INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Cell culture
Plasmid construction
Table 1
DNA sequences of the oligonucleotides used in this study

Reporter gene assays
Quantitative real-time PCR
Promoter enzyme immunoassay
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays
Nkx-2.5 knockdown
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Transactivation of the human MDR1 USP by Nkx-2.5
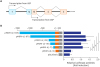 | Fig. 1Human MDR1 upstream promoter activity in MCF7 breast cancer cells. (A) Schematic diagram for the two transcription initiation sites of the human MDR1 gene. Numbers indicate number of exon in the human MDR1 gene. (B) MCF7 cells were transfected with the pMDR1-U (−1391) or plasmids harboring a series of 5′ deletion mutants of the human MDR1 upstream promoter, and their promoter activities were analyzed using reporter gene assays. Relative luciferase activities were normalized as fold value versus pMDR1-U (−1391). Results are expressed as the means ± SDs. of at least three independent experiments.USP = upstream promoter, DSP = downstream promoter, LUC, luciferase gene.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test.
|
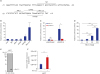 | Fig. 2Nkx-2.5 increased MDR1 upstream promoter activity in MCF7 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the nt −71 to +13 region of MDR1 upstream promoter. Numbers indicate positions from the transcriptional start site in the human MDR1 upstream promoter. The binding sites of putative transcription factors, which were identified using the TFBIND program (http://tfbind.hgc.jp), are underlined. (B) MCF7 cells were co-transfected with the pMDR1-U construct and the indicated transcription factors or control vector (pcDNA3.1), and reporter gene assays were performed. The relative luciferase activities were expressed as fold value versus the pcDNA3.1 vector. Results are expressed as the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; as determined using the unpaired Student's t-test. (C) The pMDR1-U (−1391) or pGL3/basic vector was co-transfected with Nkx-2.5 expression vector or pcDNA3.1 vector into MCF7 cells. Relative luciferase activities were normalized as fold values versus pMDR1-U (−1391) in the absence of Nkx-2.5. Results are expressed as the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; as determined by the unpaired Student's t-test. (D) The pMDR1-U (−1391) construct was co-transfected with the indicated amount of Nkx-2.5 expression vector into MCF7 cells. Relative luciferase activities were normalized as fold values versus pMDR1-U (−1391) in the absence of Nkx-2.5. Results are expressed as the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001 as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test. (E) MCF7 cells were infected with retrovirus encoding Nkx-2.5-FLAG or retrovirus from pMxs-IRES-puro vector (Control), and Nkx-2.5 expression was examined by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibody. (F) Real-time PCR analysis of MDR1 mRNA in MCF7 cells infected with retrovirus encoding Nkx-2.5 or retrovirus from pMXs-IRES-puro vector. Results are expressed as the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 as determined by the unpaired Student's t-test. |
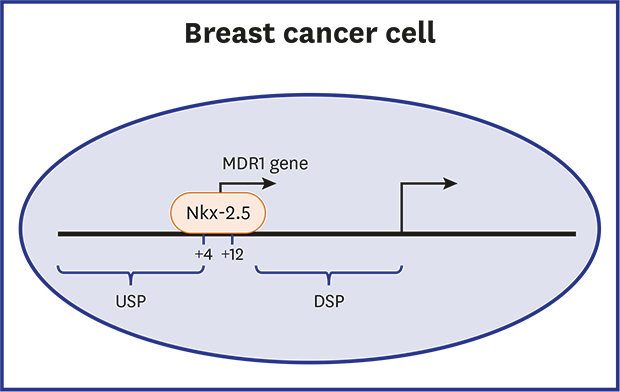
The Nkx-2.5-responsive element was located at the nt +4 to +10 region of the MDR1 USP
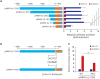 | Fig. 3Identification of the Nkx-2.5-binding site in MDR1 upstream promoter. (A) pMDR1-U (−1391) and plasmids harboring a series of 5′ deletion mutants of human MDR1 upstream promoter were co-transfected with Nkx-2.5 expression vector or control vector (pcDNA3.1) into MCF7 cells. Relative luciferase activities were expressed as fold over that of each promoter in the presence of pcDNA3.1 vector. Results are expressed as the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test. (B) Schematic representation of pMDR1-U (−1391/+136) with mutations in the Nkx-2.5-binding site. (C) pMDR1-U (−1391) or a mutated MDR1 upstream promoter construct were co-transfected with plasmid encoding Nkx-2.5 or control vector (pcDNA3.1) into MCF7 cells. Relative luciferase activities were expressed as fold over that of each promoter in the presence of pcDNA3.1 vector. Results are expressed as the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; as determined by the unpaired Student's t-test. |
Nkx-2.5 bound to the Nkx-2.5-responsive element in human MDR1 USP
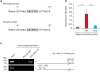 | Fig. 4Nkx-2.5 directly bound to the Nkx-2.5-binding site at nt +4 to +10 region of human MDR1 upstream promoter. (A) Schematic representation of biotinylated probes used in promoter enzyme immunoassay. (B) Streptavidin-coated microplates were conjugated with biotin-labeled oligonucleotides containing Wt or Mut Nkx-2.5-binding sites and then incubated with nuclear extracts from MCF7 cells transfected with plasmid encoding Nkx-2.5. After incubation for 2 hours, Nkx-2.5-DNA complex formation was analyzed colorimetrically using anti-Nkx-2.5 and HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. Results are presented as the means ± SDs (n = 3). (C) Soluble chromatin was prepared from MCF7 cells and immunoprecipitated with anti-Nkx-2.5 antibody or an isotype-matched IgG. Immunoprecipitated chromatin was subjected to PCR using primers specific for the Nkx-2.5-responsive element in MDR1 upstream promoter (upper panel). As a negative control, primers for the distal region (nt −1062 to −1221) of MDR1 upstream promoter were used (lower panel).Wt = wild-type, Mut = mutated.
**P < 0.01; as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test.
|
Nkx-2.5 knockdown leads to reduction of MDR1 expression in breast cancer cells
 | Fig. 5Nkx-2.5 knockdown leads to reduction in MDR1 expression in breast cancer cells. (A) Nkx-2.5 expression was analyzed in MCF7, MDA-MB-231, and 4T1-luc cells by Western blot. A representative result is shown. (B, C) MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with Nkx-2.5 siRNAs or control siRNA, and the expressions of Nkx-2.5 (B) and MDR1 mRNA (C) were analyzed by real-time PCR. Results are expressed as the means ± SDs of at least three independent experiments.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download