Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the changes in upper and lower eyelid positions after upper blepharoplasty in elderly patients.
Methods
Patients diagnosed with dermatochalasis and treated with upper blepharoplasty were included in the study. Clinical photographs taken preoperatively and immediately after surgery were retrospectively reviewed. Marginal reflex distance (MRD) 1, MRD2 and palpebral fissure height (PFH) were measured from the photographs using Image J software.
Results
A total of 184 patients (72 males and 112 females) were included in the study. The preoperative mean MRD1, MRD2, and PFH were 1.97 ± 1.27 mm, 4.74 ± 0.97 mm, and 6.70 ± 1.69 mm, respectively. The postoperative mean MRD1, MRD2, and PFH were 1.79 ± 0.79 mm, 4.16 ± 0.92 mm, and 5.95 ± 1.36 mm, respectively. Preoperative and postoperative MRD1 were not significantly different (p = 0.256), but the postoperative MRD2 and PFH significantly decreased compared to preoperative values (both, p < 0.001).
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1), MRD2 and palpebral fissure height (PFH). MRD1 is the distance from the corneal light reflex to the level of the upper eyelid margin. MRD2 is the distance from the corneal light reflex to the level of the lower eyelid margin. PFH is the distance from the level of the upper eyelid margin to the level of the lower eyelid margin.
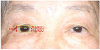
Figure 2
A case of 61-year old male patient. (A) Preoperative photograph. Marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1), MRD2, and palpebral fissure height (PFH) of right eye was 2.90 mm, 5.60 mm, and 8.50 mm, respectively. (B) Postoperative photograph. MRD1, MRD2, and PFH of right eye was 2.19 mm, 3.01 mm, and 5.20 mm, respectively. The arrows show that reverse ptosis was worsened immediately after surgery compared with preoperative status.

Notes
References
1. Dar SA, Rubinstein TJ, Perry JD. Eyebrow position following upper blepharoplasty. Orbit. 2015; 34:327–330.


2. Lee JM, Lee TE, Lee H, et al. Change in brow position after upper blepharoplasty or levator advancement. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:434–436.


3. Fagien S. Eyebrow analysis after blepharoplasty in patients with brow ptosis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992; 8:210–214.


4. Starck WJ, Griffin JE Jr, Epker BN. Objective evaluation of the eyelids and eyebrows after blepharoplasty. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996; 54:297–302.


5. Lee S, Park J, Lee J, et al. Upper and lower eyelid positions in several Korean age groups. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018; 59:606–612.

6. Bartley GB, Frueh BR, Holds JB, et al. Lower eyelid reverse ptosis repair. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002; 18:79–83.


7. Wladis EJ, Gausas RE. Transient descent of the contralateral eyelid in unilateral ptosis surgery. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 24:348–351.


8. Park DM, Song JW, Han KH, Kang JS. Anthropometry of normal Korean eyelids. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 17:822.
9. Moon CS, Moon SH, Jang JW. Topographic anatomic difference of the eyelid according to age in Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1865–1871.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download