INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study design and registry implementation
Study population and data collection
Primary variable of the subgroup setting
Table 1
Defined combination criteria of previous researchers' and KoCARC TOR rules

1) International BLS TOR rule (TOR-BLS): the combinations were unwitnessed by EMS personnel, no shock delivered, and no prehospital ROSC.11
2) International ALS TOR rule (TOR-ALS): the combinations were unwitnessed by bystanders or EMS personnel, no bystander CPR, no shock delivered, and no prehospital ROSC.11
3) Goto's TOR rule: the combinations were unwitnessed by a bystander, non-shockable rhythm in the field, and no pre-hospital ROSC.12
4) SOS-KANTO's TOR rule: the combinations were unwitnessed by a bystander, asystole in the field and the hospital.13
5) New TOR model 1: the combinations were unwitnessed by a bystander, asystole in the field, and no pre-hospital ROSC.
6) New TOR model 2: the combinations were unwitnessed by a bystander, asystole in the hospital, and no pre-hospital ROSC.
Main outcome measurement
Statistical analysis
Ethics statement
RESULTS
Characteristics of the entire study subjects
Characteristics of patients with initial ECG at field and in the ED
Table 2
Patient characteristics by type of documented ECG rhythm in the field and in-hospital (n = 4,219)

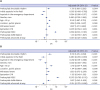
Table 3
Results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses of factors associated with favorable survival outcomes

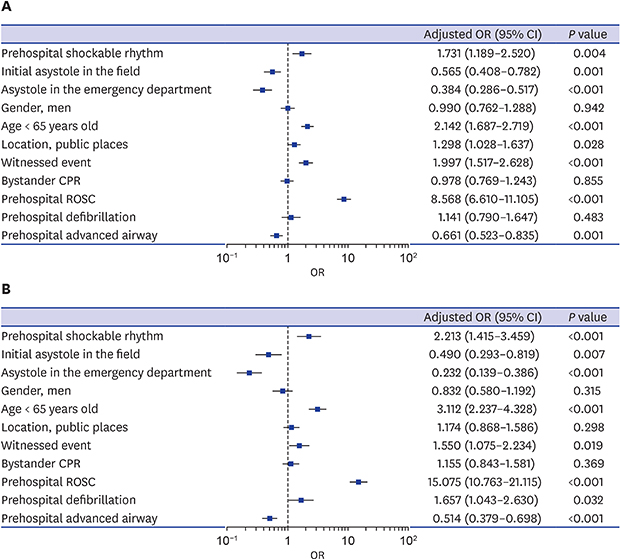
Fig. 2
Adjusted odds ratios for survival outcomes after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. (A) Forest plot showing survival to discharge. (B) Forest plot showing favorable neurologic outcomes at discharge.
Validation of various TOR rules for predicting outcomes at discharge
Table 4
Performance of the new TOR rules for predicting death prior to discharge (n = 4,608)

Table 5
Neurologic outcomes of patients after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest matching each of 6 rules (n = 4,608)





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download