INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
KAERS
Selection of SCAR ICSRs
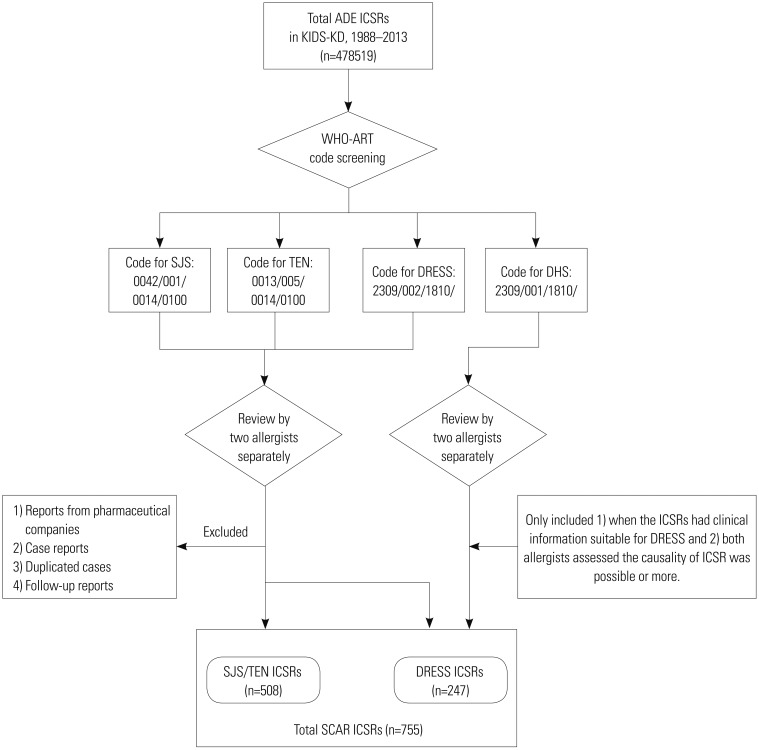 | Fig. 1Scheme of the selection process for ICSRs of SCARs in the KIDS-KD. ICSRs, individual case safety reports; SCARs, severe cutaneous adverse reactions; KIDS-KD, Korea Institute of Drug Safety and Risk Management-Korea Adverse Event Reporting System database; ADE, adverse drug event; SJS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis; DRESS syndrome, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome; DHS, drug hypersensitivity syndrome; WHO-ART, World Health Organization Adverse Reactions Terminology. |
RESULTS
Summary of SCAR ICSRs
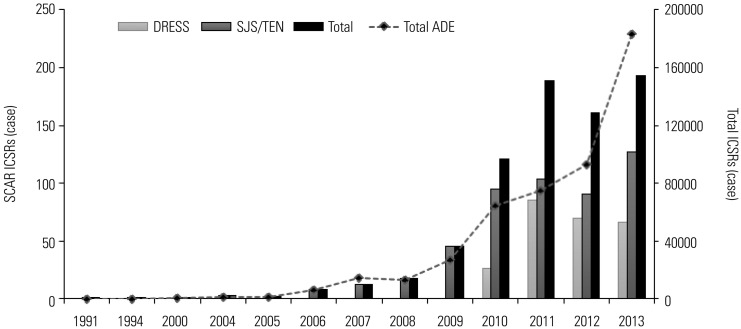 | Fig. 2Trends in annual numbers of ICSRs of SCARs in KAERS. ICSRs, individual case safety reports; SCARS, severe cutaneous adverse reactions; KAERS, Korea Adverse Event Reporting System; SJS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis; DRESS syndrome, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome. |
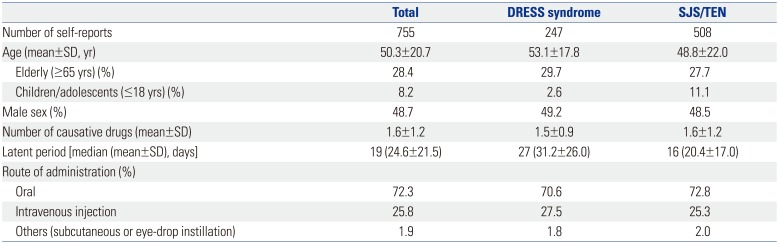
Table 1
Baseline Characteristics in Individual Case Safety Reports of SCARs
Causative drugs
Table 2
Common SCAR-Causing Drugs and Drug Labeling Information
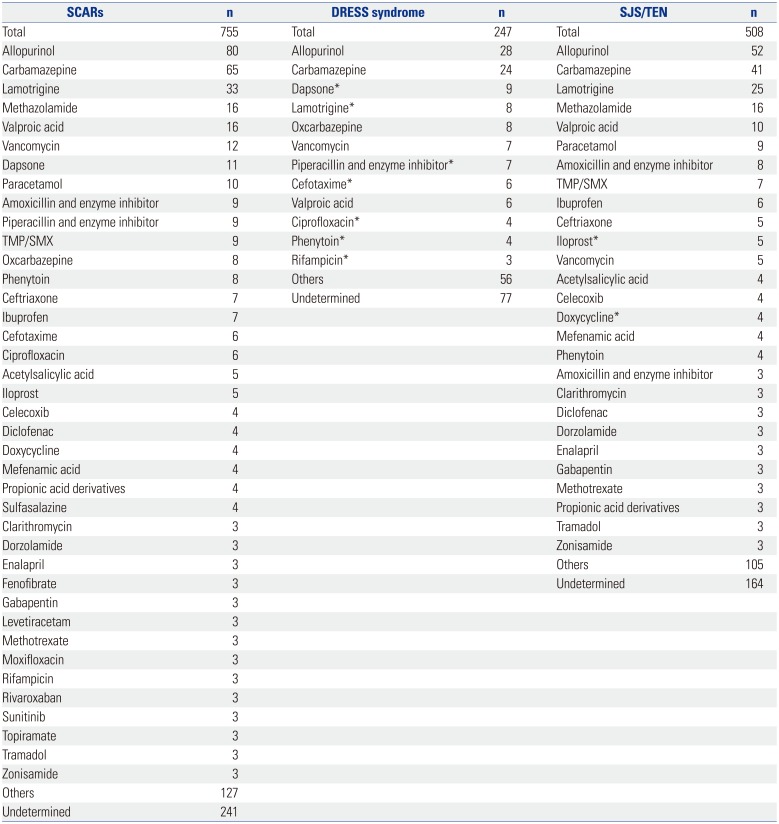
SCARs, severe cutaneous adverse reactions; DRESS syndrome, drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome; SJS/TEN, Stevens-Johnsons syndrome/Toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Others: drugs for which less than three cases were reported. Undetermined: cases in which two or more drugs were simultaneously reported as a causative agent so that the culprit drug could not be identified. TMP/SMX: trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole.
