1. Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992; 6:3051–3064.


2. Nakano H, Ide H, Ogasa T, Osanai S, Imada M, Nonaka S, et al. Ambient oxygen regulates epithelial metabolism and nitric oxide production in the human nose. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002; 93:189–194.


3. Antošová M, Strapková A, Mikolka P, Mokrý J, Medvedová I, Mokrá D. The influence of L-NAME on iNOS expression and markers of oxidative stress in allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015; 838:1–10.


4. Gustafsson LE, Leone AM, Persson MG, Wiklund NP, Moncada S. Endogenous nitric oxide is present in the exhaled air of rabbits, guinea pigs and humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991; 181:852–857.


5. Alving K, Weitzberg E, Lundberg JM. Increased amount of nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatics. Eur Respir J. 1993; 6:1368–1370.

6. Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987; 327:524–526.


7. Coleman JW. Nitric oxide in immunity and inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001; 1:1397–1406.


10. Moore WC, Meyers DA, Wenzel SE, Teague WG, Li H, Li X, et al. Identification of asthma phenotypes using cluster analysis in the severe asthma research program. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 181:315–323.


11. Kawamoto H, Takumida M, Takeno S, Watanabe H, Fukushima N, Yajin K. Localization of nitric oxide synthase in human nasal mucosa with nasal allergy. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998; 539:65–70.

12. Bartley J, Fergusson W, Moody A, Wells AU, Kolbe J. Normal adult values, diurnal variation, and repeatability of nasal nitric oxide measurement. Am J Rhinol. 1999; 13:401–405.


13. Marthin JK, Nielsen KG. Choice of nasal nitric oxide technique as first-line test for primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur Respir J. 2011; 37:559–565.


14. Kharitonov S, Alving K, Barnes PJ. Exhaled and nasal nitric oxide measurements: recommendations. The European Respiratory Society task force. Eur Respir J. 1997; 10:1683–1693.

15. Liu C, Zheng M, He F, Wang X, Zhang L. Role of exhaled nasal nitric oxide in distinguishing between chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2017; 31:389–394.


16. Delclaux C, Malinvaud D, Chevalier-Bidaud B, Callens E, Mahut B, Bonfils P. Nitric oxide evaluation in upper and lower respiratory tracts in nasal polyposis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1140–1147.


17. Struben VM, Wieringa MH, Feenstra L, de Jongste JC. Nasal nitric oxide and nasal allergy. Allergy. 2006; 61:665–670.

18. Bauchau V, Durham SR. Prevalence and rate of diagnosis of allergic rhinitis in Europe. Eur Respir J. 2004; 24:758–764.


19. Nathan RA, Meltzer EO, Derebery J, Campbell UB, Stang PE, Corrao MA, et al. The prevalence of nasal symptoms attributed to allergies in the United States: findings from the burden of rhinitis in an America survey. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008; 29:600–608.


20. Zhang Y, Zhang L. Prevalence of allergic rhinitis in china. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:105–113.


21. Zhang L, Luo XR, Liu CY, Zhao Y, Han DM. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide in healthy Chinese. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009; 44:302–306.

22. Rochat MK, Illi S, Ege MJ, Lau S, Keil T, Wahn U, et al. Allergic rhinitis as a predictor for wheezing onset in school-aged children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:1170–5.e2.


23. Dreborg S. Skin testing. The safety of skin tests and the information obtained from using different methods and concentrations of allergen. Allergy. 1993; 48:473–475.
24. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:912–930.

25. Stark H, Purokivi M, Kiviranta J, Randell J, Tukiainen H. Short-term and seasonal variations of exhaled and nasal NO in healthy subjects. Respir Med. 2007; 101:265–271.


26. Dressel H, Bihler A, Jund F, de la Motte D, Nowak D, Jörres RA, et al. Diurnal variation of nasal nitric oxide levels in healthy subjects. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2008; 18:316–317.

27. Lundberg JO, Rinder J, Weitzberg F, Alving K, Lundberg JM. Heavy physical exercise decreases nitric oxide levels in the nasal airways in humans. Acta Physiol Scand. 1997; 159:51–57.


28. Marthin JK, Nielsen KG. Hand-held tidal breathing nasal nitric oxide measurement--a promising targeted case-finding tool for the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e57262.
29. Leng G, Li Z, Wang Q. Detection of exhaled nitric oxide of healthy in Nanjing. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012; 26:769–771.
30. Kovesi T, Kulka R, Dales R. Exhaled nitric oxide concentration is affected by age, height, and race in healthy 9- to 12-year-old children. Chest. 2008; 133:169–175.


31. You S, Zhang J, Bai Y, Ji L, Wang H. Normal values of nasal NO and exhaled NO in young Chinese people aged 9–22 years. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016; 2:22–27.
32. Nesic VS, Djordjevic VZ, Tomic-Spiric V, Dudvarski ZR, Soldatovic IA, Arsovic NA. Measuring nasal nitric oxide in allergic rhinitis patients. J Laryngol Otol. 2016; 130:1064–1071.


