INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
Study implants
Surgical procedure
 | Figure 2Clinical photographs from the present study. Before tooth extraction (A), after tooth extraction (B), 1 month after tooth extraction (C), horizontal incision and flap reflection (D), implant placement (E), suture with 5/0 Vicryl (F). |
Histologic processing
Histologic and histomorphometric examination
 | Figure 3Schematics of linear measurements illustrating vertical marginal bone loss at the buccal and lingual aspects of the implants (b-MBL and l-MBL, respectively) (a, b). |
1) b-MBL: the vertical marginal bone loss at the buccal aspect of the implant.
2) l-MBL: the vertical marginal bone loss at the lingual aspect of the implant.
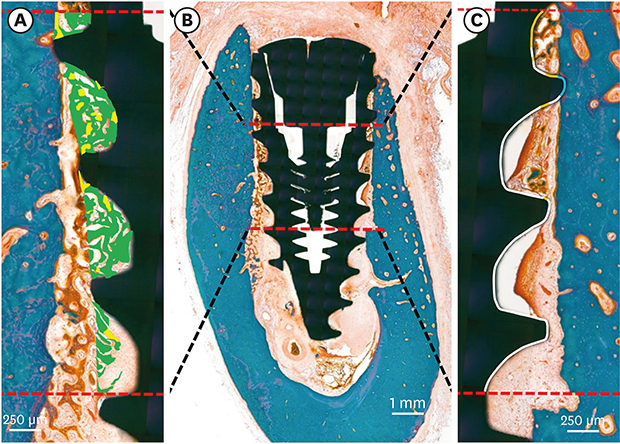
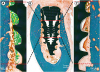 | Figure 4Histomorphometric analysis in the ROI, beginning at 3 mm and ending at 6 mm below the implant shoulder (B). Areas of the osteoid (green) and mineralized bone (yellow) were defined within the thread (A). Tissue-to-implant contact within the ROI (C) was differentiated into osteoid (orange), mineralized bone (blue), and void (white).ROI: region of interest.
|
Statistical analysis
Table 1
Results of the histomorphometric analysis

RESULTS
Clinical observations
Histologic analysis
Two-week healing
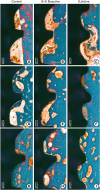 | Figure 5Histologic photograph of dental implants with IS-III Active, IS-III Bioactive, and SLActive surfaces at 2, 4, and 12 weeks following implant placement. |
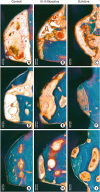 | Figure 6Histologic photograph of dental implants with IS-III Active, IS-III Bioactive, and SLActive surfaces at 2, 4, and 12 weeks following implant placement. Week 2 showed osteoid and woven bone formation within implant threads. Week 4 exhibited primary peri-implant bone mixed with woven and lamella bones. At 12 weeks, primary plexiform formation nearly ceased, and secondary remodeling was ongoing around all types of implants. |
Four-week healing
Twelve-week healing
Histomorphometric analysis
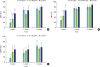
 | Figure 7Bar graphs of mBIC, tBIC, and mBAFO for different implant surfaces after 2, 4, and 12 weeks of healing. Red, yellow, and green bars indicate 2, 4, and 12 weeks of healing, respectively. The X-axes represent the implant surface. (A) mBIC, (B) tBIC, and (C) mBAFO values for different implant surfaces with 2, 4, and 12 weeks of healing.mBIC: mineralized bone-to-implant contact, tBIC: total bone-to-implant contact, mBAFO: mineralized bone area fraction occupied.
a,b)Statistically significant difference among 2 weeks, 4 weeks and 12 weeks of healing in each implant surface (adjusted P<0.0056).
|
 | Figure 8Bar graphs of mBIC, tBIC, and mBAFO for 2, 4, and 12 weeks of healing with 4 different implant surfaces. Orange, blue, and purple bars indicate IS-III Active, IS-III Bioactive, and SLActive implant surfaces, respectively. The X-axes represent healing time. (A) mBIC, (B) tBIC, and (C) mBAFO values for 2, 4, and 12 weeks of healing with different implant surfaces.mBIC: mineralized bone-to-implant contact, tBIC: total bone-to-implant contact, mBAFO: mineralized bone area fraction occupied.
a,b)Statistically significant difference among implant surfaces for each healing time (adjusted P<0.0056).
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download