Abstract
Purpose
This study was conducted to analyze research on reflection in Korean nursing, and suggest future directions for effective application of reflective practice in Korean nursing education and practice.
Methods
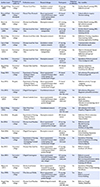
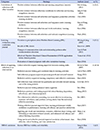
A review was performed using domestic databases including RISS, KISS, DBpia, and NDSL. Twenty-three papers were analyzed according to general characteristics, key variables regarding reflection, and findings regarding reflection.
Results
Reflection in nursing research has received attention since 2005, generating almost half the publications in the last 3 years. Key variables regarding reflection were classified into reflection-related general term (34.7%), reflective action (8.6%), and reflection writing method (56.7%). Findings regarding reflection were categorized into correlation of reflection with other variables (26.1%), learning evaluation using a reflective journal (22.2%), effects of applying reflection as an intervention (47.4%), and Korean Self-Reflection and Insight Scale validation (4.3%).
Conclusion
Results indicate that reflection or reflective practice is an important component in integrating theories to practice, and that reflective practice is a prerequisite to becoming a professional nurse as well as a crucial tool for ideal changes in nursing. Considerable effort should be made to define the concept of reflective practice and effectively apply it to nursing education and practice in Korea.
Figures and Tables
Appendix
Appendix
A List of the Literature Reviewed for the Study
A1. Hwang SY, Jang KS. Perception about problem-based learning in reflective journals among undergraduate nursing students. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35(1):65-76. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.65
A2. Park S, Kwon IG. Factors influencing nurses' clinical decision making: Focusing on critical thinking disposition. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37(6):863-871. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.863
A3. Kim KJ, Yoon J, Hyoung HK. Analysis of problem based learning based on the self-reflection journals and class evaluation of nursing students. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2009;16(4):438-448.
A4. Lee SO, Park YS. A study on a students general recognition of web-based PBL and learning activity of students by their reflective thinking level. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2009;15(2):194-204. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2009.15.2.194
A5. Kim H, Jang KS. Comparison of reflection hierarchy, team learning climate, and learning organization building on nursing competency in clinical nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2013;19(2):282-291. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2013.19.2.282
A6. Lim SJ, Park EY. Changes in communication and relationship pattern for undergraduate nursing students after Satir Communication Education. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2013;19(2):151-162. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2013.19.2.151
A7. Yoon J, Kim KJ, Choi MS. The effects of OSCE application before clinical practice for nursing students. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2013;19(2):273-284. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2013.19.2.273
A8. Kim EJ. Nursing students' clinical judgment skills in simulation: Using Tanner's clinical judgment model. Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2014;20(2):212-222. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2014.20.2.212
A9. Jang KS, Kim H. A study of reflective thinking levels and conditions for reflection affecting on nursing competency in clinical nurses. Journal of the Korean Data Analysis Society. 2014; 16(6):3393-3407.
A10. Kang HJ. Development and evaluation of a self-reflection program for intensive care unit nurses who experienced the death of pediatric patients [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University; 2015. p. 1-150.
A11. Kim HJ. The effect of reflective activity using concept mapping on nurses' competency [master's thesis]. Seoul: Kyung Hee University; 2015. p. 1-133.
A12. Cho MK. The relationships among happiness, happiness promotion activities and self-reflection in the convergence society. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2015;13(7):305-313. https://doi.org/10.14400/jdc.2015.13.7.305
A13. Jo MJ, Jun WH. Effects of end-of-life care education using self-reflection diary on spirituality, death orientation, and attitudes toward nursing care of the dying patients in nursing students. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association. 2015;15(12):294-303. https://doi.org/10.5392/jkca.2015.15.12.294
A14. Kim JM, Hong SK. Influence of self-reflection, self-esteem, and empathy on happiness index in nursing students. Journal of East-West Nursing Research. 2016;22(2):113-120. https://doi.org/10.14370/jewnr.2016.22.2.113
A15. Koo JS. Mediating effect of reflection on the relationship between work motivation and nursing competency according to the nursing clinical ladder among staff nurses working in general hospital [master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonsei University; 2016. p. 1-76.
A16. Jho MY. Effects of writing reflective journal on meta-cognition and problem solving ability in nursing students taking a fundamental nursing skills course applying blended learning. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2016;23(4):430-439. https://doi.org/10.7739/jkafn.2016.23.4.430
A17. Park SY. Relationship between self-reflection, critical thinking disposition, multi-cultural experience and cultural competence in nursing students. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2016;14(12):345-355. https://doi.org/10.14400/jdc.2016.14.12.345
A18. Bang S. Educational program development and effect of debriefing using reflection questions and writing with simulation of patient care after abdominal surgery[dissertation]. Gyeongsang National University; 2017. p. 1-128.
A19. Jho MY. Effects of the type of writing reflective journals on academic self-efficacy and problem solving ability. Journal of the Korean Data Analysis Society. 2017;19(5):2825-2839.
A20. Kim SO. Effects of self-directed practice through writing selfreflective journal on basic nursing performance ability, confidence in performance, learning self-efficacy and practice satisfaction. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2017;15(10):293-306.
A21. Shim GG, Son MS, Ji ES. The effectiveness of child nursing simulation using standardized patient on nursing student's anxiety, self-efficacy and critical thinking disposition. Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society. 2017; 18(10):299-308.
A22. Kim H. Effect of the fundamental nursing lessons that take advantage of the movie and the reflective journal. The Journal of Educational Information and Media. 2018;24(1):79-94. https://doi.org/10.15833/kafeiam.24.1.079
A23. Song MO, Kim H. Validity and reliability of the self-reflection and insight scale for Korean nursing students. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2018;25 (1):1-21. https://doi.org/10.7739/jkafn.2018.25.1.11
References
1. Dewey J. How we think: A restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process. 2nd ed. Boston: New York D. C. Heath and Co;1934.
2. Osterman KF. Reflective practice: A new agenda for education. Education and Urban Society. 1990; 22(2):133–152. DOI: 10.1177/0013124590022002002.
3. Schön DA. The reflective practitioner: How professionals think in action. New York: Basic Books;1983.
4. Schön DA. Educating the reflective practitioner: Toward a new design for teaching and learning in the professions. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass;1987.
5. Atkins S, Murphy K. Reflection: A review of the literature. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1993; 18(8):1188–1192.


