Abstract
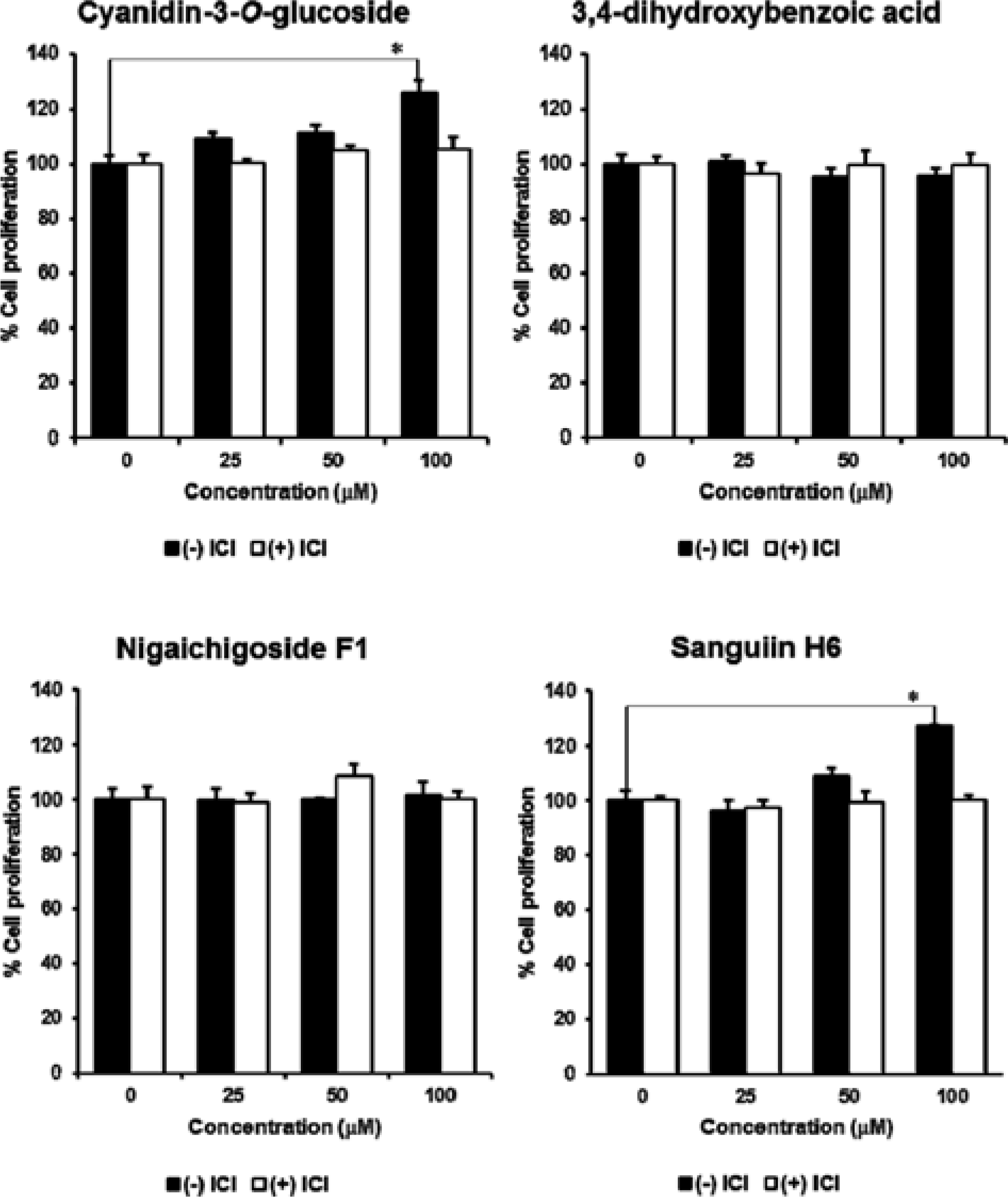
A popular approach for the study of estrogen receptor α inhibition is to investigate the protein-protein interaction between the estrogen receptor (ER) and the coactivator surface. In our study, we investigated phytochemicals from Rubus coreanus that were able to disrupt ERα and coactivator interaction with an ERα antagonist. The E-screen assay and molecular docking analysis were performed to evaluate the effects of the estrogenic activity of R. coreanus extract and its constituents on the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. At 100μ g/mL, R. coreanus extract significantly stimulated cell proliferation (574.57 ± 8.56%). Sanguiin H6, which was isolated from R. coreanus, demonstrated the strongest affinity for the ERα coactivator-binding site in molecular docking analysis, with a binding energy of -250.149. The initial results of the study indicated that sanguiin H6 contributed to the estrogenic activity of R. coreanus through the activation of the ERα coactivator-binding site.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
(1). Oh C. M., Won Y. J., Jung K. W., Kong H. J., Cho H., Lee J. K., Lee D. H., Lee K. H.Cancer Res. Treat. 2016; 48:436–450.
