Abstract
Background
The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) has been commonly used to measure cognitive change over time. The aim of present study was to investigate the normative rates of change for the MMSE across test-retest intervals.
Methods
We administered the Korean MMSE (K-MMSE) to 1055 community-dwelling middle aged and older adults three times over 6 years. Based on the Christensen's health screening criteria (1991), 234 middle-aged healthy adults (104 men, 130 women; mean age 55.95±6.20 years; age range 45-64 years; mean education 7.63±4.06 years) and 505 healthy elderly (200 men, 305 women; mean age 71.00±4.62 years; age range 65-79 years; mean education 5.61±5.12 years) were selected for the statistical analysis. Reliable change indices were computed using two different statistical methods, the Reliable Change Index adjusted for practice effects (RCIPE; Chelune et al., 1993) and the Standardized Regression-Based Change Index (SRBCI; McSweeny et al., 1993).
Results
For the middle-aged healthy adult group, the 90% confidence intervals of the RCIPE and SRBCI were the same such as ±4 in 2-year, ±5 in 4-year, and ±6 in 6-year test-retest intervals. For the healthy elderly group, the 90% confidence intervals of the RCIPE were -5 and +4 in 2-year interval and -7 and +5 in 4- & 6-year intervals. The 90% confidence intervals of the SRB change index were ±4 in 2-year interval and ±6 in 4- & 6-year intervals.
Figures and Tables
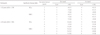
Table 1
Reliable change scores and their formulas

RCIPE, Reliable Change Index adjusted for Practice Effect; SRBCI, Standardized Regression-Based Change Index; T1, score at Time 1; T2, score at Time 2; D, mean of difference of score at Time 2 and score at Time 1; SED, Standard Error of the Difference; T'2, predicted score at Time 2 based on the regression model; SEE, Standard Error of the Estimate of the regression model.
References
1. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini-Mental State": a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975. 12:189–198.

2. Bondi MW, Salmon DP, Kaszniak AW. Grant I, Adams KM, editors. The neuropsychology of dementia. Neuropsychological assessment of neuropsychiatric disorders. 1996. New York: Oxford University Press.

3. Kang Y. A normative study of the Korean-Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in the elderly. Korean J Psychol Gen. 2006. 25:1–12.

4. Schmand B, Lindeboom J, Launer L, Dinkgreve M, Hooijer C, Jonker C. What is a significant score change on the Mini-Mental State examination? Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1995. 10:411–414.

5. Heilbronner RL, Sweet JJ, Attix DK, Krull KR, Henry GK, Hart RP. Official position of the American Academy of Clinical Neuropsychology on serial neuropsychological assessments: the utility and challenges of repeat test administrations in clinical and forensic contexts. Clin Neuropsychol. 2010. 24:1267–1278.

6. Duff K. Evidence-based indicators of neuropsychological change in the individual patient: relevant concepts and methods. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2012. 27:248–261.

7. Dirks J. The effect of a commercial game on children's block design scores in the WISC-R IQ test. Intelligence. 1892. 6:109–123.

8. Rapport LJ, Brines DB, Axelrod BN, Theisen ME. Full scale IQ as a mediator of practice effects: the rich get richer. Clin Neuropsychol. 1997. 11:375–380.

9. Beglinger LJ, Gaydos B, Tangphao-Daniels O, Duff K, Kareken DA, Crawford J, et al. Practice effects and the use of alternate forms in serial neuropsychological testing. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2005. 20:517–529.

10. Heaton RK, Temkin N, Dikmen S, Abitable N, Taylor MJ, Marcotte TD, et al. Detecting change: a comparison of three neuropsychological methods, using normal and clinical samples. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2001. 16:75–91.
11. Tombaugh TN. Test-retest reliable coefficients and 5-year change scores for the MMSE and 3MS. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2005. 20:485–503.
12. Hensel A, Angermeyer MC, Riedel-Heller SG. Measuring cognitive change in older adults: reliable change in dices for the MMSE. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007. 78:1298–1303.
13. Frerichs RJ, Tuokko HA. A comparison of methods for measuring cognitive change in older adults. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2005. 20:321–333.

14. Chelune GJ, Naugle RI, Luders H, Sedlak J, Awad IA. Individual change after epilepsy surgery: practice effects and base-rate information. Neuropsychology. 1993. 7:41–52.

15. McSweeny AJ, Naugle RI, Chelune GJ, Luders H. T scores for change: an illustration of a regression approach to depicting change in clinical neuropsychology. Clin Neuropsychol. 1993. 7:300–312.

16. Hallym Institue of Aging. Quality of life in the Korean elderly. 2006. Chuncheon: Hallym University Press.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download