1. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell. 2014; 159:676–690. PMID:
25417114.
2. Kunstman JW, Juhlin CC, Goh G, Brown TC, Stenman A, Healy JM, et al. Characterization of the mutational landscape of anaplastic thyroid cancer via whole-exome sequencing. Hum Mol Genet. 2015; 24:2318–2329. PMID:
25576899.

3. Ibrahimpasic T, Xu B, Landa I, Dogan S, Middha S, Seshan V, et al. Genomic alterations in fatal forms of non-anaplastic thyroid cancer: identification of MED12 and RBM10 as novel thyroid cancer genes associated with tumor virulence. Clin Cancer Res. 2017; 23:5970–5980. PMID:
28634282.

4. Landa I, Ibrahimpasic T, Boucai L, Sinha R, Knauf JA, Shah RH, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic hallmarks of poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancers. J Clin Invest. 2016; 126:1052–1066. PMID:
26878173.

5. Pozdeyev N, Gay LM, Sokol ES, Hartmaier R, Deaver KE, Davis S, et al. Genetic analysis of 779 advanced differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2018; 24:3059–3068. PMID:
29615459.

6. Fagin JA, Wells SA Jr. Biologic and clinical perspectives on thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:2307.

7. Leboeuf R, Baumgartner JE, Benezra M, Malaguarnera R, Solit D, Pratilas CA, et al. BRAFV600E mutation is associated with preferential sensitivity to mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition in thyroid cancer cell lines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:2194–2201. PMID:
18381570.

8. Knauf JA, Luckett KA, Chen KY, Voza F, Socci ND, Ghossein R, et al. Hgf/Met activation mediates resistance to BRAF inhibition in murine anaplastic thyroid cancers. J Clin Invest. 2018; 128:4086–4097. PMID:
29990309.

9. ElMokh O, Ruffieux-Daidie D, Roelli MA, Stooss A, Phillips WA, Gertsch J, et al. Combined MEK and Pi3'-kinase inhibition reveals synergy in targeting thyroid cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:24604–24620. PMID:
28445948.

10. Roelli MA, Ruffieux-Daidie D, Stooss A, ElMokh O, Phillips WA, Dettmer MS, et al. PIK3CA(H1047R)-induced paradoxical ERK activation results in resistance to BRAF (V600E) specific inhibitors in BRAF(V600E) PIK3CA (H1047R) double mutant thyroid tumors. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:103207–103222. PMID:
29262556.
11. Hyman DM, Puzanov I, Subbiah V, Faris JE, Chau I, Blay JY, et al. Vemurafenib in multiple nonmelanoma cancers with BRAF V600 mutations. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:726–736. PMID:
26287849.

12. Subbiah V, Kreitman RJ, Wainberg ZA, Cho JY, Schellens JHM, Soria JC, et al. Dabrafenib and trametinib treatment in patients with locally advanced or metastatic BRAF V600-mutant anaplastic thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:7–13. PMID:
29072975.

13. Knauf JA, Ma X, Smith EP, Zhang L, Mitsutake N, Liao XH, et al. Targeted expression of BRAFV600E in thyroid cells of transgenic mice results in papillary thyroid cancers that undergo dedifferentiation. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:4238–4245. PMID:
15899815.

14. Rusinek D, Swierniak M, Chmielik E, Kowal M, Kowalska M, Cyplinska R, et al. BRAFV600E-associated gene expression profile: early changes in the transcriptome, based on a transgenic mouse model of papillary thyroid carcinoma. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0143688. PMID:
26625260.

15. Franco AT, Malaguarnera R, Refetoff S, Liao XH, Lundsmith E, Kimura S, et al. Thyrotrophin receptor signaling dependence of Braf-induced thyroid tumor initiation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:1615–1620. PMID:
21220306.

16. Charles RP, Iezza G, Amendola E, Dankort D, McMahon M. Mutationally activated BRAF(V600E) elicits papillary thyroid cancer in the adult mouse. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:3863–3871. PMID:
21512141.

17. Shimamura M, Shibusawa N, Kurashige T, Mussazhanova Z, Matsuzaki H, Nakashima M, et al. Mouse models of sporadic thyroid cancer derived from BRAFV600E alone or in combination with PTEN haploinsufficiency under physiologic TSH levels. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0201365. PMID:
30086162.