(2). Jung K. W., Won Y. J., Oh C. M., Kong H. J., Lee D. H., Lee K. H.Cancer Res. Treat. 2017; 49:306–312.
(3). Carmichael A. R., Mokbel K.Arch. Plast. Surg. 2016; 43:222–223.
(4). Irelli A., Cocciolone V., Cannita K., Zugaro L., Di Staso M., Lanfiuti Baldi P. L., Paradisi S., Sidoni T., Ricevuto E., Ficorella C.Bone. 2016; 87:169–175.
(5). de Pedro M., Baeza S., Escudero M. T., Dierssen-Sotos T., Gómez-Acebo I., Pollán M., Llorca J.Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015; 149:525–536.
(6). Esteva F. J., Hortobagyi G. N.Sci. Am. 2008; 298:58–65.
(7). Jameera Begam A., Jubie S., Nanjan M. J.Bioorg. Chem. 2017; 71:257–274.
(8). Howell S. J., Johnston S. R. D., Howell A.Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004; 18:47–66.
(9). Zheng J., Zhou Y., Li Y., Xu D. P., Li S., Li H. B.Nutrients. 2016; 8:495.
(10). Lee J., Dossett M., Finn C. E.Molecules. 2014; 19:10524–10533.
(11). Heo J.Donguibogam; Yeogang: Korea. 1994; 946–947.
(12). Li J., Du L. F., He Y., Yang L., Li Y. Y., Wang Y. F., Chai X., Zhu Y., Gao X. M.Chem. Biodivers. 2015; 12:1809–1847.
(13). Ju H. K., Cho E. J., Jang M. H., Lee Y. Y., Hong S. S., Park J. H., Kwon S. W. J.Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009; 49:820–827.
(14). Choung M. G., Lim J. D.Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2012; 20:259–269.
269.(15) Körner W.., Hanf V.., Schuller W.., Kempter C.., Metzqer J.., Haqenmaier H.Sci. Total Environ. 1999. 225:33–48.
(16). Soto A. M., Sonnenschein C., Chung K. L., Fernandez M. F., Olea N., Serrano F. O.Environ. Health Perspect. 1995; 103:113–122.
(17). Lee S., Barron M. G.PloS One. 2017; 12:1–14.
(18). Ng H. W., Zhang W., Shu M., Luo H., Ge W., Perkins R., Tong W., Hong H.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014; 15:1–15.
(19). Pang X., Fu W., Wang J., Kang D., Xu L., Zhao Y., Liu A. L., Du G. H.Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018; 2018:1–11.
(20). Jordan V. C. J.Med. Chem. 2003; 46:883–908.
(21). McDonnell D. P., Chang C. Y., Norris J. D. J.Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000; 74:327–335.
(22). Sun A., Moore T. W., Gunther J. R., Kim M. S., Rhoden E., Du Y., Fu H., Snyder J. P., Katzenellenbogen J. A.Chem. Med. Chem. 2011; 6:654–666.
(23). Park E. J., Lee D., Baek S. E., Kim K. H., Kang K. S., Jang T. S., Lee H. L., Song J. H., Yoo J. E.Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017; 27:4389–4392.
(24). Park E. H., Park J. Y., Yoo H. S., Yoo J. E., Lee H. L.Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016; 26:3291–3294.
(25). Choi M. H., Shim S. M., Kim G. H. J.Food Sci. Technol. 2016; 53:1214–1221.
(26). Ko H., Jeon H., Lee D., Choi H. K., Kang K. S., Choi K. C.Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015; 25:5508–5513.
(27). Helferich W. G., Andrade J. E., Hoagland M. S.Inflammophar-macology. 2008; 16:219–226.
(28). Hsieh C. Y., Santell R. C., Haslam S. Z., Helferich W. G.Cancer Res. 1998; 58:3833–3838.
(29). Lee J. Y., Kim H. S., Song Y. S. J.Tradit. Complement. Med. 2012; 2:96–104.
