as psoriasis, bacterial infections, and Langerhans cell histiocytosis must considered on a case-to-case basis
9. In cases when psoriasis or Langerhans cell histiocytosis is suspected, histopathological evaluation should be considered.
Clinical diagnostic criteria aid the dermatologist in identifying this condition. Three criteria (scrotal erythema, a burning sensation or pain, and a lack of topical treatment response) have been employed in the literature to define RSS
14. In our experience, the main complaint in patients with RSS is a burning sensation, pain or dysesthesia/hyperesthesia. Pruritus as a main symptomatology must raise suspicion of another diagnosis. Histological examination may reveal in some cases mild lymphocytic perivascular infiltrate and ectatic venules
134. Histopathological examination was not performed in our cases and is not recommended in RSS unless certain specific diseases are suspected.
Treatment of RSS is challenging. Topical treatments are mostly ineffective and not encouraged. Furthermore, systemic therapy has been evaluated in few reports. Large case series and clinical trials are impeded by the rarity of this entity, and there is little current information. Abbas et al.
2 first reported doxycycline treatment in RSS in a case series of 7 patients. A variable improvement of 50% to 80% was noted in the first 2 weeks with a resolution between 2 to 3 months and a mean treatment time of 3.5 months. Another case was reported in 2012 with resolution after 8 months of doxycycline
6. Wollina
9 reported two patients treated with doxycycline, one of which had remission after 1 month of therapy and another with no improvement and switched to gabapentin with mild response. Additionally, Prevost and English
8 reported a patient with symptom improvement after gabapentin but with persistent erythema. Combination treatment was published by Narang et al.
1 in a case series of 12 patients treated with doxycycline and either amitriptyline or pregabalin. Most patients had resolution with 4 to 6 months of therapy, although 2 had relapse after discontinuation. Carvedilol has recently been employed in two patients with good response attributed to vasoconstriction
7.
Pregabalin is a GABAergic anticonvulsant that binds to voltage-sensitive calcium channels
4. It is recommended as one of the first-line treatments of neuropathic pain
12. It has shown some clinical superiority evidence against gabapentin in neuropathic pain
13. Pregabalin effectivity in RSS as monotherapy has only been reported once in two patients who failed or had adverse effects to gabapentin. Both had remission of symptoms despite long-standing disease
4. All cases published so far, including the five ones presented herein, have used low doses of 150 mg/daily. Adverse effects are generally mild and dose dependent. The most common are dizziness and somnolence, which may retreat after several weeks. Discontinuation due to adverse effects is uncommon
14. The four patients with pregabalin monotherapy and one with combination treatment with doxycycline reported herein had complete and prompt remission with a low, nightly dose which suggests that this drug may be considered as part of RSS therapeutic armamentarium.
In our case series of RSS, low-dose pregabalin represented a well-tolerated and effective treatment. No adequate effectiveness or comparison between RSS treatments has been determined, and no first-line option is currently available. Pregabalin monotherapy was previously reported effective in two cases unresponsive to doxycycline and gabapentin. Due to the successful and swift response, we considered pregabalin could be considered a first-line option. Additionally, it has a safe adverse effect profile, and been considered superior to gabapentin in several conditions related to pain. No conclusive evidence between medications effectiveness is currently available, highlighting the need for more reports and disease recognition
4. Additional case series and clinical trials are needed to confirm the best treatment.
 XML Download
XML Download ePub Link
ePub Link Download Citation
Download Citation
 Print
Print