Abstract
Purpose
This study tries to analyze the concept of Yangsaeng in the Korean aged, with focus on nursing.
Methods
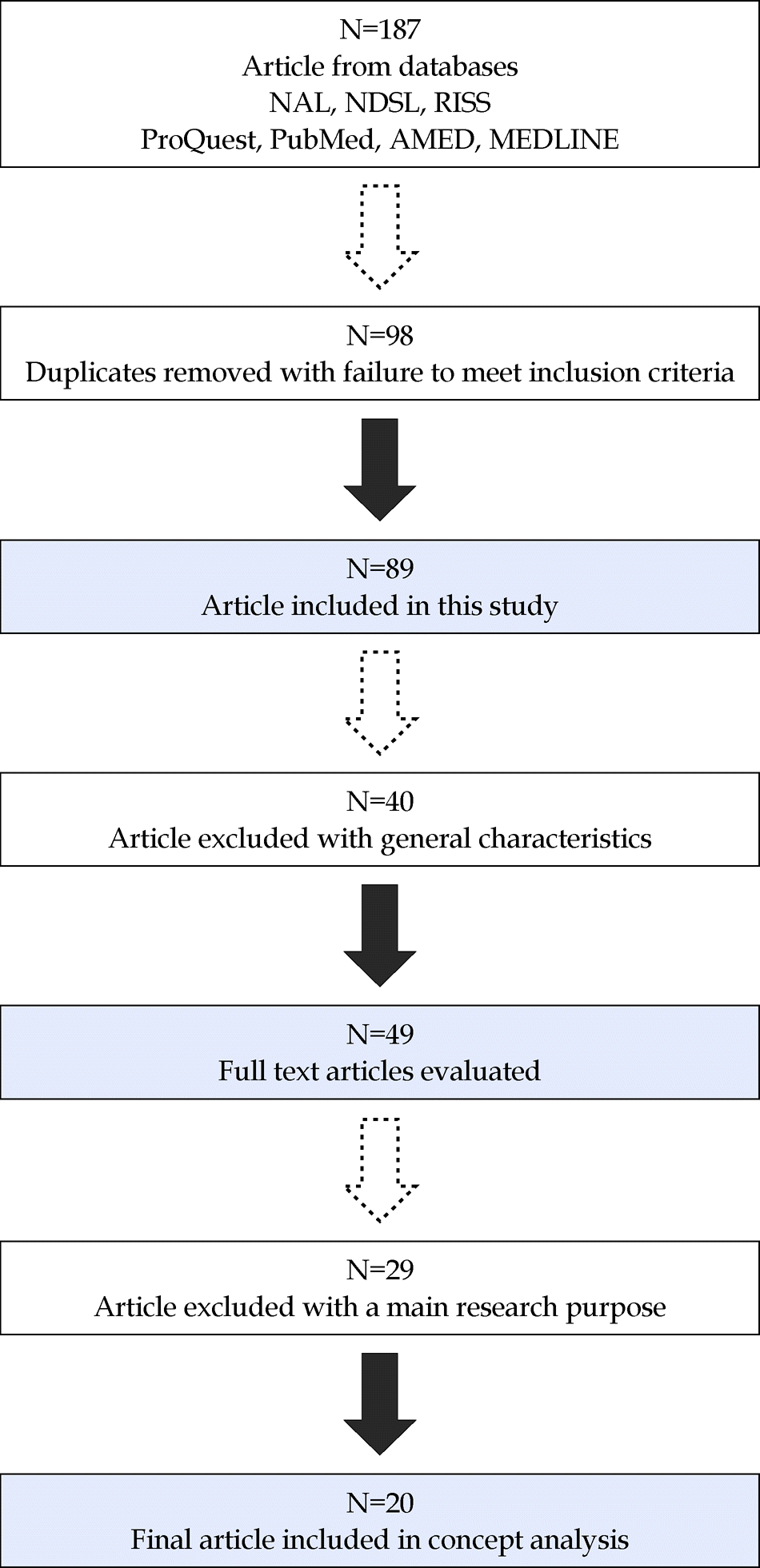
Rodgers' evolutionary approach was used to identify the common definitions, attributes, antecedents, and consequences of the Yangsaeng concept for the aged. Literature search was conducted at the NAL, NDSL, RISS, ProQuest, PubMed, AMED, and MEDLINE databases from 2004 to 2016, using the keywords “Yangsaeng,” “health promotion,” “health management,” “traditional oriental methods,” and “traditional oriental nursing.”Finally, 20 relevant articles were selected and thoroughly reviewed.
Results
The analysis shows that the model of Yangsaeng for the Korean aged is that of personal adaptive-capacity, totality, challenging, and coping resource and includes physical, social and psychological health and wellness.
Conclusion
This work provides some implications on the development of nursing intervention related with Yangsaeng for the Korean aged, and suggests the implementation of such intervention in the practice of Yangsaeng for the Korean aged. Therefore, a better understanding of the Korean aged and Yangsaeng within the context of nursing can be achieved.
Go to : 
References
1. Ahn HM, Kim SS, Kim WG, Yu HD, Chong MS, Lee KN. A study on the relations between Yangseng level and stress in industrial workers. Journal of Society of Preventive Korean Medicine. 2007; 11(1):109–129.
2. Park YS, Lee HY, Kwon YH. Validation of a path model on elderly women's Yangsaeng (養生: traditional oriental health promotion). Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2011; 22(3):325–332.
3. Kim AJ. Development of a tool in measuring Yangsaeng. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004; 34(5):729–738.