Go to : 
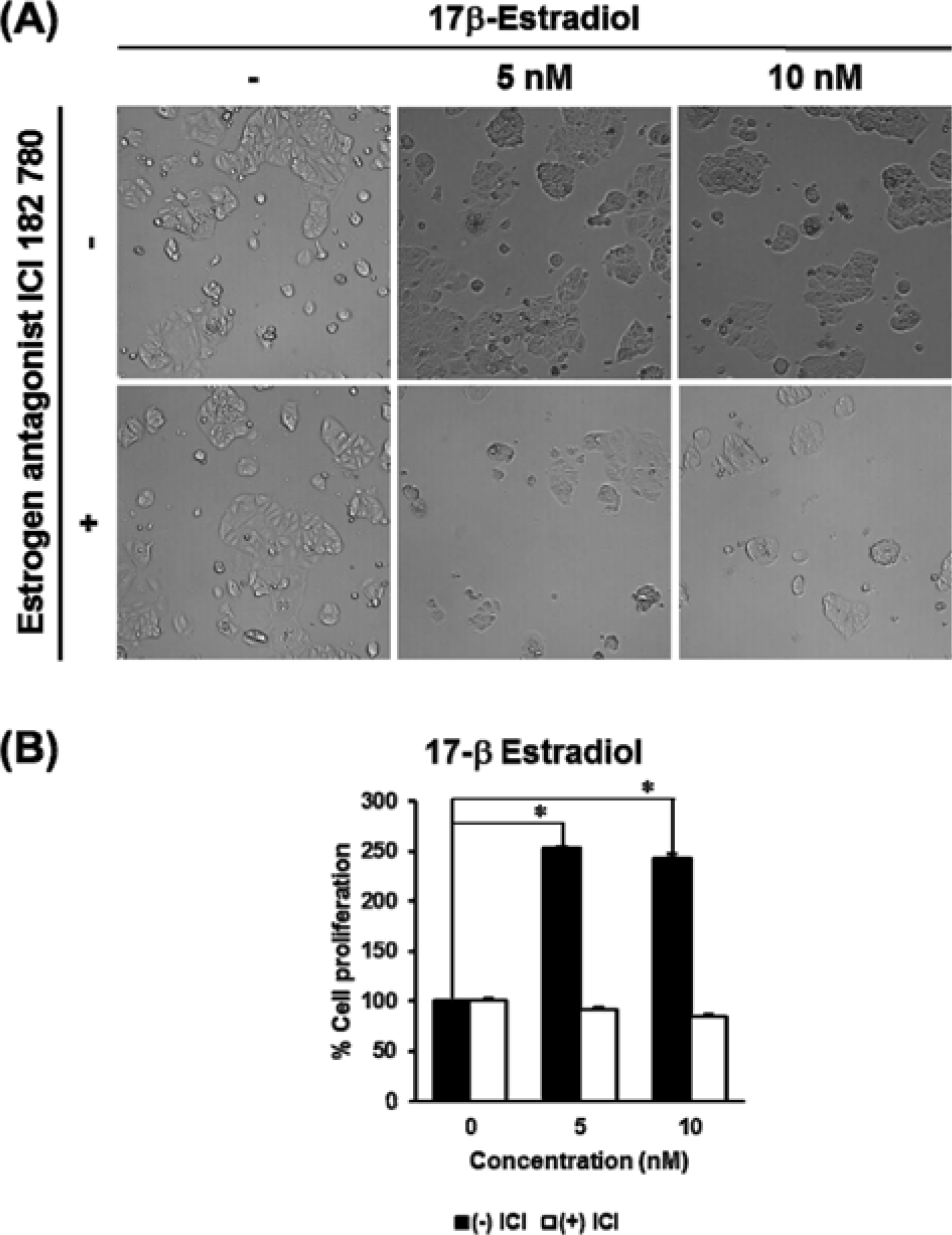 | Fig. 1.The estrogenic effect of 17β-estradiol on the proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. (A) The microscopic pictures from E-screen assay results of 17β-estradiol. (B) The comparative graph illustrates the percentage increase in cell proliferation compared with the untreated group. In this E-screen assay, 17β-estradiol was used as a positive control. MCF-7 cells were incubated in 24-well plates and treated with tested sample in phenol red-free RPMI medium supplemented with 5% charcoal-dextran-stripped human for 144 hours. For the antagonistic test, the pure estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182 780 was added with the test materials. Ez-Cytox reagent was added to each well for 1hour and the cell viability was then calculated from the measure-ment of the optical density at 450 nm using a microplate reader. P values of less than 0.001 were considered statistically significant. |
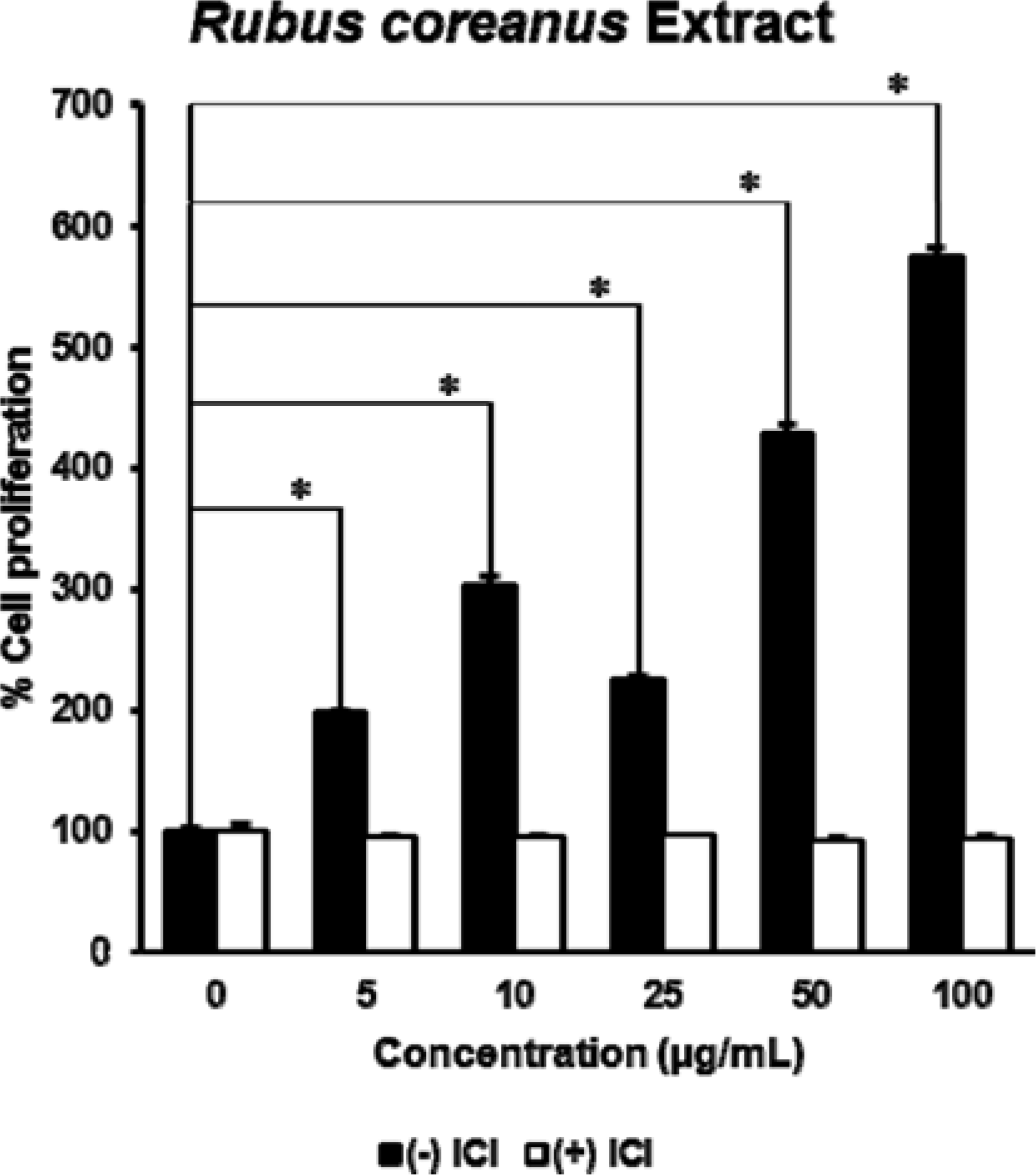 | Fig. 2.The estrogenic effect of Rubus coreanus extract on the proliferation of MCF-7 cells. The extract of R. coreanus significantly stimulated cell growth in a dose-dependent manner, especially at the concentration of 100 μ g/mL. P values of less than 0.001 were considered statistically significant. |