18. Chakravarty D, Santos E, Ryder M, Knauf JA, Liao XH, West BL, et al. Small-molecule MAPK inhibitors restore radioiodine incorporation in mouse thyroid cancers with conditional BRAF activation. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121:4700–4711. PMID:
22105174.

19. Nagarajah J, Le M, Knauf JA, Ferrandino G, Montero-Conde C, Pillarsetty N, et al. Sustained ERK inhibition maximizes responses of BrafV600E thyroid cancers to radioiodine. J Clin Invest. 2016; 126:4119–4124. PMID:
27669459.

20. Charles RP, Silva J, Iezza G, Phillips WA, McMahon M. Activating BRAF and PIK3CA mutations cooperate to promote anaplastic thyroid carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2014; 12:979–986. PMID:
24770869.

21. McFadden DG, Vernon A, Santiago PM, Martinez-McFaline R, Bhutkar A, Crowley DM, et al. p53 constrains progression to anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in a Braf-mutant mouse model of papillary thyroid cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:E1600–E1609. PMID:
24711431.

22. Knauf JA, Sartor MA, Medvedovic M, Lundsmith E, Ryder M, Salzano M, et al. Progression of BRAF-induced thyroid cancer is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition requiring concomitant MAP kinase and TGFβ signaling. Oncogene. 2011; 30:3153–3162. PMID:
21383698.

23. Shimamura M, Nakahara M, Orim F, Kurashige T, Mitsutake N, Nakashima M, et al. Postnatal expression of BRAFV600E does not induce thyroid cancer in mouse models of thyroid papillary carcinoma. Endocrinology. 2013; 154:4423–4430. PMID:
23970782.

24. Zou M, Baitei EY, Al-Rijjal RA, Parhar RS, Al-Mohanna FA, Kimura S, et al. TSH overcomes Braf(V600E)-induced senescence to promote tumor progression via downregulation of p53 expression in papillary thyroid cancer. Oncogene. 2016; 35:1909–1918. PMID:
26477313.

25. Chen Y, Sadow PM, Suh H, Lee KE, Choi JY, Suh YJ, et al. BRAF(V600E) is correlated with recurrence of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a systematic review, multi-institutional primary data analysis, and meta-analysis. Thyroid. 2016; 26:248–255. PMID:
26671072.

26. Cetani F, Tonacchera M, Vassart G. Differential effects of NaCl concentration on the constitutive activity of the thyrotropin and the luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptors. FEBS Lett. 1996; 378:27–31. PMID:
8549796.

27. Mitsutake N, Knauf JA, Mitsutake S, Mesa C Jr, Zhang L, Fagin JA. Conditional BRAFV600E expression induces DNA synthesis, apoptosis, dedifferentiation, and chromosomal instability in thyroid PCCL3 cells. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:2465–2473. PMID:
15781663.

28. Liu D, Hu S, Hou P, Jiang D, Condouris S, Xing M. Suppression of BRAF/MEK/MAP kinase pathway restores expression of iodide-metabolizing genes in thyroid cells expressing the V600E BRAF mutant. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:1341–1349. PMID:
17317846.

29. Ho AL, Grewal RK, Leboeuf R, Sherman EJ, Pfister DG, Deandreis D, et al. Selumetinib-enhanced radioiodine uptake in advanced thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:623–632. PMID:
23406027.

30. Ishii N, Harada N, Joseph EW, Ohara K, Miura T, Sakamoto H, et al. Enhanced inhibition of ERK signaling by a novel allosteric MEK inhibitor, CH5126766, that suppresses feedback reactivation of RAF activity. Cancer Res. 2013; 73:4050–4060. PMID:
23667175.

31. Rothenberg SM, Daniels GH, Wirth LJ. Redifferentiation of iodine-refractory BRAF V600E-mutant metastatic papillary thyroid cancer with dabrafenib-response. Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 21:5640–5641. PMID:
26672087.

32. Dunn LA, Sherman EJ, Baxi SS, Tchekmedyian V, Grewal RK, Larson SM, et al. Vemurafenib redifferentiation of BRAF mutant, RAI-refractory thyroid cancers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 9. 25. [Epub]. DOI:
10.1210/jc.2018-01478.

33. Shi H, Hong A, Kong X, Koya RC, Song C, Moriceau G, et al. A novel AKT1 mutant amplifies an adaptive melanoma response to BRAF inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014; 4:69–79. PMID:
24265152.

34. Shi H, Hugo W, Kong X, Hong A, Koya RC, Moriceau G, et al. Acquired resistance and clonal evolution in melanoma during BRAF inhibitor therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014; 4:80–93. PMID:
24265155.

