1. Martí MJ, Tolosa E, Campdelacreu J. Clinical overview of the synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2003; 18(Suppl 6):S21–S27. PMID:
14502652.
2. Jellinger KA. Neuropathological spectrum of synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2003; 18(Suppl 6):S2–S12. PMID:
14502650.

3. Rizzo G, Copetti M, Arcuti S, Martino D, Fontana A, Logroscino G. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology. 2016; 86:566–576. PMID:
26764028.
4. Adler CH, Beach TG, Hentz JG, Shill HA, Caviness JN, Driver-Dunckley E, et al. Low clinical diagnostic accuracy of early vs advanced Parkinson disease: clinicopathologic study. Neurology. 2014; 83:406–412. PMID:
24975862.

5. Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992; 55:181–184. PMID:
1564476.

6. Litvan I, MacIntyre A, Goetz CG, Wenning GK, Jellinger K, Verny M, et al. Accuracy of the clinical diagnoses of Lewy body disease, Parkinson disease, and dementia with Lewy bodies: a clinicopathologic study. Arch Neurol. 1998; 55:969–978. PMID:
9678315.
7. Nelson PT, Jicha GA, Kryscio RJ, Abner EL, Schmitt FA, Cooper G, et al. Low sensitivity in clinical diagnoses of dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurol. 2010; 257:359–366. PMID:
19795154.

8. Joutsa J, Gardberg M, Röyttä M, Kaasinen V. Diagnostic accuracy of parkinsonism syndromes by general neurologists. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014; 20:840–844. PMID:
24816002.

9. Noyce AJ, Lees AJ, Schrag AE. The prediagnostic phase of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016; 87:871–878. PMID:
26848171.

10. Braak H, de Vos RA, Bohl J, Del Tredici K. Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett. 2006; 396:67–72. PMID:
16330147.
11. Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Mutlu E, Dodiya HB, Daian D, Jaglin JA, et al. Alpha-synuclein in colonic submucosa in early untreated Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2012; 27:709–715. PMID:
21766334.

12. Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Dodiya HB, Jakate S, Kordower JH. Is alpha-synuclein in the colon a biomarker for premotor Parkinson’s disease? Evidence from 3 cases. Mov Disord. 2012; 27:716–719. PMID:
22550057.

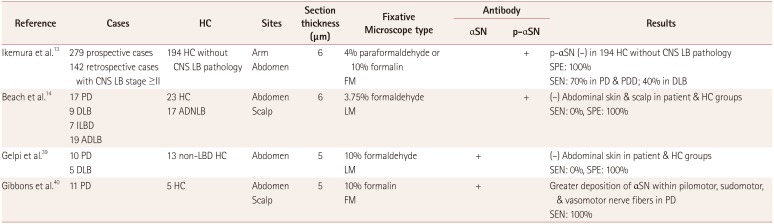
13. Ikemura M, Saito Y, Sengoku R, Sakiyama Y, Hatsuta H, Kanemaru K, et al. Lewy body pathology involves cutaneous nerves. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008; 67:945–953. PMID:
18800013.

14. Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Vedders L, Lue L, White Iii CL, et al. Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2010; 119:689–702. PMID:
20306269.
15. Fumimura Y, Ikemura M, Saito Y, Sengoku R, Kanemaru K, Sawabe M, et al. Analysis of the adrenal gland is useful for evaluating pathology of the peripheral autonomic nervous system in Lewy body disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007; 66:354–362. PMID:
17483692.

16. Orimo S, Uchihara T, Nakamura A, Mori F, Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, et al. Axonal alpha-synuclein aggregates herald centripetal degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2008; 131:642–650. PMID:
18079166.
17. Schneider SA, Boettner M, Alexoudi A, Zorenkov D, Deuschl G, Wedel T. Can we use peripheral tissue biopsies to diagnose Parkinson’s disease? A review of the literature. Eur J Neurol. 2016; 23:247–261. PMID:
26100920.

18. Pouclet H, Lebouvier T, Coron E, des Varannes SB, Rouaud T, Roy M, et al. A comparison between rectal and colonic biopsies to detect Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2012; 45:305–309. PMID:
21878391.

19. Gibbons CH, Griffin JW, Polydefkis M, Bonyhay I, Brown A, Hauer PE, et al. The utility of skin biopsy for prediction of progression in suspected small fiber neuropathy. Neurology. 2006; 66:256–258. PMID:
16434668.

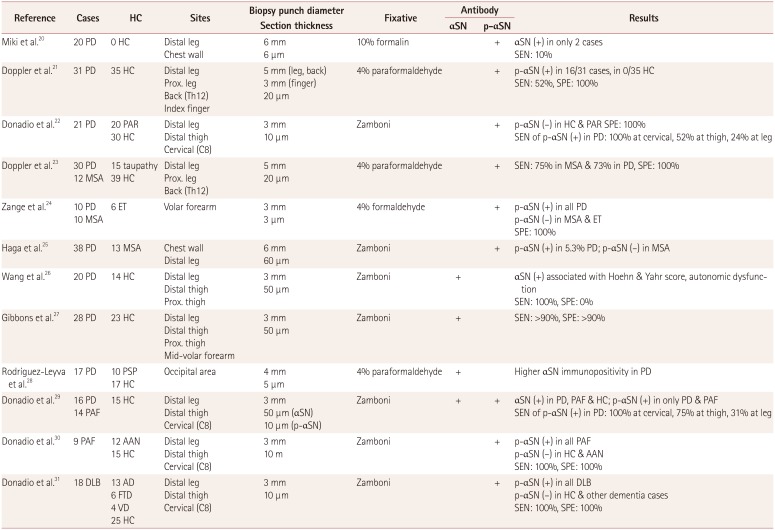
20. Miki Y, Tomiyama M, Ueno T, Haga R, Nishijima H, Suzuki C, et al. Clinical availability of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2010; 469:357–359. PMID:
20026177.

