INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Preparation of the Tumor Mimic Model
CT Examination
RF Ablation
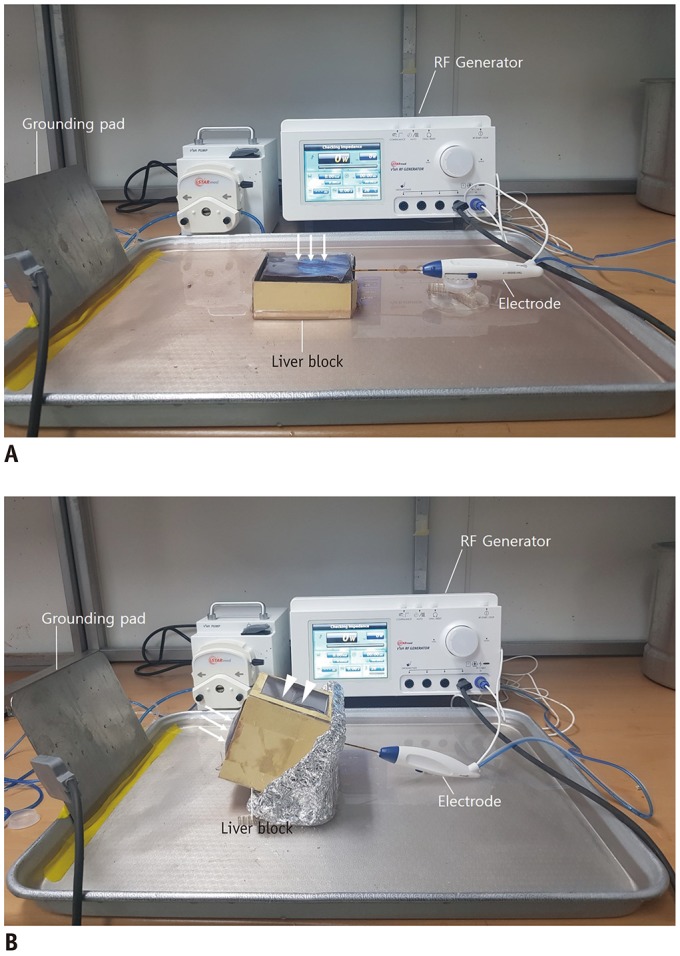 | Fig. 2Photographs of experimental models and RF ablation system.Sectioned bovine liver block with tumor mimic created in subcapsular portion is placed in water plate. (A) Electrode is inserted at lateral surface of liver block and advanced parallel to capsule (arrows). (B) Electrode is inserted at bottom of liver block opposite capsule and advanced through tumor mimic towards capsule (arrows). Lateral side of paper case is open for US guidance (arrowheads). RF = radiofrequency
|
RF Ablation Protocols
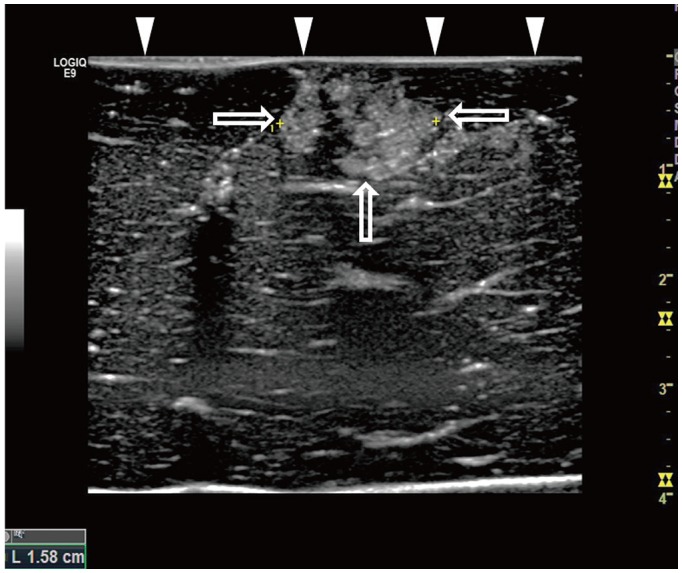
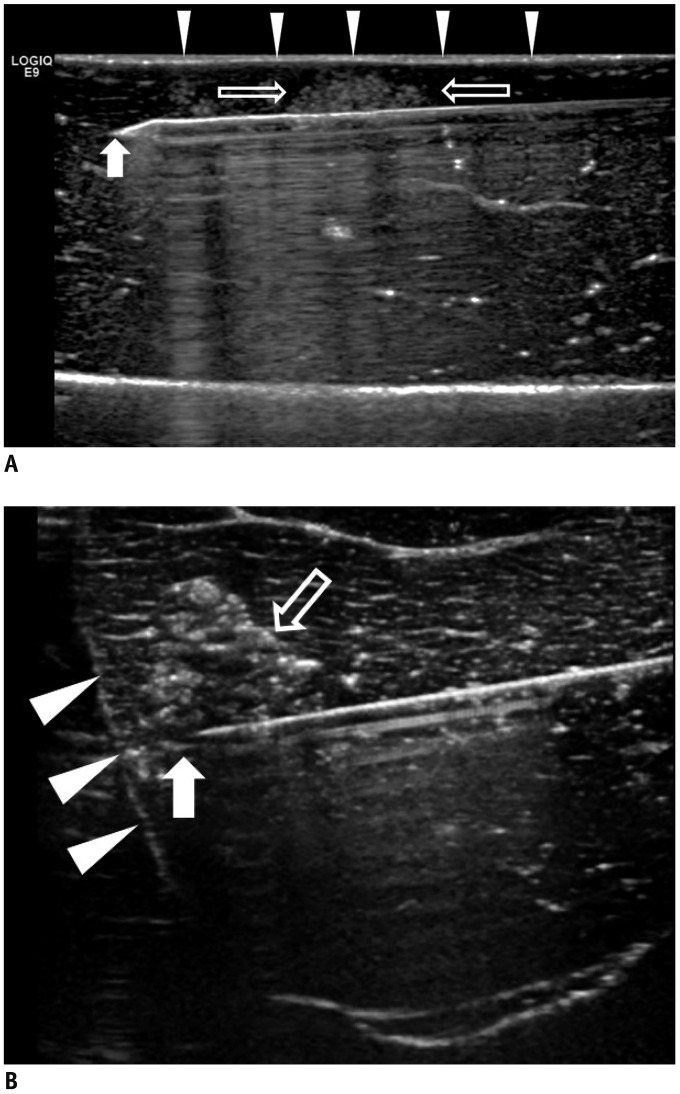 | Fig. 3US of parallel and perpendicular access methods.