35. Hugo W, Shi H, Sun L, Piva M, Song C, Kong X, et al. Non-genomic and immune evolution of melanoma acquiring MAPKi resistance. Cell. 2015; 162:1271–1285. PMID:
26359985.

36. Schram AM, Gandhi L, Mita MM, Damstrup L, Campana F, Hidalgo M, et al. A phase Ib dose-escalation and expansion study of the oral MEK inhibitor pimasertib and PI3K/MTOR inhibitor voxtalisib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 2018; 119:1471–1476. PMID:
30425349.

37. Kakadia S, Yarlagadda N, Awad R, Kundranda M, Niu J, Naraev B, et al. Mechanisms of resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors and clinical update of US Food and Drug Administration-approved targeted therapy in advanced melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018; 11:7095–7107. PMID:
30410366.

38. Welsh SJ, Rizos H, Scolyer RA, Long GV. Resistance to combination BRAF and MEK inhibition in metastatic melanoma: Where to next? Eur J Cancer. 2016; 62:76–85. PMID:
27232329.

39. Lito P, Rosen N, Solit DB. Tumor adaptation and resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat Med. 2013; 19:1401–1409. PMID:
24202393.

40. Sullivan RJ, Flaherty KT. Resistance to BRAF-targeted therapy in melanoma. Eur J Cancer. 2013; 49:1297–1304. PMID:
23290787.

41. Shi H, Moriceau G, Kong X, Lee MK, Lee H, Koya RC, et al. Melanoma whole-exome sequencing identifies (V600E) B-RAF amplification-mediated acquired B-RAF inhibitor resistance. Nat Commun. 2012; 3:724. PMID:
22395615.

42. Johnson DB, Menzies AM, Zimmer L, Eroglu Z, Ye F, Zhao S, et al. Acquired BRAF inhibitor resistance: a multicenter meta-analysis of the spectrum and frequencies, clinical behaviour, and phenotypic associations of resistance mechanisms. Eur J Cancer. 2015; 51:2792–2799. PMID:
26608120.

43. Rizos H, Menzies AM, Pupo GM, Carlino MS, Fung C, Hyman J, et al. BRAF inhibitor resistance mechanisms in metastatic melanoma: spectrum and clinical impact. Clin Cancer Res. 2014; 20:1965–1977. PMID:
24463458.

44. Ofir Dovrat T, Sokol E, Frampton G, Shachar E, Pelles S, Geva R, et al. Unusually long-term responses to vemurafenib in BRAF V600E mutated colon and thyroid cancers followed by the development of rare RAS activating mutations. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018; 19:871–874. PMID:
30036146.

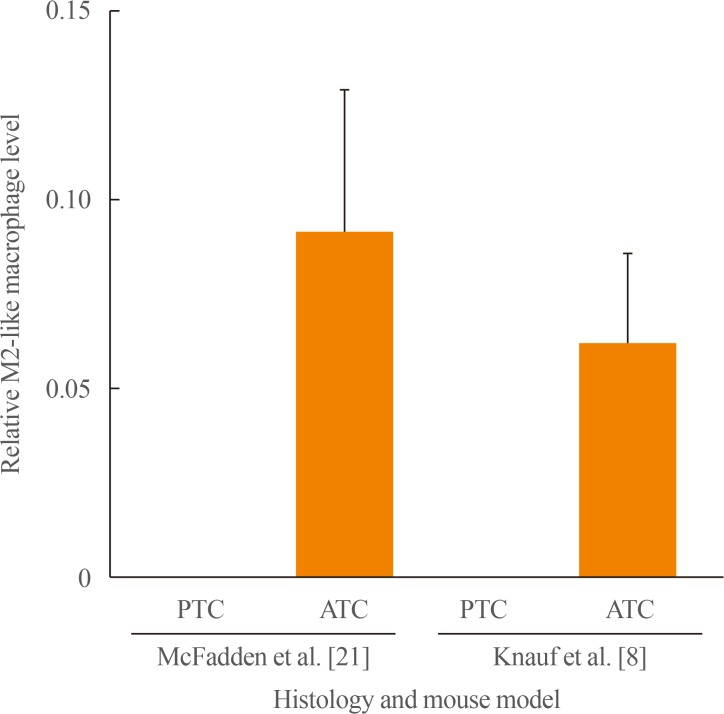
45. Ryder M, Ghossein RA, Ricarte-Filho JC, Knauf JA, Fagin JA. Increased density of tumor-associated macrophages is associated with decreased survival in advanced thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008; 15:1069–1074. PMID:
18719091.

46. Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. 2015; 12:453–457. PMID:
25822800.

47. Lin EY, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages press the angiogenic switch in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:5064–5066. PMID:
17545580.
48. Laoui D, Van Overmeire E, Di Conza G, Aldeni C, Keirsse J, Morias Y, et al. Tumor hypoxia does not drive differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages but rather fine-tunes the M2-like macrophage population. Cancer Res. 2014; 74:24–30. PMID:
24220244.

49. Schoppmann SF, Birner P, Stockl J, Kalt R, Ullrich R, Caucig C, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages express lymphatic endothelial growth factors and are related to peritumoral lymphangiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2002; 161:947–956. PMID:
12213723.

50. Werchau S, Toberer F, Enk A, Dammann R, Helmbold P. Merkel cell carcinoma induces lymphatic microvessel formation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012; 67:215–225. PMID:
22050913.

51. Weizman N, Krelin Y, Shabtay-Orbach A, Amit M, Binenbaum Y, Wong RJ, et al. Macrophages mediate gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma by upregulating cytidine deaminase. Oncogene. 2014; 33:3812–3819. PMID:
23995783.

52. Qian BZ, Pollard JW. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell. 2010; 141:39–51. PMID:
20371344.

53. Gocheva V, Wang HW, Gadea BB, Shree T, Hunter KE, Garfall AL, et al. IL-4 induces cathepsin protease activity in tumor-associated macrophages to promote cancer growth and invasion. Genes Dev. 2010; 24:241–255. PMID:
20080943.

54. Wyckoff JB, Wang Y, Lin EY, Li JF, Goswami S, Stanley ER, et al. Direct visualization of macrophage-assisted tumor cell intravasation in mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:2649–2656. PMID:
17363585.

55. Liu CY, Xu JY, Shi XY, Huang W, Ruan TY, Xie P, et al. M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells, partially through TLR4/IL-10 signaling pathway. Lab Invest. 2013; 93:844–854. PMID:
23752129.

56. Wang D, Sun H, Wei J, Cen B, DuBois RN. CXCL1 is critical for premetastatic niche formation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2017; 77:3655–3665. PMID:
28455419.

57. Kim DI, Kim E, Kim YA, Cho SW, Lim JA, Park YJ. Macrophage densities correlated with CXC chemokine receptor 4 expression and related with poor survival in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016; 31:469–475. PMID:
27491720.

58. Ryder M, Gild M, Hohl TM, Pamer E, Knauf J, Ghossein R, et al. Genetic and pharmacological targeting of CSF-1/CSF-1R inhibits tumor-associated macrophages and impairs BRAF-induced thyroid cancer progression. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e54302. PMID:
23372702.

59. Kaneda MM, Messer KS, Ralainirina N, Li H, Leem CJ, Gorjestani S, et al. PI3Kγ is a molecular switch that controls immune suppression. Nature. 2016; 539:437–442. PMID:
27642729.

60. De Henau O, Rausch M, Winkler D, Campesato LF, Liu C, Cymerman DH, et al. Overcoming resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy by targeting PI3Kγ in myeloid cells. Nature. 2016; 539:443–447. PMID:
27828943.

61. Chintakuntlawar AV, Rumilla KM, Smith CY, Jenkins SM, Foote RL, Kasperbauer JL, et al. Expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 in anaplastic thyroid cancer patients treated with multimodal therapy: results from a retrospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:1943–1950. PMID:
28324060.

62. Bastman JJ, Serracino HS, Zhu Y, Koenig MR, Mateescu V, Sams SB, et al. Tumor-infiltrating T cells and the PD-1 checkpoint pathway in advanced differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 101:2863–2873. PMID:
27045886.

63. Zwaenepoel K, Jacobs J, De Meulenaere A, Silence K, Smits E, Siozopoulou V, et al. CD70 and PD-L1 in anaplastic thyroid cancer: promising targets for immunotherapy. Histopathology. 2017; 71:357–365. PMID:
28383817.
64. Caillou B, Talbot M, Weyemi U, Pioche-Durieu C, Al Ghuzlan A, Bidart JM, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) form an interconnected cellular supportive network in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e22567. PMID:
21811634.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download