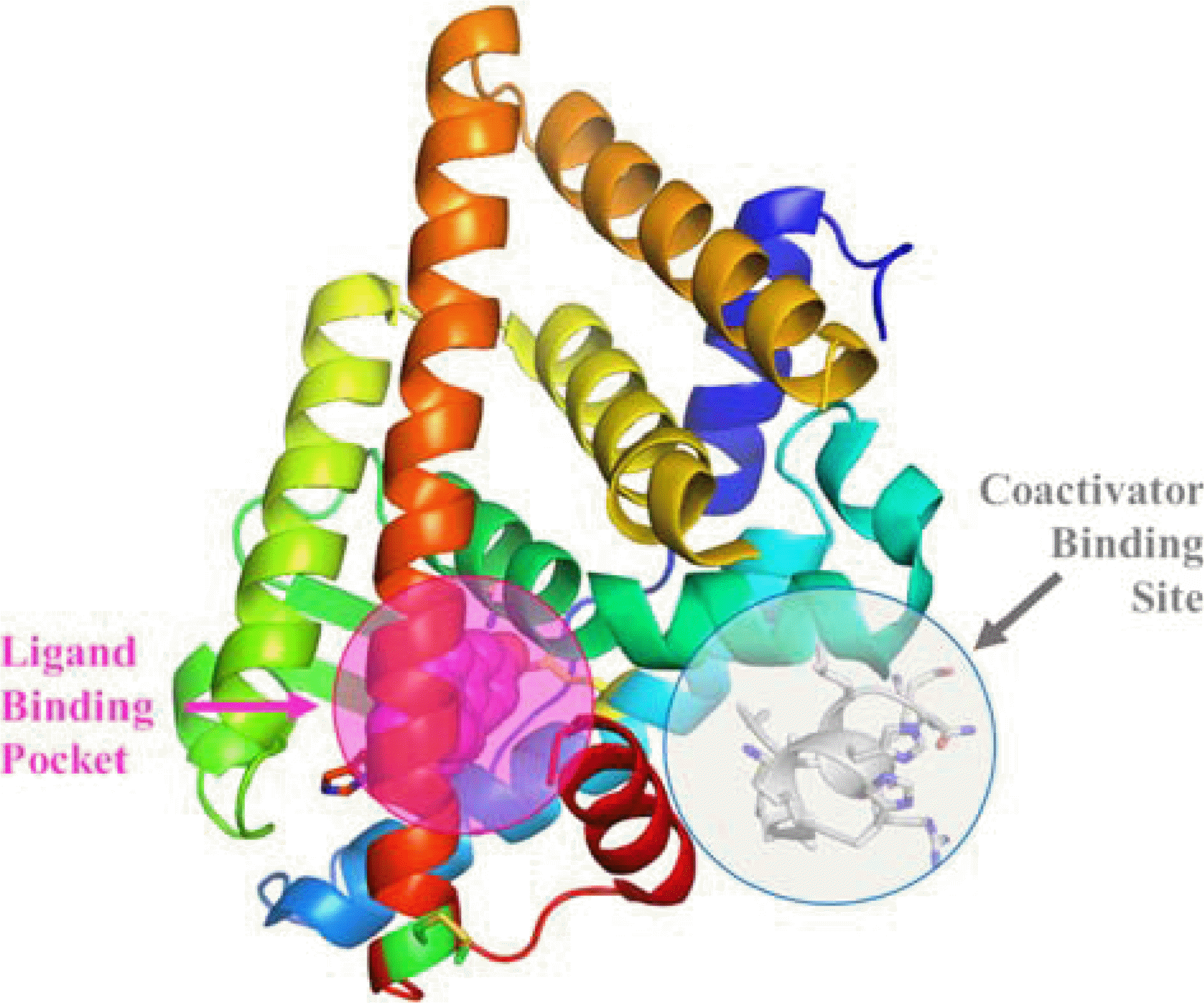 | Fig. 3.Structure of ligand-binding domain of estrogen receptor α with the ligand-binding pocket and coactivator-binding site. Not only the binding between estrogen and its ligand binding pocket, the protein-protein interactions between coactivator proteins and their binding sites also results in cell proliferation. Competitive blockade of the coactivator binding site could effectively halt cell proliferation for breast cancer therapeutics. |
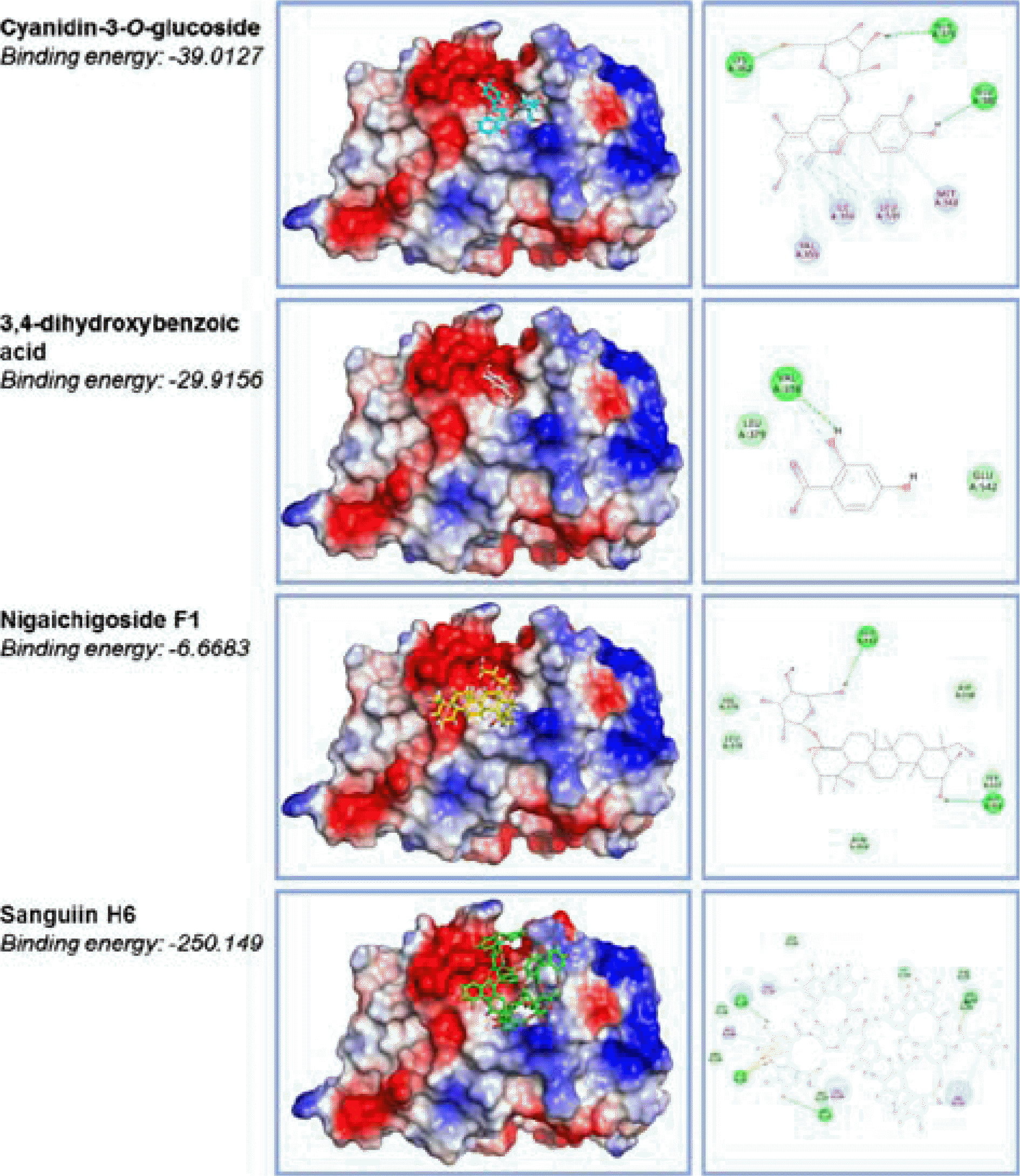 | Fig. 4.The docking structures of R. coreanus compounds with coactivator-binding site of estrogen receptor α. Molecular docking assay was constructed from the X-ray structure of ERα complexed with estradiol and a synthesized stable peptide inhibitor in the coactivator-binding groove. The atomic coordinates were obtained from the Protein Data Bank and manipulated using Discovery Studio molecular modeling package. The docking simulation was implemented by CDOCKER program. All atomic charges of ligands were assigned using the Momany-Rone partial charge and CHARMM force fields. Among four compounds isolated from R. coreanus, Sanguiin H6 showed the strongest affinity for the ERα coactivator-binding site. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download