1. Murray CJ, Salomon JA, Mathers C. A critical examination of summary measures of population health. Bull World Health Organ. 2000; 78(8):981–994.


2. GBD 2013 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Murray CJ, Barber RM, Foreman KJ, Abbasoglu Ozgoren A, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 306 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 188 countries, 1990–2013: quantifying the epidemiological transition. Lancet. 2015; 386(10009):2145–2191.


3. Ock M, Han JW, Lee JY, Kim SH, Jo MW. Estimating quality-adjusted life-year loss due to noncommunicable diseases in Korean adults through to the year 2040. Value Health. 2015; 18(1):61–66.


4. Love-Koh J, Asaria M, Cookson R, Griffin S. The social distribution of health: estimating quality-adjusted life expectancy in England. Value Health. 2015; 18(5):655–662.


5. Jia H, Zack MM, Thompson WW, Dube SR. Quality-adjusted life expectancy (QALE) loss due to smoking in the United States. Qual Life Res. 2013; 22(1):27–35.


6. Hyder AA, Puvanachandra P, Morrow RH. Measuring the health of populations: explaining composite indicators. J Public Health Res. 2012; 1(3):222–228.

7. Jia H, Zack MM, Thompson WW. State quality-adjusted life expectancy for U.S. adults from 1993 to 2008. Qual Life Res. 2011; 20(6):853–863.

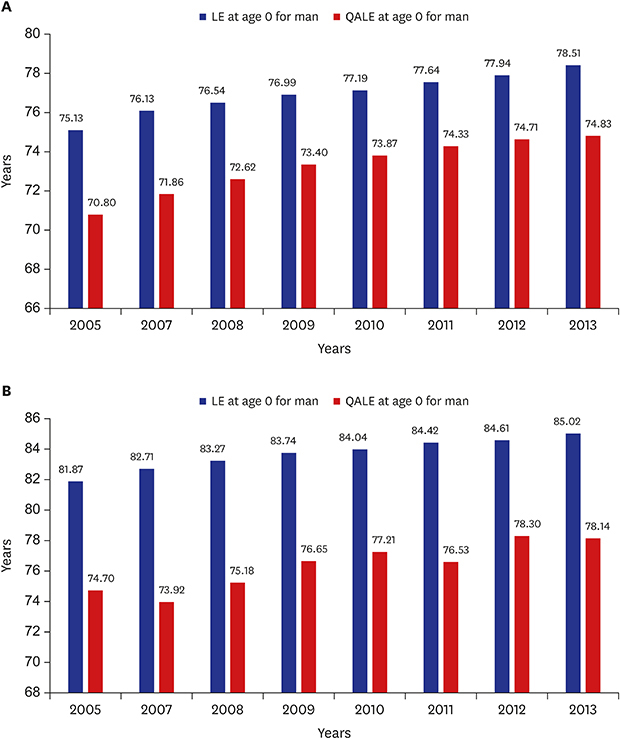
8. Lee JY, Ock M, Kim SH, Go DS, Kim HJ, Jo MW. Health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE) in Korea: 2005–2011. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:Suppl 2. S139–S145.

9. Salomon JA, Wang H, Freeman MK, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Lopez AD, et al. Healthy life expectancy for 187 countries, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012; 380(9859):2144–2162.


11. Gheorghe M, Wubulihasimu P, Peters F, Nusselder W, Van Baal PH. Health inequalities in the Netherlands: trends in quality-adjusted life expectancy (QALE) by educational level. Eur J Public Health. 2016; 26(5):794–799.


12. Jia H, Zack MM, Thompson WW. The effects of diabetes, hypertension, asthma, heart disease, and stroke on quality-adjusted life expectancy. Value Health. 2013; 16(1):140–147.


13. Lee HY, Hwang JS, Jeng JS, Wang JD. Quality-adjusted life expectancy (QALE) and loss of QALE for patients with ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage: a 13-year follow-up. Stroke. 2010; 41(4):739–744.
14. Brønnum-Hansen H, Juel K, Davidsen M, Sørensen J. Impact of selected risk factors on quality-adjusted life expectancy in Denmark. Scand J Public Health. 2007; 35(5):510–515.


15. Hung MC, Lai WW, Chen HH, Su WC, Wang JD. Comparison of expected health impacts for major cancers: integration of incidence rate and loss of quality-adjusted life expectancy. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015; 39(1):126–132.


16. Kang EJ, Kim NY, Yoon SJ. An estimation of health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE) for Koreans. Health Policy Manag. 2008; 18(1):108–126.
18. Reed LJ, Merrell M. A short method for constructing an abridged life table. 1939. Am J Epidemiol. 1995; 141(11):993–1022.

20. Lee YK, Nam HS, Chuang LH, Kim KY, Yang HK, Kwon IS, et al. South Korean time trade-off values for EQ-5D health states: modeling with observed values for 101 health states. Value Health. 2009; 12(8):1187–1193.


22. Ministry of Health and Welfare. The National Health Plan 2020. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2011.
24. Choo J, Jeon S, Lee J. Gender differences in health-related quality of life associated with abdominal obesity in a Korean population. BMJ Open. 2014; 4(1):e003954.

26. Noh JW, Kim J, Park J, Kim HJ, Kwon YD. Gender difference in relationship between health-related quality of life and work status. PLoS One. 2015; 10(12):e0143579.

27. Kim SH, Kim HJ, Lee SI, Jo MW. Comparing the psychometric properties of the EQ-5D-3L and EQ-5D-5L in cancer patients in Korea. Qual Life Res. 2012; 21(6):1065–1073.


30. Kim IK. Socioeconomic concentration in the Seoul metropolitan area and its implications in the urbanization process of Korea. Korean J Sociol. 2010; 44(3):111–128.






 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download