Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the cause of infectious mononucleosis, which is characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, and sore throat. On the other hand, gastrointestinal symptoms of EBV infection like dyspepsia, abdominal pain are non-specific and rarely encountered, which means it is difficult to diagnose gastric involvement of EBV infection without suspicion. The relation between gastric carcinoma and gastric lymphoma associated with EBV infection is well defined, but relations with other EBV-associated gastrointestinal diseases such as gastritis and peptic ulcer disease have rarely been reported. We report a case of benign gastric ulcer with EBV infection confirmed by endoscopic and histological findings.
Figures and Tables
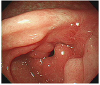
Fig. 1
Initial endoscopic examination revealed a large ulcer with thick yellowish exudate and an irregular margin on the lesser curvature of antrum of the stomach.
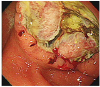
Fig. 2
Histopathological findings showing chronic active gastritis with necrotic detritus (H&E, ×100).
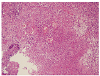
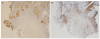
Fig. 3
Immunohistochemistry results of the gastric specimen were negative for pan cytokeratin [AE1/AE3] (A) and L26 (B) (original magnification, ×40).
References
1. Hisamatsu A, Nagai T, Okawara H, et al. Gastritis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Intern Med. 2010; 49:2101–2105.


2. Lee SS, Jang JJ, Cho KJ, Khang SK, Kim CW. Epstein-Barr virus-associated primary gastrointestinal lymphoma in non-immunocompromised patients in Korea. Histopathology. 1997; 30:234–242.


3. Sidagis J, Ueno K, Tokunaga M, Ohyama M, Eizuru Y. Molecular epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in EBV-related malignancies. Int J Cancer. 1997; 72:72–76.


4. Lee JH, Eum SW, Kim GY, et al. One case of infectious mononucleosis concurrent with acute erosive EBV gastritis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 35:91–95.
5. Kim JM, Song CW, Song KS, Kim JY. Acute gastritis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in a child. Korean J Pediatr. 2016; 59:Suppl 1. S68–S71.

6. Iwakiri D. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs: key molecules in viral pathogenesis. Cancers (Basel). 2014; 6:1615–1630.



7. Gulley ML, Tang W. Laboratory assays for Epstein-Barr virus-related disease. J Mol Diagn. 2008; 10:279–292.

9. Varga MG, Cai H, Waterboer T, et al. Epstein-Barr virus antibody titers are not associated with gastric cancer risk in East Asia. Dig Dis Sci. 2018; 63:2765–2772.



10. Kim Y, Shin A, Gwack J, et al. Epstein-Barr virus antibody level and gastric cancer risk in Korea: a nested case-control study. Br J Cancer. 2009; 101:526–529.



11. Chen XZ, Chen H, Castro FA, Hu JK, Brenner H. Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: a systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e792.
12. Yanai H, Takada K, Shimizu N, Mizugaki Y, Tada M, Okita K. Epstein-Barr virus infection in non-carcinomatous gastric epithelium. J Pathol. 1997; 183:293–298.


13. Cárdenas-Mondragón MG, Torres J, Flores-Luna L, Carreón-Talavera R, Camorlinga-Ponce M, Fuentes-Pananá EM. Epstein-Barr virus association with peptic ulcer disease. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2015; 2015:164840.

14. Shukla SK, Prasad KN, Tripathi A, et al. Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and its association with Helicobacter pylori infection in gastroduodenal diseases. Braz J Infect Dis. 2011; 15:583–590.


15. Kusano Y, Terui Y, Ueda K, Hatake K. Epstein-Barr virus gastric ulcer associated with ruxolitinib. Ann Hematol. 2016; 95:1741–1742.



16. Hiejima E, Yasumi T, Kubota H, et al. Gastric ulcer and gastroenteritis caused by Epstein-Barr virus during immunosuppressive therapy for a child with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012; 51:2107–2109.


17. Ryan JL, Shen YJ, Morgan DR, et al. Epstein-Barr virus infection is common in inflamed gastrointestinal mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 2012; 57:1887–1898.







 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download