Introduction
Materials and Methods
Antigen preparation
ELISA
Antigen coating
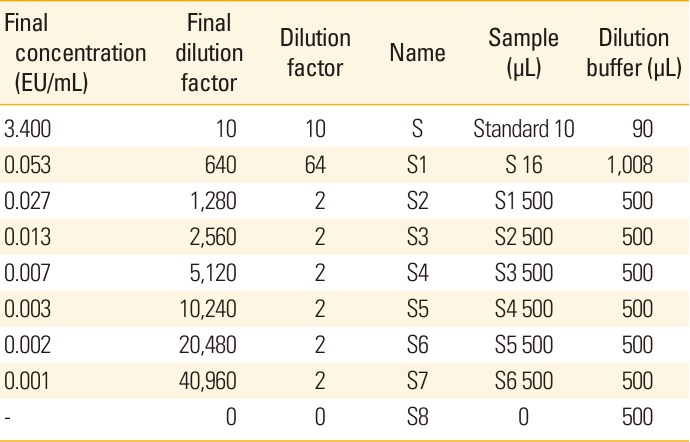
(1) Dilution of reference standard (National Institute for Biological Standard and Control [NIBSC] standard serum).
(2) NIBSC 97/642 obtained from the NIBSC (UK) was serially diluted with casein buffer (37528, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) from 3.4 to 0.001 ELISA unit (EU)/mL.
(3) Dilution of quality control sample.
(4) To verify the system suitability, reference standards were diluted to concentrations of 0.027, 0.013, and 0.003 EU/mL and used as high-, middle-, and low-quality control samples, respectively.
(5) Dilution of conjugate and streptavidin horseradish peroxidase (SA-HRP).
(6) Conjugate (31800, biotin-labeled anti-mouse IgG antibody, Thermo Fisher Scientific) was diluted by 200-fold with PBS and then diluted by 200-fold with casein buffer. Secondary antibody and SA-HRP was diluted by 1,000-fold with 1% bovine serum albumin in PBS.
(7) Dilution of samples.
(8) The samples were diluted by 10-fold (P) with PBS and then diluted by 10-fold with casein buffer (P1). Next, P1 was serially diluted in multiples of two.
(9) Dilution of reference standards.
(10) The NIBSC reference standard was diluted by 10-fold with PBS and then diluted stepwise, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1
Dilution method for NIBSC standard
Measurement method
Calculation of results
Acceptance criteria
Results
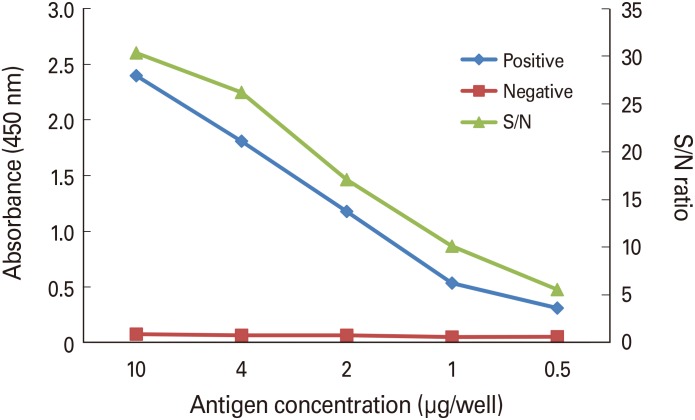
Determination of optimal PT coating concentration
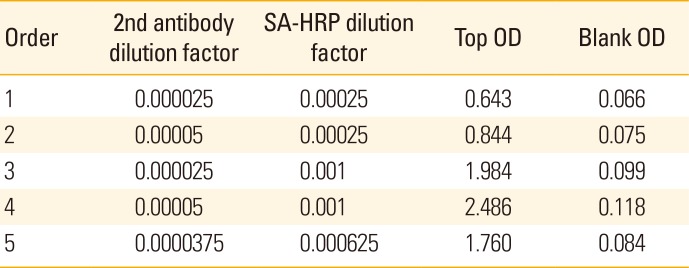
Selection of optimal conditions of conjugate and SA-HRP dilution factor
Table 2
Determination of proper dilution factors between secondary antibody and SA-HRP
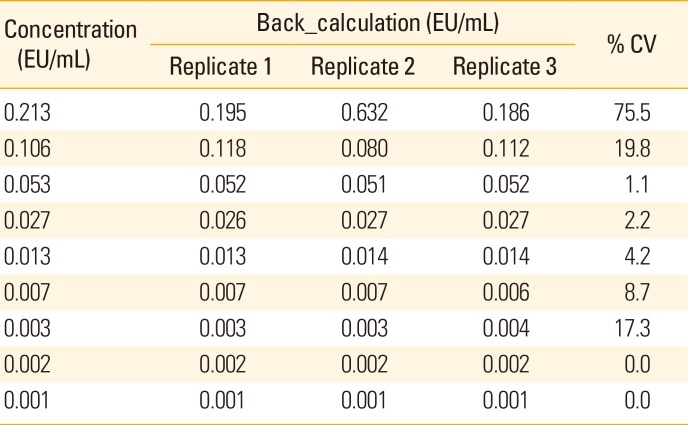
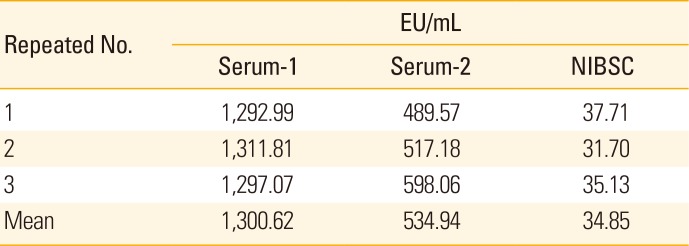
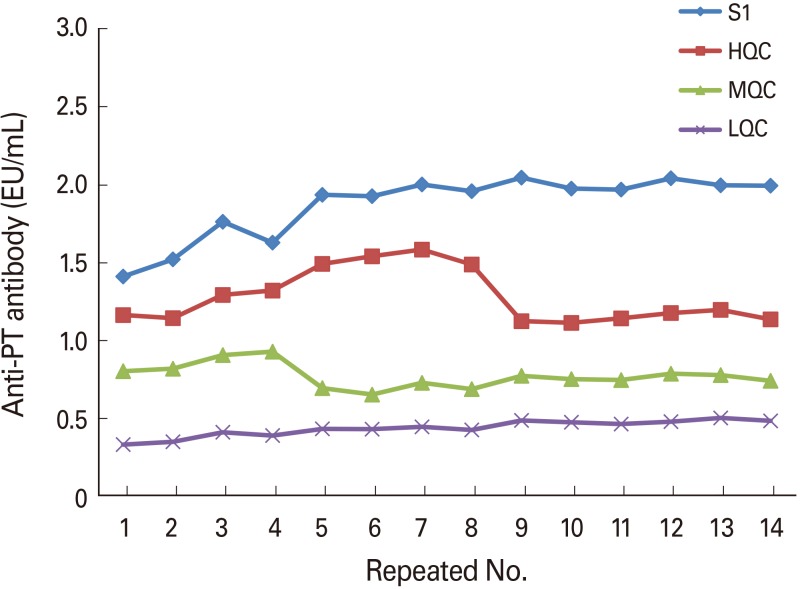
Determination of quantitative range
Table 3
Result of repeated experiments to determine a quantitative range




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download