Abstract
White matter hyperintensity (WMH) is commonly observed on the brain MRI of elderly subjects. It has been considered as an important biomarker for the micro-vascular damages of white matter of the brain. Aging, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hyperhomocysteinemia have been associated with WMH development. WMH is an important risk factor for the vascular dementia (VD), however it also considered as one of risk factors for conversion of mild cognitive impairment to dementia and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). WMH has impact on gait, bladder control, and fine motor coordination. It also has negative effects on memory retrieval, mental flexibility, mental processing speed, and executive function by disconnecting nerve fibers that convey signals for normal cognition. Control of vascular risk factors can delay progression of WMH and this may be beneficial for VD as well as AD with ischemic changes, especially in the early state of diseases. In this paper, we will review clinical significance of WMH and three important diseases, subcortical vascular dementia, cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, and cerebral amyloid angiopathy that associated with cerebral micro-vascular damages.
Figures and Tables
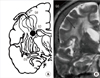 | Fig. 1(A) Blood supply of cerebral white matter (WM) by (a) medullary artery (b) lenticulostriate artery and (c) choroidal artery. Dark circle represents a pneumbra zone of three arteries. (B) Area (a) is the most frequently affected WM regions of the subcortical vascular dementia patients. |
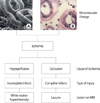 | Fig. 2Microvascular changes of the brain in patients with subcortical vascular ischemic dementia. Toruous and elongated (A) and stenotic (B) changes of arterioles cause complete or incomplete infarcts in the white matter with two different mechanisms of ischemia. |
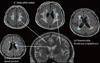 | Fig. 3Visual rating scale of the white matter hyperintensities (WMH). Severity of WMH can be measured in the (a) periventricular area around the fontal and occipital horns of lateral ventricle (b) periventicular area long the lateral ventricle (c) deep white matter area. |
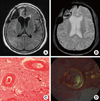 | Fig. 4MRI and histopathologic features of the 72-year-old female with dementia and recurrent lobar hemorrhages. FLAIR axial MRI shows periventricular white matter hyperintensity and cortical lobar hemorrhage in the right frontal area (A). On gradient echo MRI, there are numerous microbleedings mostly on the cortex (B). Thickened homogeneous pink material is noted in the H&E stain (C). Apple-green birefringence of amyloid deposits is proved under the polarized light on Congo red stain (D). |
References
1. de Leeuw FE, de Groot JC, Achten E, Oudkerk M, Ramos LM, Heijboer R, et al. Prevalence of cerebral white matter lesions in elderly people: a population based magnetic resonance imaging study. The Rotterdam Scan Study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001. 70:9–14.

2. Jeerakathil T, Wolf PA, Beiser A, Massaro J, Seshadri S, D'Agostino RB, et al. Stroke risk profile predicts white matter hyperintensity volume: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 2004. 35:1857–1861.

3. Schmahmann JD, Smith EE, Eichler FS, Filley CM. Cerebral white matter: neuroanatomy, clinical neurology, and neurobehavioral correlates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. 1142:266–309.
4. Schmidt R, Fazekas F, Kapeller P, Schmidt H, Hartung HP. MRI white matter hyperintensities: three-year follow-up of the Austrian Stroke Prevention Study. Neurology. 1999. 53:132–139.

5. Fernando MS, Simpson JE, Matthews F, Brayne C, Lewis CE, Barber R, et al. MRC Cognitive Function and Ageing Neuropathology Study Group. White matter lesions in an unselected cohort of the elderly: molecular pathology suggests origin from chronic hypoperfusion injury. Stroke. 2006. 37:1391–1398.

6. Roman GC. Brain hypoperfusion: a critical factor in vascular dementia. Neurol Res. 2004. 26:454–458.

7. Kapeller P, Barber R, Vermeulen RJ, Ader H, Scheltens P, Freidl W, et al. Visual rating of age-related white matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging: scale comparison, interrater agreement, and correlations with quantitative measurements. Stroke. 2003. 34:441–445.

8. Erkinjuntti T. Subcortical ischemic vascular disease and dementia. Int Psychogeriatr. 2003. 15:Suppl 1. 23–26.

9. Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer's dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987. 149:351–356.

10. Scheltens P, Barkhof F, Leys D, Pruvo JP, Nauta JJ, Vermersch P, et al. A semiquantative rating scale for the assessment of signal hyperintensities on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Sci. 1993. 114:7–12.

11. Pantoni L, Poggesi A, Inzitari D. Cognitive decline and dementia related to cerebrovascular diseases: some evidence and concepts. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009. 27:Suppl 1. 191–196.

