Abstract
Eleven steroid hormones (SHs: androstene-3,17-dione, estrone, β-estradiol, α-estradiol, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone, 17á-hydroxyprogesterone, medroxyprogesterone, megestrol acetate, progesterone, and androsterone) were detected from New Zealand deer (Cervus elaphus var. scoticus) velvet antler (NZA, 鹿茸). A method for the quantification of eleven SHs was established by using ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC)-MS/MS. The linearities (R2 > 0.991), limits of quantification (LOQ values, 0.3 ng/mL to 23.1 ng/mL), intraday and interday precisions (relative standard deviation: RSD<2.43%), and recovery rates (97.3% to 104.6%) for all eleven SHs were determined. In addition, a method for the quantification of three 7-oxycholesterols (7-O-CSs: 7-ketocholesterol, 7α-hydroxycholesterol, and 7β-hydroxycholesterol) in the NZA was established by using an HPLC-photodiode array (PDA) method. The linearities (R2 > 0.999), LOQ values (30 ng/mL to 350 ng/mL), intraday and interday precisions (RSD < 1.93%), and recovery rates (97.2% to 103.5%) for the three 7-O-CSs were determined. These quantitative methods are accurate, precise, and reproducible. As a result, it is suggested that the five steroid compounds of androstene-3,17-dione, androsterone, 7-ketocholesterol, 7α-hydroxycholesterol, and 7β-hydroxycholesterol could be marker steroids of NZA. These methods can be applied to quantify or standardize the marker steroids present in NZA.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
(1). Hattori M., Yang X. W., Kaneko S., Nomura Y., Namba T.Jap. Soc. Pharmacog. 1989; 43:173–176.
(2). Sunwoo H. H., Nakano T., Hudson R. J., Sim J. S. J.Agric. Food Chem. 1995; 43:2846–2849.
(3). Lee N. K., Shin H. J., Kim W. S., Lee J. T., Park C. K.Nat. Prod. Sci. 2014; 20:160–169.
(4). Chang I. M.Treatise on Asian Herbal Medicines I; Haksulpyunsukwan press, Korea. 2003; 90. 111, 184.
(5). Ker D. F. E., Wang D., Sharma R., Zhang B., Passarelli B., Neff N., Li C., Maloney W., Quake S., Yang Y. P.Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018; 31:292–306.
(6). Lu C., Wang M., Mu J., Han D., Bai Y., Zhang H.Food Chem. 2013; 141:1796–1806.
(7). Griffiths W. J., Abdel-Khalik J., Crick P. J., Yutuc E., Wang Y. J.Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016; 162:4–26.
(8). Lund B. C., Bever-Stille K. A., Perry P. J.Pharmacotherapy. 1999; 19:951–956.
(9). Frye C. A.Minerva Ginecol. 2009; 61:541–562.
(10). Funder J. W., Krozowski Z., Myles K., Sato A., Sheppard K. E., Young M.Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1997; 52:247–260.
(11). Gleixner A., Meyer H. H. D.Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1997; 357:1198–1201.
(12). Gupta B. B. P., Lalchhandama K.Current Sci. 2002; 83:1103–1111.
(13). Jeanneret F., Tonoli D., Rossier M. F., Saugy M., Boccard J., Rudaz S. J.Chromatogr. A. 2016; 1430:97–112.
(14). McDonald J. G., Smith D. D., Stiles A. R., Russell D. W. J.Lipid Res. 2012; 53:1399–1409.
(15). Rodriguez I. R., Alam S., Lee J. W.Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004; 45:2830–2837.
(16). International Conference on Harmonization ICH (Q2) R1. Validation of Analytical Procedures Test and Methodology; ICH;Switzerland: 2005. p. 6–13.
(17). Kaminski R. M., Marini H., Kim W. J., Rogawski M. A.Epilepsia. 2005; 46:819–827.
(18). Yang Y., Shao B., Zhang J., Wu Y., Duan H. J.Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009; 877:489–496.
