Abstract
Mesalazine suppositories are widely used to treat ulcerative colitis and have a guaranteed safety profile, but although rare, they can cause pulmonary toxicity. A 35-year-old woman with ulcerative colitis was diagnosed to have acute eosinophilic pneumonia after 29 days of oral mesalazine use and improved after mesalazine and corticosteroid were withdrawn. Reintroduction of mesalazine suppositories resulted in acute eosinophilic pneumonia recurrence after 28 days. Mesalazine re-administration (even via a different route) in patients with a history of mesalazine-induced eosinophilic pneumonia should be undertaken cautiously, because eosinophilic pneumonia may recurrence.
Figures and Tables
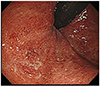 | Fig. 1Endoscopic image. Colonoscopy showed edema, granular change, and a diminished rectal vascular pattern. |
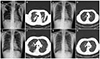 | Fig. 2Chest radiograph and CT scan images. (A) Chest radiograph showing consolidations in both lung fields. (B) CT image showing multifocal dense consolidations in the right upper, left upper, and left lower lobes. (C) Chest radiograph showing improvement of consolidations. (D) CT scan showing resolution of previous consolidations. (E) Chest radiograph showing pneumonic infiltrations in right middle and left lower lung fields. (F) CT image showing subtle GGOs in right upper, right lower, and left upper lobes. (G) Chest radiograph showing improvement of pneumonic infiltrations. (H) CT image showing resolution of GGOs. CT, computed tomography; GGOs, ground glass opacities. |
References
1. Park JE, Hwangbo Y, Chang R, et al. Mesalazine-induced eosinophilic pneumonia in a patient with Crohn’s disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009; 53:116–120.

2. Foster RA, Zander DS, Mergo PJ, Valentine JF. Mesalamine-related lung disease: clinical, radiographic, and pathologic manifestations. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2003; 9:308–315.


3. Abraham A, Karakurum A. Acute respiratory failure secondary to mesalamine-induced interstitial pneumonitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013:pii: bcr2013009834.

4. Kim JH, Lee JH, Koh ES, et al. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia related to a mesalazine suppository. Asia Pac Allergy. 2013; 3:136–139.



5. Bartal C, Sagy I, Barski L. Drug-induced eosinophilic pneumonia: a review of 196 case reports. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e9688.
6. Marchand E, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Lauque D, Durieu J, Tonnel AB, Cordier JF. Idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. A clinical and follow-up study of 62 cases. The groupe d'etudes et de recherche sur les maladies “orphelines” pulmonaires (GERM“O”P). Medicine (Baltimore). 1998; 77:299–312.

7. Camus P. The drug-induced respiratory disease website.[Internet]. Dijon: Pneumotox®;2018. 09. 29. cited 2018 Oct 1. Available from: http://www.pneumotox.com/drug/index.
8. Nielsen OH. Sulfasalazine intolerance. A retrospective survey of the reasons for discontinuing treatment with sulfasalazine in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1982; 17:389–393.

9. Sehgal P, Colombel JF, Aboubakr A, Narula N. Systematic review: safety of mesalazine in ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 47:1597–1609.


10. Sesin GP, Mucciardi N, Almeida S. Mesalamine-associated pleural effusion with pulmonary infiltration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1998; 55:2304–2305.


11. Franco AI, Escobar L, García XA, et al. Mesalazine-induced eosinophilic pneumonia in a patient with ulcerative colitis disease: a case report and literature review. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2016; 31:927–929.


12. Gupta A, Gulati S. Mesalamine induced eosinophilic pneumonia. Respir Med Case Rep. 2017; 21:116–117.



13. Park JY, Kang HM, Kim SY, et al. A case of mesalazine-induced eosinophilic pneumonia in a patient with ulcerative colitis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2001; 51:474–481.

14. Azad Khan AK, Piris J, Truelove SC. An experiment to determine the active therapeutic moiety of sulphasalazine. Lancet. 1977; 2:892–895.

15. Kim KH, Kim TN, Jang BI. A case of acute pancreatitis caused by 5-aminosalicylic acid suppositories in a patient with ulcerative colitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007; 50:379–383.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download