*Drugs for which the labeling information did not include the risk of SCARs.
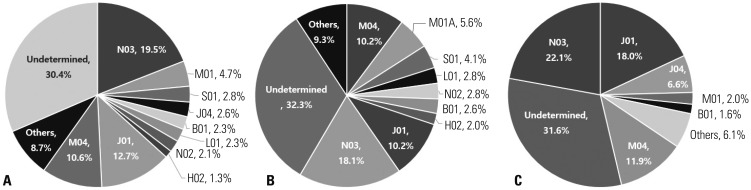 | Fig. 3Proportion of causative drugs for SCARs categorized by the main therapeutic group (second level) per ATC classification. (A) Total, (B) SJS/TEN, (C) DRESS syndrome. SCARs, severe cutaneous adverse reactions; ATC, anatomical therapeutic chemical; SJS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis; DRESS syndrome, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptom syndrome. ATC code: B01 (antithrombotic agents), H02 (corticosteroids for systemic use), J01 (antibacterials for systemic use), J04 (antimycobacterials), L01 (antineoplastic agents), M01 (anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products), M04 (anti-gout preparations), N02 (analgesics), N03 (antiepileptics), S01 (ophthalmologicals), and undetermined (cases in which two or more drugs were simultaneously reported as a causative agent so that the culprit drug could not be identified). |
Drug labeling information
Mortality review
Table 3
Summary of Cases of SCAR-Related Deaths and Drug Labeling Information for SCARs
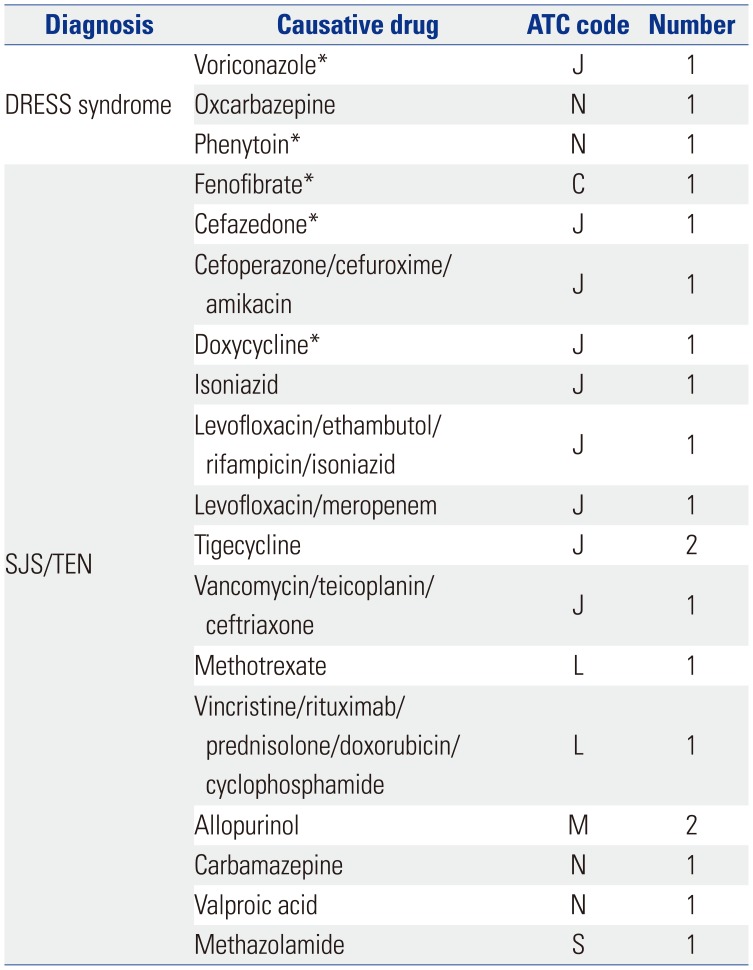
SCARs, severe cutaneous adverse reactions; DRESS syndrome, drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptom syndrome; SJS/TEN, Stevens-Johnsons syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis; ATC, anatomical therapeutic chemical.
*Drugs for which the labeling information did not include the risk of SCARs.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download