Go to : 
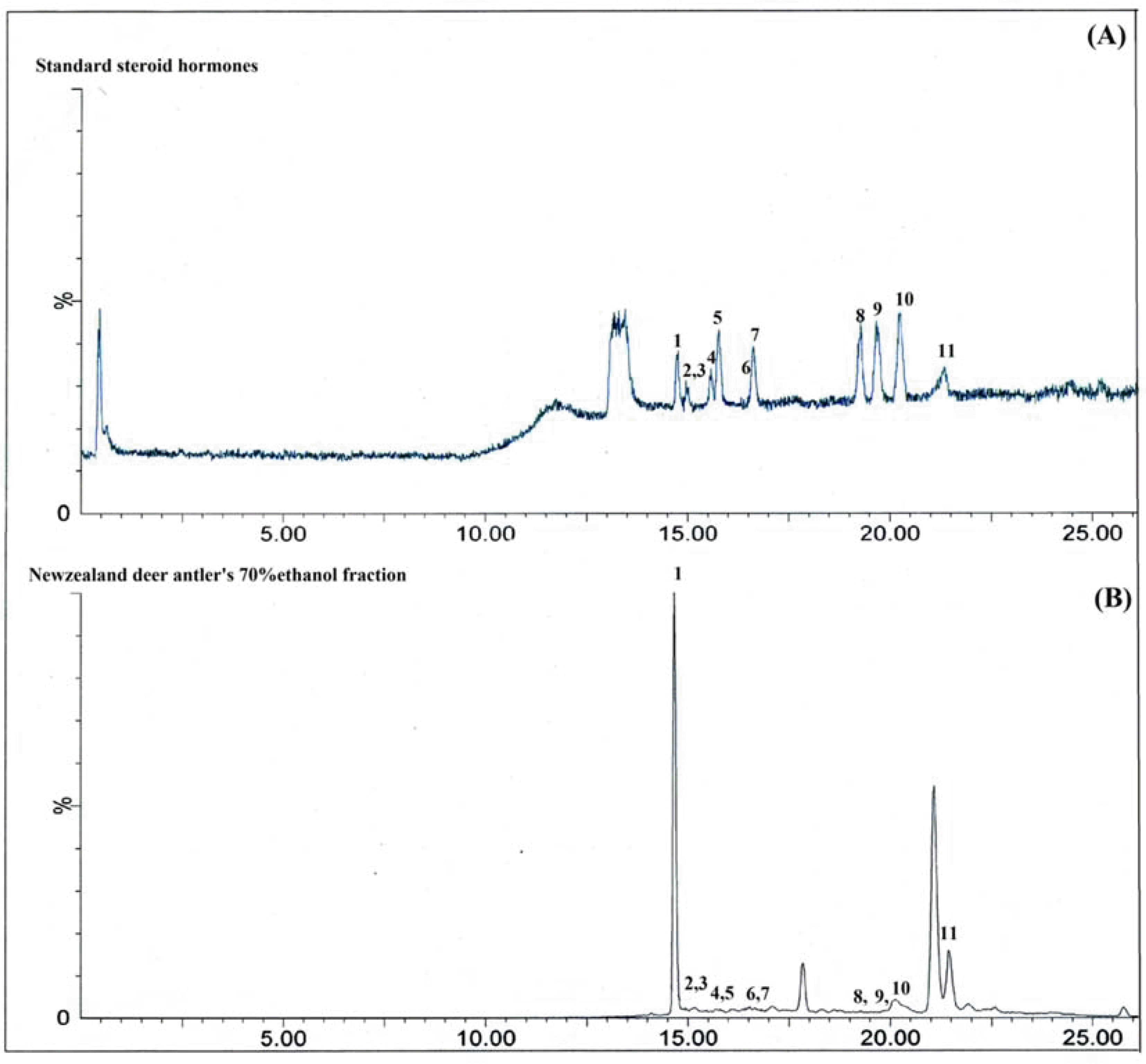 | Fig. 1.The total ion chromatograms for the eleven standard steroid hormones (1. androstene-3, 17-dione; 2. estrone; 3. β-estradiol; 4. α-estradiol; 5. testosterone; 6. dehydroepiandrosterone; 7. 17α-hydroxyprogesterone; 8. medroxyprogesterone; 9. megestrol acetate; 10. progesterone; 11. androsterone) (A) and New Zealand deer antler's 70% ethanol fraction (B) by UPLC-MS/MS in multiple reaction monitoring mode. |
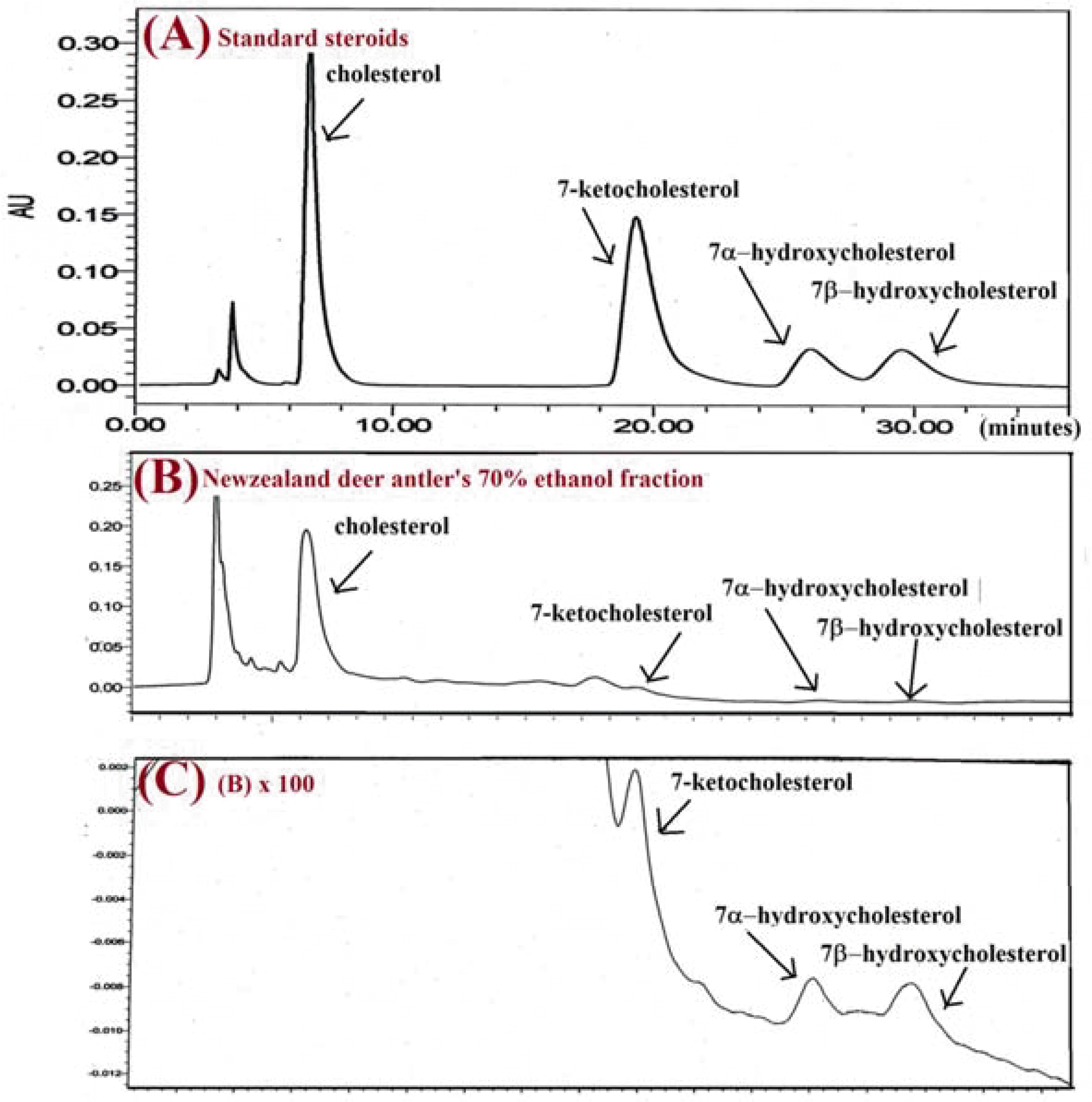 | Fig. 2.The chromatograms for (A): the standard of three 7-oxycholesterols (7-ketocholesterol, 7α-hydroxycholesterol, and 7β-hydroxycholesterol); (B): the 70% ethanol fraction (mixture of tip, upper, middle, and base) of New Zealand deer antler; (C): the chromatograph of 100 times the height of (B) by HPLC-PDA. |
Table 1.
UPLC-MS/MS detection conditions for the eleven SHs
Table 2.
Regression equation, correlation coefficients (R2), linear range, the LODs, and the LOQs for eleven SHs and three 7-O-CSs
Table 3.
Intraday and interday precisions of eleven SHs and three 7-O-CSs (n=3)
Table 4.
Recovery of eleven SHs and three 7-O-CSs
Table 5.
The levels of eleven SHs and three 7-O-CSs in NZA
The data (mean±standard deviation) are based on the triplicate determinations; A: New Zealand deer antler marker steroid; Mixture: mixture of 4 part (tip, upper, middle, and base); RM: raw material; AE: alcohol extract.; WE: water extract; SH: steroid hormone; 7-O-CS: 7-oxycholesterol; NZA: New Zealand deer antler




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download