A. US image illustrating parallel access method. Electrode (arrow) is placed parallel to liver capsule (arrowheads) through tumor mimic (open arrows). B. US image illustrating perpendicular access method. Tip of electrode (arrow) extends towards liver capsule (arrowheads) through tumor mimic (open arrow).
|
Evaluation of the CT Images and Liver Specimens
Statistical Analysis
RESULTS
 | Fig. 4RF ablation with low-power protocol and parallel access.
A, B. Pre- and post-RF ablation CT images. Post-RF ablation CT image (B) reveals no visible contrast leak on upper hepatic surface, compared to that observed on pre-RF ablation CT image (A). C. Liver specimen corresponding to CT images. Analysis of specimen revealed no visible contrast leak on surface of liver. CT = computed tomography, RF = radiofrequency
|
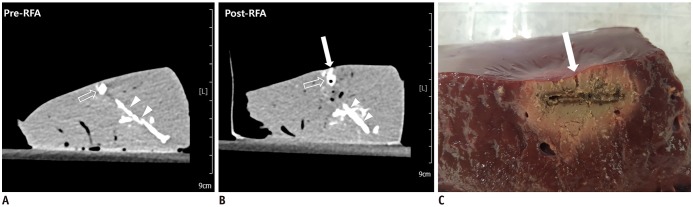 | Fig. 5RF ablation with high-power protocol and parallel access.
