Abstract
Methods
A retrospective, observational case series of 9 patients who were diagnosed with molluscum contagiosum of the eyelid margin.
Results
Subjects included 8 female patients and 1 male patient with an average age of 6.1 years. The patients were all healthy without any underlying disease, and their blood analyses and chest X-rays excluded any infectious disease or immune-related problem. Each patient had 1–6 skin lesions. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed lobular hyperplasia of the squamous epithelium, which invaded into the underlying dermis. Staining also revealed inclusion bodies in the cytoplasm of keratinocytes above the basal layer. All patients were maintained without complications or recurrence after surgical treatment.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
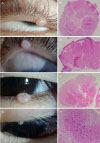
Clinical photographs and histopathologic findings of patients. (A, B) Case 1. (C, D) Case 2. (E, F) Case 3. (G, H) Case 4. All the patients had small, flesh-colored mass on the eyelid margin (A, C, E, G), and pathologic examination revealed multiple lobular hyperplasia of squamous epithelium invading into the dermis with large, homogenous inclusion bodies in the keratinocytes displacing the cell nucleus peripherally (arrows in H) (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×40 [B, D, F], ×100 [H]).
References
1. Charteris DG, Bonshek RE, Tullo AB. Ophthalmic molluscum contagiosum: clinical and immunopathological features. Br J Ophthalmol. 1995; 79:476–481.



2. Schornack MM, Siemsen DW, Bradley EA, et al. Ocular manifestations of molluscum contagiosum. Clin Exp Optom. 2006; 89:390–393.


3. Chronister CL. Review of external ocular disease associated with aids and HIV infection. Optom Vis Sci. 1996; 73:225–230.


4. Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, et al. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006; 54:47–54.


5. Neff AG, Carter KD. Benign eyelid lesions. In : Yanoff M, Duker JS, editors. Ophthalmology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2014. v. 1. chap. 12.9.
6. Wolfe OD, Wolfe RM. Molluscum contagiosum and conjunctivitis; case report. Eye Ear Nose Throat Mon. 1949; 28:129.

8. Niizeki K, Kano O, Kondo Y. An epidemic study of molluscum contagiosum. Relationship to swimming. Dermatologica. 1984; 169:197–198.

9. Choong KY, Roberts LJ. Molluscum contagiosum, swimming and bathing: a clinical analysis. Australas J Dermatol. 1999; 40:89–92.


10. Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Molluscum contagiosum: histologic patterns and associated lesions. A study of 578 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001; 23:99–103.

11. Husak R, Garbe C, Orfanos CE. Mollusca contagiosa in HIV infection. Clinical manifestation, relation to immune status and prognostic value in 39 patients. Hautarzt. 1997; 48:103–109.

12. Konya J, Thompson CH. Molluscum contagiosum virus: antibody responses in persons with clinical lesions and seroepidemiology in a representative Australian population. J Infect Dis. 1999; 179:701–704.


13. Watanabe T, Nakamura K, Wakugawa M, et al. Antibodies to molluscum contagiosum virus in the general population and susceptible patients. Arch Dermatol. 2000; 136:1518–1522.


14. Sherwani S, Farleigh L, Agarwal N, et al. Seroprevalence of molluscum contagiosum virus in German and UK populations. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e88734.

15. Bugert JJ, Darai G. Recent advances in molluscum contagiosum virus research. Arch Virol Suppl. 1997; 13:35–47.

16. Khaskhely NM, Maruno M, Hoshiyama Y, et al. Molluscum contagiosum appearing as a solitary lesion on the eyelid. J Dermatol. 2000; 27:68–70.


17. van der Wouden JC, van der Sande R, van Suijlekom Smit LW, et al. Interventions for cutaneous molluscum contagiosum. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009; 7:CD004767.

18. Köse O, Özmen I, Arca E. An open, comparative study of 10% potassium hydroxide solution versus salicylic and lactic acid combination in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Dermatolog Treat. 2013; 24:300–304.


19. Short KA, Fuller LC, Higgins EM. Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the use of topical 10% potassium hydroxide solution in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006; 23:279–281.


20. Forbat E, Al-Niaimi F, Ali FR. Molluscum contagiosum: review and update on management. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017; 34:504–515.


21. Al-Mutairi N, Al-Doukhi A, Al-Farag S, Al-Haddad A. Comparative study on the efficacy, safety, and acceptability of imiquimod 5% cream versus cryotherapy for molluscum contagiosum in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010; 27:388–394.


22. Binder B, Weger W, Komericki P, Kopera D. Treatment of molluscum contagiosum with a pulsed dye laser: pilot study with 19 children. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2008; 6:121–125.


23. Piggott C, Friedlander SF, Tom W. Poxvirus infections. In : Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education LLC;2012. v. 1. chap. 195.
24. Beutler BD, Cohen PR. Molluscum contagiosum of the eyelid: case report in a man receiving methotrexate and literature review of molluscum contagiosum in patients who are immunosuppressed secondary to methotrexate or HIV infection. Dermatol Online J. 2016; 22:pii: 13030/qt8vz669cj.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download