33. Gelardi M, Abbattista G, Quaranta VN, Quaranta N, Seccia V, Buttafava S, et al. Standardization procedure for the nasal nitric oxide measurement method using Niox MINO® and the tidal-breathing technique with velum-closure. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016; 30:853–858.

34. Leigh MW, Hazucha MJ, Chawla KK, Baker BR, Shapiro AJ, Brown DE, et al. Standardizing nasal nitric oxide measurement as a test for primary ciliary dyskinesia. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013; 10:574–581.


35. Beydon N, Chambellan A, Alberti C, de Blic J, Clément A, Escudier E, et al. Technical and practical issues for tidal breathing measurements of nasal nitric oxide in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015; 50:1374–1382.


36. Menou A, Babeanu D, Paruit HN, Ordureau A, Guillard S, Chambellan A. Normal values of offline exhaled and nasal nitric oxide in healthy children and teens using chemiluminescence. J Breath Res. 2017; 11:036008.

37. Ren L, Zhang L, Duan S, Zhang W, Zhang Y. Nasal airflow resistance measured by rhinomanometry in a healthy population of China. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018; 8:1308–1314.


39. Liu D, Huang Z, Huang Y, Yi X, Chen X. Measurement of nasal and fractional exhaled nitric oxide in children with upper airway inflammatory disease: preliminary results. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; 79:2308–2311.


41. Henriksen AH, Sue-Chu M, Holmen TL, Langhammer A, Bjermer L. Exhaled and nasal NO levels in allergic rhinitis: relation to sensitization, pollen season and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Eur Respir J. 1999; 13:301–306.


42. Alexanderson C, Olin AC, Dahlman-Höglund A, Finizia C, Torén K. Nasal nitric oxide in a random sample of adults and its relationship to sensitization, cat allergen, rhinitis, and ambient nitric oxide. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012; 26:e99–103.

43. Mahr TA, Malka J, Spahn JD. Inflammometry in pediatric asthma: a review of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in clinical practice. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013; 34:210–219.


44. Olthoff A, Rohrbach S, Faber M, Götz W, Laskawi R. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the nasal mucosa of patients with idiopathic and allergic rhinitis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2002; 64:180–185.


45. Takeno S, Osada R, Furukido K, Chen JH, Yajin K. Increased nitric oxide production in nasal epithelial cells from allergic patients--RT-PCR analysis and direct imaging by a fluorescence indicator: DAF-2 DA. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:881–888.

46. Kang BH, Chen SS, Jou LS, Weng PK, Wang HW. Immunolocalization of inducible nitric oxide synthase and 3-nitrotyrosine in the nasal mucosa of patients with rhinitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000; 257:242–246.


47. Kawamoto H, Takeno S, Yajin K. Increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in nasal epithelial cells in patients with allergic rhinitis. Laryngoscope. 1999; 109:2015–2020.


48. Hou J, Lou H, Wang Y, He F, Cao F, Wang C, et al. Nasal ventilation is an important factor in evaluating the diagnostic value of nasal nitric oxide in allergic rhinitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018; 8:686–694.


49. Takeno S, Okabayashi Y, Kohno T, Yumii K, Hirakawa K. The role of nasal fractional exhaled nitric oxide as an objective parameter independent of nasal airflow resistance in the diagnosis of allergic rhinitis. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017; 44:435–441.


50. Lundberg JO, Farkas-Szallasi T, Weitzberg E, Rinder J, Lidholm J, Anggåard A, et al. High nitric oxide production in human paranasal sinuses. Nat Med. 1995; 1:370–373.


51. Suojalehto H, Vehmas T, Lindström I, Kennedy DW, Kilpeläinen M, Plosila T, et al. Nasal nitric oxide is dependent on sinus obstruction in allergic rhinitis. Laryngoscope. 2014; 124:E213–8.

52. Song WJ, Kwon JW, Kim EJ, Lee SM, Kim SH, Lee SY, et al. Clinical application of exhaled nitric oxide measurements in a Korean population. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:3–13.


53. Kharitonov SA, Rajakulasingam K, O'Connor B, Durham SR, Barnes PJ. Nasal nitric oxide is increased in patients with asthma and allergic rhinitis and may be modulated by nasal glucocorticoids. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:58–64.


54. Buchvald F, Baraldi E, Carraro S, Gaston B, De Jongste J, Pijnenburg MW, et al. Measurements of exhaled nitric oxide in healthy subjects age 4 to 17 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 115:1130–1136.




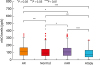
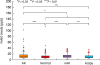
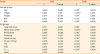
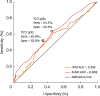




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download