A, B. Pre- and post-RF ablation CT images. Post-RF ablation CT image (B) reveals contrast leak on hepatic surface (arrow) compared to that observed on pre-RF ablation CT image (A). High-density lines (arrowheads) inferior to tumor mimic (open arrows) is track through which tumor mimic material was injected. C. Liver specimen corresponding to CT images. Specimen image illustrates track of contrast leak corresponding to tract on post-RF ablation CT (arrow).
|
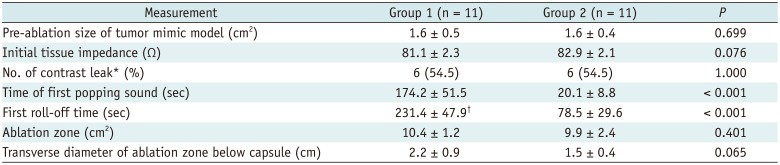
Table 1
Comparison of RF Ablation between Two Groups with Parallel Access
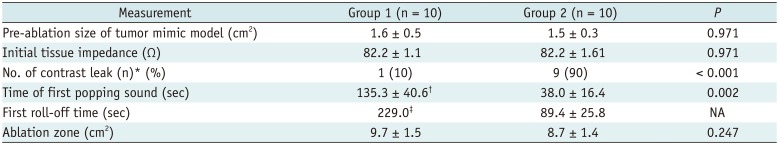
Unless otherwise indicated, data are mean ± standard deviation. Group 1 means RF ablation with low RF protocol, Group 2 means RF ablation with high RF protocol. p value could not be obtained since Group 1 had only one case with roll-off. *Values are number of tumor mimic models, with percentage in parentheses, †n = 4, ‡n = 1. NA = not applicable, RF = radiofrequency
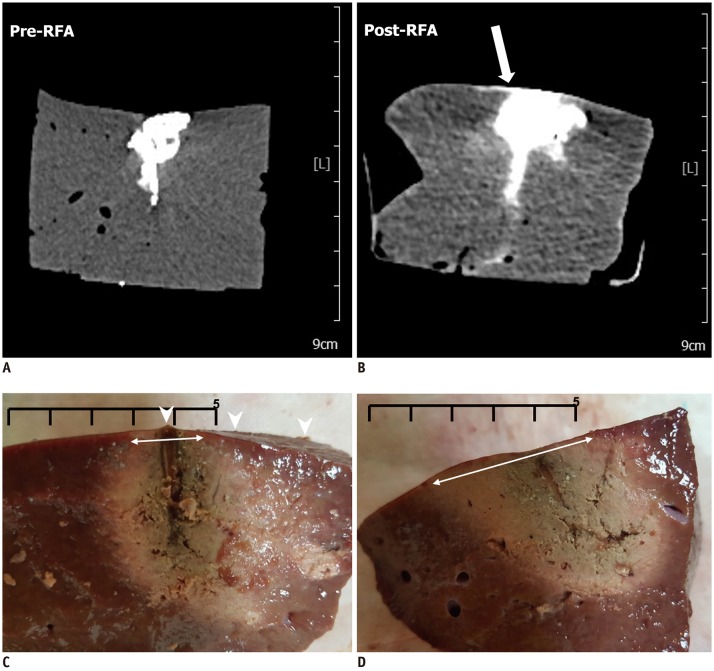 | Fig. 6RF ablation with high-power protocol and perpendicular access.
A, B. Pre- and post-RF ablation CT images. Post-RF ablation CT image (B) reveals contrast leak on hepatic surface after RF ablation, compared to that observed on pre-RF ablation CT image (A) (arrow). C. Liver specimen corresponding to CT images. Analysis of specimen reveals contrast leak on hepatic surface (arrowheads). D. Another liver specimen with low-power protocol and perpendicular access. Analysis of specimen reveals no contrast leak on hepatic surface, and diameter of ablation zone just beneath capsule is larger than that of specimen shown in (C) (double-headed arrows on C, D) (Scale bar: 5 cm).
|
Table 2
Comparison of RF Ablation between Two Groups with Perpendicular Access




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download