4. Yi SJ, Kim AK. Factors influencing Yangsaeng in middle aged women. The Korean Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2014; 21(1):39–47.

5. Park YS, Seo DS, Kwon YH. Factors influencing Yangsaeng in elders (Yangsaeng 養生: traditional oriental health promotion). Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2011; 41(1):72–79.
6. Cha NH. A study on Yangsaeng in Korean elders. Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2010; 21(3):293–302.

7. Kwag OG, Kwon YH. A study on daily living abilities, self-efficacy and Yangsaeng behavior in elderly men (Yangsaeng; 養生 traditional oriental health promotion). Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2013; 24(1):11–19.
8. Statistics Korea. Statistics of aged [Internet]. Seoul: Statistics Korea;2016. [cited 2017 August 31]. Available from:. http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1IN1602&vw_cd.
9. Lee BJ, Hong SW. The effect of older people's leisure activities on their self-esteem and life satisfaction. Journal of Northeast Asia Tourism. 2012; 8(2):139–156.
10. Chung MS, Song JH. Social support and health status based on characteristics of leisure activity of middle-aged women. The Korean Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2011; 18(1):97–106.
11. Pender NJ. Health promotion in nursing practice. 3rd ed.Stamford Connecticut: Appleton & Lange;1996. p. 320 p.
12. Rodgers BL. Concept analysis: an evolutionary view. Rodgers BL, Knafl KA editors, editors. Concept development in nursing: Foundations, techniques, and applications. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2000. p. p. 77–102.
13. Sakisian CA, Prohaska TR, Wong MD, Hirsch S, Mangione CM. The relationship between expectations for aging and physical activity among older adults. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2005; 20(10):911–915. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2005.0204.x.
14. Park HS, Kim AJ. Adaptation to menopause and use of Yang-saeng in middle aged Korean women. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2010; 16(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2010.16.1.1.
15. Kim AK. Yangsaeng and health related quality of life (HRQOL) in middle aged women. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2010; 16(3):297–306.

16. Wang MJ. Relationship among Yangsaeng, activities of daily living, and physical function in Korean elders. Journal of East-West Nursing Research. 2010; 16(1):19–25.
17. Kang JS, Shin MK. The empowerment and Yangsaeng according to depression for the elderly. Journal of Korean Gerontological Society. 2012; 32(4):1137–1146.
18. Wang MJ, Cha NH. An approach of eastern nursing science for regimen on the oldman. Journal of East-West Nursing Research. 2002; 7(1):7–17.
19. An HG, Shin YH, Gu BS. A study of Gigong-Yangsaeng (Good life) and the old-health care. Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry. 2000; 11(2):177–187.
20. Kim KW, Kim AJ. Yangsaeng and quality of life (WHOQOL-BREF) in adult and elderly Koreans practicing Dan-Jeon breathing (DJB). The Korean Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2010; 17(2):231–239.
21. Chong D, Chong M, Lee K. A comparison of influencing factors on Yangseng level in urban and rural elderly. Journal of Society of Preventive Korean Medicine. 2007; 11(2):1–21.
22. Park GS. Lived experience of Yangsaeng exercise through Kouk-Sun-Do among Korean elderly. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2009; 21(1):62–76.
23. Kim JS, Heo IU. Potential values of traditional curing martial Art-Sunsool in the aspect of silver sport: Based on curing regimen prescribed in Dongeui bogam. The Journal of Korean Allance of Martial Arts. 2010; 12(2):1–14.
24. Choi EK, Kwon SH, Kim AJ, Park JS, Park JS, Lee KN. Relationship between actual health and Yangseng of the elderly in urbanites- Focused on certain parts of urban areas in Jeonbuk province. Journal of Korean Academy of Medical Gi-Gong. 2005; 8(1):96–114.
25. Kim AK. The study of Yangsaeng and fatigue in adult men. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2011; 18(1):79–86.
26. Poland B, Dooris M. A green health future: The settings approach to building health, equity and sustain ability. Critical Public Health. 2010; 20(3):281–298. https://doi.org/10.1080/09581596.2010.502931.
27. Langford R, Bonell C, Jones H, Pouliou T, Murphy S, Waters E. . The World Health Organization's health promoting schools framework: A Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. Bio Medical Central Public Health. 2015; 15:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1360-y.

28. Frilander H, Lallukka T, Viikari J, Heliövaara M, Solovieva S. Health problems during compulsory military service predict disability retirement: A register-based study on secular trends during 40 years of follow-up. Public Library of Science One. 2016; 11(8):e0159786. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159786.

Go to : 
Table 1.
Rodgers' Evolutionary Approach to Concept Analysis
Table 2.
Conceptual Diagram of Yangsaeng for the Aged




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download