Abstract
Sjögren's syndrome (SS)-associated polyradiculopathy is rarely reported. A 51-year-old woman presented with a history of gradual weakness in all four extremities for several months. Based on electrophysiological studies, spinal magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid examination, inflammatory polyradiculopathy was confirmed. During a search for the aetiol-ogy, the patient was ultimately diagnosed with SS. This study introduces SS-associated poly-radiculopathy that primarily presented with motor symptoms, thus mimicking motor neuron disease.
Go to : 
References
2. Asmussen K, Andersen V, Bendixen G, Schi⊘dt M, Oxholm P. A new model for classification of disease manifestations in primary Sjögren's syndrome: evaluation in a retrospective longterm study. J Intern Med. 1996; 239:475–482.
3. Pavlakis PP, Alexopoulos H, Kosmidis ML, Mamali I, Moutsopoulos HM, Tzioufas AG, et al. Peripheral neuropathies in Sjögren's syndrome: a critical update on clinical features and pathogenetic mechanisms. J Autoimmun. 2012; 39:27–33.

4. Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, et al. Classification criteria for Sjögren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the Amer-ican-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:554–558.
5. Lafitte C. Neurological manifestations in Sjögren's syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2000; 57:411–413.
6. Delalande S, de Seze J, Fauchais AL, Hachulla E, Stojkovic T, Ferriby D, et al. Neurologic manifestations in primary Sjögren syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004; 83:280–291.

7. Mori K, Iijima M, Koike H, Hattori N, Tanaka F, Watanabe H, et al. The wide spectrum of clinical manifestations in Sjögren's syndrome-as-sociated neuropathy. Brain. 2005; 128(Pt 11):2518–2534.

Go to : 
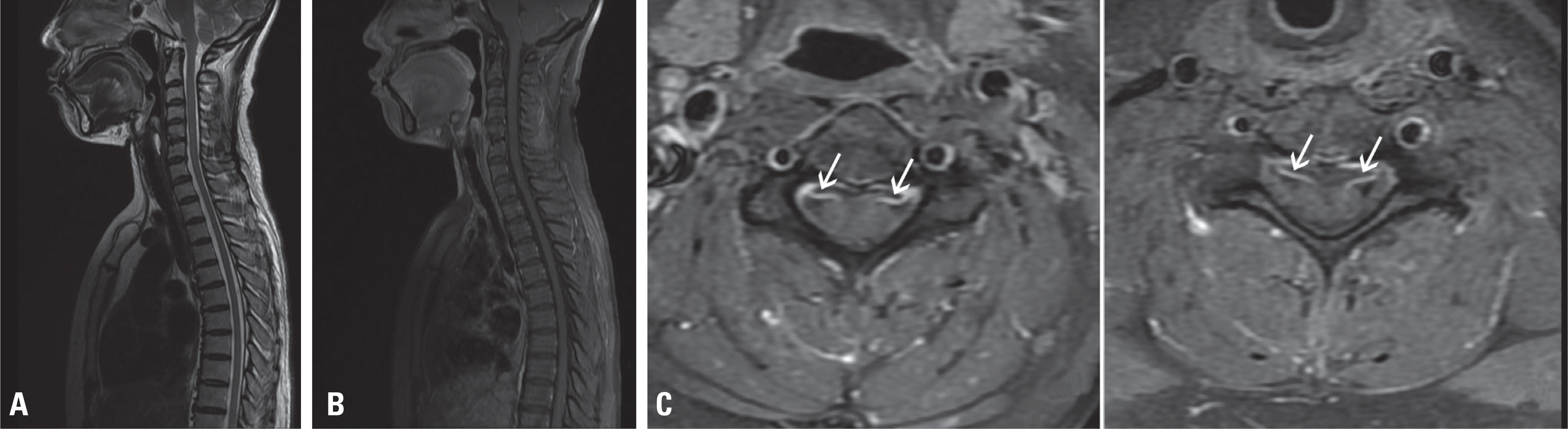 | Fig. 1.Cervical and thoracic spinal MRI. A T2 sagittal image (A) and T1 gadolinium-enhanced sagittal image (B) show unremarkable findings. T1 gadolini-um-enhanced axial images at the (C) C4 level and (D) C6 level show enhancement of the ventral nerve rootletsof the ventral nerve rootlets (white arrows). MRI, magnetic resonance imaging. |
Table 1.
The results of nerve conduction study
Table 2.
The findings of electromyography




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download