21. Doppler K, Ebert S, Uçeyler N, Trenkwalder C, Ebentheuer J, Volkmann J, et al. Cutaneous neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease: a window into brain pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2014; 128:99–109. PMID:
24788821.

22. Donadio V, Incensi A, Leta V, Giannoccaro MP, Scaglione C, Martinelli P, et al. Skin nerve α-synuclein deposits: a biomarker for idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2014; 82:1362–1369. PMID:
24634456.

23. Doppler K, Weis J, Karl K, Ebert S, Ebentheuer J, Trenkwalder C, et al. Distinctive distribution of phospho-alpha-synuclein in dermal nerves in multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord. 2015; 30:1688–1692. PMID:
26175301.

24. Zange L, Noack C, Hahn K, Stenzel W, Lipp A. Phosphorylated α-synuclein in skin nerve fibres differentiates Parkinson’s disease from multiple system atrophy. Brain. 2015; 138:2310–2321. PMID:
26017579.

25. Haga R, Sugimoto K, Nishijima H, Miki Y, Suzuki C, Wakabayashi K, et al. Clinical utility of skin biopsy in differentiating between Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Parkinsons Dis. 2015; 2015:167038. PMID:
25945280.

26. Wang N, Gibbons CH, Lafo J, Freeman R. α-Synuclein in cutaneous autonomic nerves. Neurology. 2013; 81:1604–1610. PMID:
24089386.

27. Gibbons CH, Garcia J, Wang N, Shih LC, Freeman R. The diagnostic discrimination of cutaneous α-synuclein deposition in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2016; 87:505–512. PMID:
27385742.

28. Rodríguez-Leyva I, Chi-Ahumada EG, Carrizales J, Rodríguez-Violante M, Velázquez-Osuna S, Medina-Mier V, et al. Parkinson disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: protein expression in skin. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2016; 3:191–199. PMID:
27042679.

29. Donadio V, Incensi A, Piccinini C, Cortelli P, Giannoccaro MP, Baruzzi A, et al. Skin nerve misfolded α-synuclein in pure autonomic failure and Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 2016; 79:306–316. PMID:
26606657.

30. Donadio V, Incensi A, Cortelli P, Giannoccaro MP, Jaber MA, Baruzzi A, et al. Skin sympathetic fiber α-synuclein deposits: a potential biomarker for pure autonomic failure. Neurology. 2013; 80:725–732. PMID:
23390175.

31. Donadio V, Incensi A, Rizzo G, Capellari S, Pantieri R, Stanzani Maserati M, et al. A new potential biomarker for dementia with Lewy bodies: skin nerve α-synuclein deposits. Neurology. 2017; 89:318–326. PMID:
28667178.
32. Malek N, Swallow D, Grosset KA, Anichtchik O, Spillantini M, Grosset DG. Alpha-synuclein in peripheral tissues and body fluids as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease-a systematic review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2014; 130:59–72. PMID:
24702516.
33. Takeda A, Hasegawa T, Matsuzaki-Kobayashi M, Sugeno N, Kikuchi A, Itoyama Y, et al. Mechanisms of neuronal death in synucleinopathy. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006; 2006:19365. PMID:
17047300.

34. Chandra S, Gallardo G, Fernández-Chacón R, Schlüter OM, Südhof TC. Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell. 2005; 123:383–396. PMID:
16269331.
35. Breydo L, Wu JW, Uversky VN. Α-synuclein misfolding and Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012; 1822:261–285. PMID:
22024360.

36. Oueslati A. Implication of alpha-synuclein phosphorylation at S129 in synucleinopathies: what have we learned in the last decade? J Parkinsons Dis. 2016; 6:39–51. PMID:
27003784.

37. Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, et al. Alpha-synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol. 2002; 4:160–164. PMID:
11813001.
38. Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:6469–6473. PMID:
9600990.
39. Gelpi E, Navarro-Otano J, Tolosa E, Gaig C, Compta Y, Rey MJ, et al. Multiple organ involvement by alpha-synuclein pathology in Lewy body disorders. Mov Disord. 2014; 29:1010–1018. PMID:
24395122.

40. Gibbons CH, Wang N, Freeman R. Cutaneous alpha-synuclein from paraffin embedded autopsy specimens in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017; 7:503–509. PMID:
28582870.

41. Wang N, Gibbons C, Garcia J, Freeman R. Phosphorylated alpha synuclein within cutaneous autonomic nerves of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD)-the implications of sample thickness on results (P1.107). Neurology. 2017; 88(16 Supplement):P1–P107.
42. Antelmi E, Donadio V, Incensi A, Plazzi G, Liguori R. Skin nerve phosphorylated α-synuclein deposits in idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder. Neurology. 2017; 88:2128–2131. PMID:
28468843.

43. Corbillé AG, Letournel F, Kordower JH, Lee J, Shanes E, Neunlist M, et al. Evaluation of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemical methods for the detection of Lewy-type synucleinopathy in gastrointestinal biopsies. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016; 4:35. PMID:
27044604.

44. Beach TG, Corbillé AG, Letournel F, Kordower JH, Kremer T, Munoz DG, et al. Multicenter assessment of immunohistochemical methods for pathological alpha-synuclein in sigmoid colon of autopsied Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. J Parkinsons Dis. 2016; 6:761–770. PMID:
27589538.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download