Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to examine the effect of self-assertive training applying the reality therapy techniques (SATART) on self-esteem and internalized stigma of schizophrenia patients.
Methods
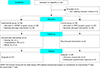
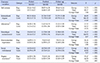
This study was a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design and enrolled 55 people with schizophrenia (experimental group=27, control group=28) from two community mental health centers. The SATART was offered twice a week for 6 weeks in a total 12 sessions. Data were collected from February to April, 2017, using the Korean version of the Internalized Stigma of Mental Illness Scale and Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale. The collected data was analyzed using χ2 test, independent t-test, one-way ANCOVA, and repeated measures ANOVA with using the SPSS/WIN 22.0 program.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Hong JP, Lee DW, Ham BJ, Lee SH, Sung SJ, Yoon T, et al. 2016 survey of mental disorders in Korea. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare (Korea);2017. 04. Report No. 11-1352000-000564-13.
2. Chang SM, Cho S-J, Jeon HJ, Hahm BJ, Lee HJ, Park JI, et al. Economic burden of schizophrenia in South Korea. Journal of Korean Medical Science. 2008; 23(2):167–175. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.167.



3. Jin H, Mosweu I. The societal cost of schizophrenia: a systematic review. Pharmacoeconomics. 2017; 35(1):25–42. DOI: 10.1007/s40273-016-0444-6.


4. Kunikata H, Mino Y, Nakajima K. Factors affecting WHOQOL-26 in community-dwelling patients with schizophrenia. Japanese Journal of Public Health. 2006; 53(4):301–309.

5. Abiri S, Oakley LD, Hitchcock ME, Hall A. Stigma related avoidance in people lining with severe mental illness (SMI): findings of an integrative review. Community Mental Health Journal. 2016; 52(3):251–261. DOI: 10.1007/s10597-015-9957-2.


6. Kim MY, Jeon SS. Development and effects of a cognitive-behavioral therapy based program in reducing internalized stigma in patients with schizophrenia. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2016; 46(3):349–363. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.349.


7. Lee HJ. The changing discourse of depression and its cultural implications in South Korea: an analysis of newspaper coverage between 1991 and 2010. Journal of Korean Cultural Anthropology. 2012; 45(1):43–88.
8. Link BG, Cullen FT, Struening E, Shrout PE, Dohrenwend BP. A modified labeling theory approach to mental disorders: an empirical assessment. American Sociological Review. 1989; 54(3):400–423. DOI: 10.2307/2095613.

9. Mittal D, Sullivan G, Chekuri L, Allee E, Corrigan PW. Empirical studies of self-stigma reduction strategies: a critical review of the literature. Psychiatric Services. 2012; 63(10):974–981. DOI: 10.1176/appi.ps.201100459.


10. Segalovich J, Doron A, Behrbalk P, Kurs R, Romem P. Internalization of stigma and self-esteem as it affects the capacity for intimacy among patients with schizophrenia. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing. 2013; 27(5):231–234. DOI: 10.1016/j.apnu.2013.05.002.


11. Tsang HWH, Ching SC, Tang KH, Lam HT, Law PYY, Wan CN. Therapeutic intervention for internalized stigma of severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophrenia Research. 2016; 173(1-2):45–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2016.02.013.


12. Lee TY, Chang SC, Chu H, Yang CY, Ou KL, Chung MH, et al. The effects of assertiveness training in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, single-blind, controlled study. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69(11):2549–2559. DOI: 10.1111/jan.12142.


13. Speed BC, Goldstein BL, Goldfried MR. Assertiveness training: a forgotten evidence-based treatment. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 2018; 25(1):1–20. DOI: 10.1111/cpsp.12216.

14. Yıldırım A, Aşılar RH, Camcıoğlu TH, Erdiman S, Karaağaç E. Effect of psychosocial skills training on disease symptoms, insight, internalized stigmatization, and social functioning in patients with schizophrenia. Rehabilitation Nursing. 2015; 40(6):341–348. DOI: 10.1002/rnj.195.


15. Fung KMT, Tsang HWH, Cheung W. Randomized controlled trial of the self-stigma reduction program among individuals with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research. 2011; 189(2):208–214. DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2011.02.013.


16. Ko KH, Yang SH, Kim YA, Kwon MS, Bang SH, Lee JM, et al. The effects of an empowerment program for chronic schizophrenic patients on their empowerment and internalized stigma. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2008; 17(4):491–499.
17. Lee WK, Hwang TY. Efficacy of a group treatment, self-stigma overcome programs for inpatients with schizophrenia. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2010; 49(5):444–452.
18. Corey G. Theory and practice of counseling and psychotherapy. 10th ed. Hague JD: Cengage Learning;2017. p. 540.
19. Kim JS. Effectiveness of reality therapy for schizophrenic patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005; 35(8):1485–1492.

20. Rosenberg M. Society and the adolescent self-image. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press;1965. p. 347.
21. Jeon BJ. Self-esteem: a test of it's measurability. Yonsei Nonchong. 1974; 11:107–130.
22. Ritsher JB, Otilingam PG, Grajales M. Internalized stigma of mental illness: psychometric properties of a new measure. Psychiatry Research. 2003; 121(1):31–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2003.08.008.


23. Hwang TY, Lee WK, Han ES, Kwon EJ. A study on the reliability and validity of the Korean version of internalized stigma of mental illness scale (K-ISMI). Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2006; 45(5):418–426.
24. Lee J, Nam S, Lee MK, Lee JH, Lee SM. Rosenberg's self-esteem scale: analysis of item-level validity. The Korean Journal of Counseling and Psychotherapy. 2009; 21(1):173–189.
25. Kunikata H, Yoshinaga N, Shiraishi Y, Okada Y. Nurse-led cognitive-behavioral group therapy for recovery of self-esteem in patients with mental disorders: a pilot study. Japan Journal of Nursing Science. 2016; 13(3):355–364. DOI: 10.1111/jjns.12114.


26. Chien WT, Leung SF, Yeung FKK, Wong WK. Current approaches to treatments for schizophrenia spectrum disorders, part II: psychosocial interventions and patient-focused perspectives in psychiatric care. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 2013; 9:1311–1332. DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S49263.



27. Knight MT, Wykes T, Hayward P. Group treatment of perceived stigma and self-esteem in schizophrenia: a waiting list trial of efficacy. Behavioral and Cognitive Psychotherapy. 2006; 34(3):305–318. DOI: 10.1017/S1352465805002705.

28. Yanos PT, Roe D, West ML, Smith SM, Lysaker PH. Group-based treatment for internalized stigma among persons with severe mental illness: findings from a randomized controlled trial. Psychological Services. 2012; 9(3):248–258. DOI: 10.1037/a0028048.



29. Kim MY, Jun SS. Factors affecting internalized stigma of patient with schizophrenia. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2012; 21(2):108–117.

30. Kim WJ, Song YJ, Ryu HS, Ryu V, Kim JM, Ha RY, et al. Internalized stigma and its psychosocial correlates in Korean patients with serious mental illness. Psychiatry Research. 2015; 225(3):433–439. DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.11.071.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download