Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
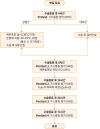 | Figure 1Flow diagram of research process.NRS=Numeric Rating Scale; TCI=thermal comfort inventory; VAS=visual analogue scale; QoR-40=Quality of Recovery 40.
|
Table 1
Homogeneity of General Characteristics, Gas Related Pain and Frequency of Painkiller Use (N=122)

Table 2
Effects of Thermotherapy on Gas Related Pain (N=122)

Table 3
Mean Differences in Postoperative Recovery (N=122)

Table 4
Comparison of Body Temperature Discomfort between Groups (N=122)

| Variable | Exp. (n=62) | Cont. (n=60) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M±SD | M±SD | |||
| TCI | 67.91±8.53 | 62.15±13.00 | 2.895 | .008 |
| VAS | 1.37±1.61 | 1.75± 2.06 | −1.133 | .260 |
Notes
Author Contributions
Data curation: Lee Ja, Jeon M.
Formal analysis: Kim J.
Investigation: Park E.
Methodology: Lee Jb.
Project administration: Lee Ja.
Resources: Ahn G.
Supervision: Lee S, Jeon M.
Validation: Kim J.
Visualization: Lee Ja.
Writing - original draft: Lee Ja, Jeon M.
Writing - review & editing: Kim J.
aJeongAe Lee; bJinAh Lee.
Summary Statement
• What is already known about this topic?
Thermotherapy is a non-pharmaceutical nursing intervention. It is usually used for laparoscopic hysterectomy patients to relieve pain and body temperature discomfort. This method has gained attention because it is very easy to apply and has few side effects.
• What this paper adds?
Thermotherapy was effective for laparoscopic hysterectomy patients in relieving gas-related pain in the epigastric area and shoulder, as well as reducing body temperature discomfort. However, it was not effective for relief of subjective body temperature discomfort in this study.
• Implications for practice, education, and/or policy
Thermotherapy is expected to be used as an adjunctive nursing intervention for patients planning to have surgery.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download