Abstract
Purpose
The efficacy of periarticular multimodal drug injection and adductor canal block after a medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy was compared in terms of the postoperative pain level.
Materials and Methods
From November 2016 to March 2017, 60 patients underwent a medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy under spinal anesthesia. Preemptive analgesic medication, intravenous patient controlled anesthesia were used for pain control in all patients. Thirty patients received a periarticular multimodal drug injection (group I), and 30 patients received an adductor canal block (group II). These two groups were compared regarding the postoperative pain level, frequency of additional tramadol injections, total amount of patient-controlled analgesia, and number of times that the patients pushed the patient-controlled analgesia button at each time interval.
Results
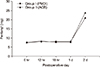
The visual analogue scale scores over the two-week postoperative period showed no statistical significance. The frequency of additional tramadol hydrochloride injections was similar in the two groups over time. The mean number of times that patients pushed the patient-controlled analgesia button was similar in two groups over time. The total amount of patient-controlled analgesia was similar in the two groups over time.
Figures and Tables
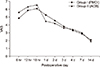 | Figure 3Comparison of postoperative VAS scores between groups. VAS, visual analogue scale; PMDI, periarticular multimodal drug injection; ACB, adductor canal block. |
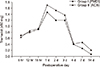 | Figure 4Comparison of frequency of additional tramadol hydrochloride injections between groups. PMDI, periarticular multimodal drug injection; ACB, adductor canal block. |
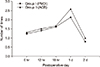 | Figure 5Comparison of mean number of times that patients pushed patient controlled analgesia button between groups. PMDI, periarticular multimodal drug injection; ACB, adductor canal block. |
References
1. Song EK. High tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2004; 39:104–107.

2. Jackson JP, Waugh W, Green JP. High tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1969; 51:88–94.

3. Coventry MB. Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1965; 47:984–990.

4. Jung WH, Chun CW, Lee JH, Ha JH, Kim JH, Jeong JH. Comparative study of medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy using 2 different implants. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:1063–1071.


5. Staubli AE. Open-wedge high tibial osteotomy with a locking plate (TomoFix) for treatment of medial monocompartment osteoarthritis. Oper Tech Orthop. 2011; 21:156–162.

6. Lee DH, Han SB, Oh KJ, et al. The weight-bearing scanogram technique provides better coronal limb alignment than the navigation technique in open high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2014; 21:451–455.

7. Takeuchi R, Ishikawa H, Aratake M, et al. Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with early full weight bearing. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25:46–53.


8. Jæger P, Zaric D, Fomsgaard JS, et al. Adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013; 38:526–532.

9. Patterson ME, Bland KS, Thomas LC, et al. The adductor canal block provides effective analgesia similar to a femoral nerve block in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study. J Clin Anesth. 2015; 27:39–44.
10. Andersen LØ, Gaarn-Larsen L, Kristensen BB, Husted H, Otte KS, Kehlet H. Analgesic efficacy of local anaesthetic wound administration in knee arthroplasty: volume vs concentration. Anaesthesia. 2010; 65:984–990.


11. Busch CA, Shore BJ, Bhandari R, et al. Efficacy of periarticular multimodal drug injection in total knee arthroplasty. A randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:959–963.
12. Cho CH, Song KS, Min BW, Jung GH, Lee YK, Shin HK. Efficacy of interscalene block combined with multimodal pain control for postoperative analgesia after rotator cuff repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23:542–547.


13. Jeong MS, Song EK, Seon JK, Byun JW, Lee KJ, Jung YW. Effectiveness of pain relief for femoral nerve block in multimodal pain control protocols in total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2011; 46:237–243.

14. Jung WH, Takeuchi R, Chun CW, et al. Efficacy of periarticular multimodal drug injection after medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a randomized, controlled study. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30:1261–1268.

15. Jaeger P, Grevstad U, Henningsen MH, Gottschau B, Mathiesen O, Dahl JB. Effect of adductor-canal-blockade on established, severe post-operative pain after total knee arthroplasty: a randomised study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012; 56:1013–1019.


16. Joo JH, Park JW, Kim JS, Kim YH. Is intra-articular multimodal drug injection effective in pain management after total knee arthroplasty? A randomized, double-blinded, prospective study. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:1095–1099.

17. Lund J, Jenstrup MT, Jaeger P, Sørensen AM, Dahl JB. Continuous adductor-canal-blockade for adjuvant post-operative analgesia after major knee surgery: preliminary results. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011; 55:14–19.


18. Jenstrup MT, Jæger P, Lund J, et al. Effects of adductor-canal-blockade on pain and ambulation after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012; 56:357–364.


19. Mei S, Jin S, Chen Z, Ding X, Zhao X, Li Q. Analgesia for total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis comparing local infiltration and femoral nerve block. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015; 70:648–653.



20. Affas F, Nygårds EB, Stiller CO, Wretenberg P, Olofsson C. Pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial comparing local infiltration anesthesia and continuous femoral block. Acta Orthop. 2011; 82:441–447.



21. Kim DH, Lin Y, Goytizolo EA, et al. Adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block for total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Anesthesiology. 2014; 120:540–550.

22. Tong QJ, Lim YC, Tham HM. Comparing adductor canal block with local infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, blinded and randomized clinical trial. J Clin Anesth. 2018; 46:39–43.


23. Mullaji A, Kanna R, Shetty GM, Chavda V, Singh DP. Efficacy of periarticular injection of bupivacaine, fentanyl, and methylprednisolone in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized trial. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25:851–857.

24. Rapley JH, Beavis RC, Barber FA. Glenohumeral chondrolysis after shoulder arthroscopy associated with continuous bupivacaine infusion. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25:1367–1373.

25. Noyes FR, Fleckenstein CM, Barber-Westin SD. The development of postoperative knee chondrolysis after intra-articular pain pump infusion of an anesthetic medication: a series of twenty-one cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:1448–1457.

26. Breu A, Rosenmeier K, Kujat R, Angele P, Zink W. The cytotoxicity of bupivacaine, ropivacaine, and mepivacaine on human chondrocytes and cartilage. Anesth Analg. 2013; 117:514–522.






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download