12. Prasad K, Wiryasaputra L, Ng A, Kandiah N. White matter disease independently predicts progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease in a clinic cohort. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2011. 31(6):431–434.

13. Longstreth WT Jr, Arnold AM, Beauchamp NJ Jr, Manolio TA, Lefkowitz D, Jungreis C, et al. Incidence, manifestations, and predictors of worsening white matter on serial cranial magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke. 2005. 36:56–61.

14. van den Heuvel DM, ten Dam VH, de Craen AJ, Admiraal-Behloul F, Olofsen H, Bollen EL, et al. Increase in periventricular white matter hyperintensities parallels decline in mental processing speed in a non-demented elderly population. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006. 77:149–153.

15. Richard E, Gouw AA, Scheltens P, van Gool WA. Vascular care in patients with Alzheimer disease with cerebrovascular lesions slows progression of white matter lesions on MRI: the evaluation of vascular care in Alzheimer's disease (EVA) study. Stroke. 2010. 41:554–556.

16. Jellinger KA. Alzheimer disease and cerebrovascular pathology: an update. J Neural Transm. 2002. 109:813–836.

17. Jellinger KA. Morphologic diagnosis of "vascular dementia" - a critical update. J Neurol Sci. 2008. 270:1–12.

18. De Groot JC, De Leeuw FE, Oudkerk M, Van Gijn J, Hofman A, Jolles J, et al. Periventricular cerebral white matter lesions predict rate of cognitive decline. Ann Neurol. 2002. 52:335–341.

19. van den Heuvel DM, ten Dam VH, de Craen AJ, Admiraal-Behloul F, Olofsen H, Bollen EL, et al. Increase in periventricular white matter hyperintensities parallels decline in mental processing speed in a non-demented elderly population. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006. 77:149–153.

20. Park KH, Lee JY, Na DL, Kim SY, Cheong HK, Moon SY, et al. Different associations of periventricular and deep white matter lesions with cognition, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and daily activities in dementia. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2011. 24:84–90.

21. Herrmann LL, Le Masurier M, Ebmeier KP. White matter hyperintensities in late life depression: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008. 79:619–624.

22. Seo SW, Lee JM, Im K, Park JS, Kim SH, Kim ST, et al. Cortical thinning related to periventricular and deep white matter hyperintensities. Neurobiol Aging. 2012. 33:1156–1167.

23. Wen W, Sachdev PS, Chen X, Anstey K. Gray matter reduction is correlated with white matter hyperintensity volume: a voxel-based morphometric study in a large epidemiological sample. Neuroimage. 2006. 29:1031–1039.

24. Selden NR, Gitelman DR, Salamon-Murayama N, Parrish TB, Mesulam MM. Trajectories of cholinergic pathways within the cerebral hemispheres of the human brain. Brain. 1998. 121(Pt 12):2249–2257.

25. Bocti C, Swartz RH, Gao FQ, Sahlas DJ, Behl P, Black SE. A new visual rating scale to assess strategic white matter hyperintensities within cholinergic pathways in dementia. Stroke. 2005. 36:2126–2131.

26. Reed BR, Eberling JL, Mungas D, Weiner M, Kramer JH, Jagust WJ. Effects of white matter lesions and lacunes on cortical function. Arch Neurol. 2004. 61:1545–1550.

27. Schmidt R, Fazekas F, Kapeller P, Schmidt H, Hartung HP. MRI white matter hyperintensities: three-year follow-up of the Austrian Stroke Prevention Study. Neurology. 1999. 53:132–139.

28. van der Flier WM, van Straaten EC, Barkhof F, Ferro JM, Pantoni L, Basile AM, et al. Medial temporal lobe atrophy and white matter hyper-intensities are associated with mild cognitive deficits in non-disabled elderly people: the LADIS study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005. 76:1497–1500.

29. Gold G, Kovari E, Herrmann FR, Canuto A, Hof PR, Michel JP, et al. Cognitive consequences of thalamic, basal ganglia, and deep white matter lacunes in brain aging and dementia. Stroke. 2005. 36:1184–1188.

30. van Den Boom R, Lesnik Oberstein SA, van Duinen SG, Bornebroek M, Ferrari MD, Haan J, et al. Subcortical lacunar lesions: an MR imaging finding in patients with cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. Radiology. 2002. 224:791–796.

31. Viitanen M, Kalimo H. CADASIL: hereditary arteriopathy leading to multiple brain infarcts and dementia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. 903:273–284.

32. Smith EE, Greenberg SM. Beta-amyloid, blood vessels, and brain function. Stroke. 2009. 40:2601–2606.
33. Weller RO, Nicoll JA. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: pathogenesis and effects on the ageing and Alzheimer brain. Neurol Res. 2003. 25:611–616.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download