6. Caldwell L, Grobbel C. The importance of reflective practice in nursing. International Journal of Caring Sciences. 2013; 6(3):319–326.
7. Gustafsson C, Asp M, Fagerberg I. Reflective practice in nursing care: Embedded assumptions in qualitative studies. International Journal of Nursing Practice. 2007; 13(3):151–160. 10.1111/j.1440-172x.2007.00620.x.

8. Schumann Scheel L, Peters MDJ, Meinertz Møbjerg AC. Reflection in the training of nurses in clinical practice settings: A scoping review protocol. JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports. 2017; 15(12):2871–2880.


9. Mezirow J. Transformative dimensions of adult learning. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass;1991.
10. Lee M, Jang KS. The significance and application of reflective practice in nursing practice. Journal of Nursing and Health Issues. 2018; 23(1):1–8.
11. Bulman C, Schutz S. Reflective practice in nursing. 5th ed. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell;2013.
12. Parrish DR, Crookes K. Designing and implementing reflective practice programs-key principles and considerations. Nurse Education in Practice. 2014; 14(3):265–270. DOI: 10.1016/j.nepr.2013.08.002.

13. Asselin ME, Schwartz-Barcott D. Exploring problems encountered among experienced nurses using critical reflective inquiry: Implications for nursing professional development. Journal for Nurses in Professional Development. 2015; 31(3):138–144. DOI: 10.1097/nnd.0000000000000145.

14. Beam RJ, O'brien RA, Neal M. Reflective practice enhances public health nurse implementation of nurse family partnership. Public Health Nursing. 2010; 27(2):131–139. DOI: 10.1111/j.1525-1446.2010.00836.x.
15. Dubé V, Ducharme F. Nursing reflective practice: An empirical literature review. Journal of Nursing Education and Practice. 2015; 5(7):91–99. DOI: 10.5430/jnep.v5n7p91.

16. Mann K, Gordon J, MacLeod A. Reflection and reflective practice in health professions education: A systematic review. Advances in Health Sciences Education. 2009; 14(4):595–621. DOI: 10.1007/s10459-007-9090-2.


17. Koo JS. Mediating effect of reflection on the relationship between work motivation and nursing competency according to the nursing clinical ladder among staff nurses working in general hospital [master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2016. 1–76.
18. Kim H, Jang KS. Comparison of reflection hierarchy, team learning climate, and learning organization building on nursing competency in clinical nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2013; 19(2):282–291. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2013.19.2.282.

19. Jang KS, Kim H. A study of reflective thinking levels and conditions for reflection affecting on nursing competency in clinical nurses. Journal of the Korean Data Analysis Society. 2014; 16(6):3393–3407.
20. Zuber-Skerritt O, Fletcher M. The quality of an action research thesis in the social sciences. Quality Assurance in Education. 2007; 15(4):413–436. DOI: 10.1108/09684880710829983.

21. Choe MA, Kim NC, Kim KM, Kim SJ, Park KS, Byeon YS, et al. Trends in Nursing Research in Korea: Research Trends for Studies Published from the Inaugural Issue to 2010 in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and the Journals Published by Member Societies under Korean Academy of Nursing Science. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2014; 44(5):484–494. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.484.


22. Taylor B. Identifying and transforming dysfunctional nursenurse relationships through reflective practice and action research. International Journal of Nursing Practice. 2001; 7(6):406–413. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-172x.2001.00323.x.

23. O'Donovan M. Reflecting during clinical placement-discovering factors that influence pre-registration psychiatric nursing students. Nurse Education in Practice. 2006; 6(3):134–140. DOI: 10.1016/j.nepr.2005.10.005.

24. Chong MC. Is reflective practice a useful task for student nurses? Asian Nursing Research. 2009; 3(3):111–120. DOI: 10.1016/s1976-1317(09)60022-0.


25. Nielsen A, Stragnell S, Jester P. Guide for reflection using the clinical judgment model. Journal of Nursing Education. 2007; 46(11):513–516.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download