INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Study population
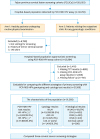 | Fig. 1Flowchart of inclusion and exclusion criteria of the study population.ASC-US, atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance; CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; HPV, human papillomavirus; HSIL, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; LEEP, loop electrosurgical excision procedure; LSIL, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; NILM, negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy; PCR-RDB, polymerase chain reaction-reverse dot blot; TCT, thinprep cytologic test.
*HR-HPV (+): including HPV-16/-18 (+) (n=1,336) and HR-HPV non-16/18 (+) (n=2,599).
|
2. Specimen collection and management
3. PCR-RDB HPV genotype testing
4. Liquid-based cytology
5. Histology
6. Comparison of different screening strategies
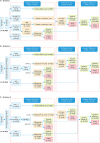 | Fig. 2Three cervical screening strategies to detect CIN2+/CIN3+. Effectiveness analysis of cervical screening strategies: primary screening algorithms. (A) Strategy I was co-testing, cytology combined with HPV using as the primary detection. (B) Strategy II was primary cytological detection with triaged by HPV testing. (C) Strategy III was primary HR-HPV testing with HPV-16/-18 genotype. In different strategies, the cases with ≥CIN2+ detected in the baseline screening, first year recall and the subsequent follow-up were listed in Fig. 2.ASC-US, atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance; CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; HPV, human papillomavirus; HR-HPV, high-risk human papillomavirus; NILM, negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy.
|
7. Statistical analysis
RESULTS
1. Clinical characteristics of the studied population
2. Cumulative incidence rate for CIN2+/CIN3+
Table 1
CIR of consensus pathology CIN2+ and CIN3+ stratified by different combinations of cervical cytology and HPV results

3. Comparison of different screening strategies for CIN2+/CIN3+
Table 2
The number of cervical screening examinations and colposcopies required for detecting CIN2+/CIN3+

 | Fig. 3The examinations consumed by the three cervical screening strategies to detect CIN2+/CIN3+. (A) The cases of CIN2+ detected by three current cervical screening strategies were determined in baseline screening, first year re-call, and subsequent follow-up. (B) The cases of CIN3+ detected by three current cervical screening strategies were calculated in baseline screening, first year re-call, and subsequent follow-up. (C) For baseline screening, according to the different cervical screening strategies, the number of cytologic assays, HPV assays, and colposcopies that should be performed as well as analysis of CIN2+ cases that could be detected. (D) The three cervical screening strategies used for CIN3+ detection, with application of cytology assay, HPV assay, and colposcopy shown.CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; HPV, human papillomavirus; TCT, thinprep cytologic test.
|
4. Evaluation of the three cervical screening strategies
Table 3
Compare the clinical performance characteristics of different screening strategies in the cervical high-grade lesions





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download