INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Table 1
Manufacture, classification, matrix, filler, filler size, volume%, and weight% of the 5 nanotech-based resin composites used in the study

Table 2
Characteristics of the burs used in the study

Methods
Table 3
Polishing–finishing sequences tested in the study

1. Vickers microhardness tests
2. Surface roughness test
3. Optical microscopy observations
4. Scanning electron microscopy observations
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Effectiveness of the finishing–polishing system sequences on surface hardness and roughness
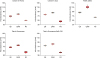 | Figure 1Box plots of the surface hardness vs. the finishing–polishing sequence for each resin composite.QB, finishing–polishing sequence using a blue-and-yellow-ring Q crosscut 12/15-fluted finishing bur and EVO-Light polisher sequentially; QWB, finishing–polishing sequence using a blue-and-yellow-ring Q crosscut 12/15-fluted finishing bur, a white-ring crosscut 30-fluted polishing bur, and an EVO-Light polisher, sequentially; MS, Mylar strip control group.
|
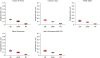 | Figure 2Box plots of the surface roughness vs. the finishing–polishing sequence for each resin composite.QB, finishing–polishing sequence using a blue-and-yellow-ring Q crosscut 12/15-fluted finishing bur and EVO-Light polisher sequentially; QWB, finishing–polishing sequence using a blue-and-yellow-ring Q crosscut 12/15-fluted finishing bur, a white-ring crosscut 30-fluted polishing bur, and an EVO-Light polisher, sequentially; MS, Mylar strip control group.
|
Finishability–polishability and surface hardness/roughness tests of the 5 resin composites
Table 4
Surface hardness (Vickers microhardness) of resin composites according to the finishing–polishing sequence

Table 5
Surface roughness (Ra, μm) of resin composites according to the finishing–polishing sequence

Optical microscopic and scanning electron microscopic observations
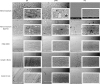 | Figure 3Scanning electron microscopic observations of 5 different resin composites after 2 finishing–polishing sequences (QB and QWB) and polymerization under a Mylar strip (MS) as the control group, at ×100 and ×500 magnifications in the white rectangular insets.QB, finishing–polishing sequence using a blue-and-yellow-ring Q crosscut 12/15-fluted finishing bur and EVO-Light polisher sequentially; QWB, finishing–polishing sequence using a blue-and-yellow-ring Q crosscut 12/15-fluted finishing bur, a white-ring crosscut 30-fluted polishing bur, and an EVO-Light polisher, sequentially; MS, Mylar strip.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download