Figures and Tables
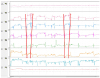 | Fig. 1Patterns of gas movement as recorded on 24-hr pH impedance testing. Air enters the proximal part of esophagus and travels downward rapidly. Impedance levels shows rapidly antegrade rise of signals in the proximal channels and progressing to the distal impedance channels. Thereafter, the air is cleared from the distal esophagus to oral side. Impedance levels shows rapid return of impedance signals from the distal to proximal impedance channels. |
References
1. Kessing BF, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ. The pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of excessive belching symptoms. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014; 109:1196–1203. (Quiz) 1204.


4. Bredenoord AJ. Belching, aerophagia, and rumination. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011; 53:Suppl 2. S19–S21.
5. Bredenoord AJ. Management of belching, hiccups, and aerophagia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:6–12.


6. Stanghellini V, Chan FK, Hasler WL, et al. Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150:1380–1392.


7. Hemmink GJ, Ten Cate L, Bredenoord AJ, Timmer R, Weusten BL, Smout AJ. Speech therapy in patients with excessive supragastric belching--a pilot study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010; 22:24, e2-3–28, e2-3.

8. Bredenoord AJ, Weusten BL, Sifrim D, Timmer R, Smout AJ. Aerophagia, gastric, and supragastric belching: a study using intraluminal electrical impedance monitoring. Gut. 2004; 53:1561–1565.



10. Cigrang JA, Hunter CM, Peterson AL. Behavioral treatment of chronic belching due to aerophagia in a normal adult. Behav Modif. 2006; 30:341–351.


11. Katzka DA. Simple office-based behavioral approach to patients with chronic belching. Dis Esophagus. 2013; 26:570–573.


12. Spiegel SB. Uses of hypnosis in the treatment of uncontrollable belching: a case report. Am J Clin Hypn. 1996; 38:263–270.


13. Blondeau K, Boecxstaens V, Rommel N, et al. Baclofen improves symptoms and reduces postprandial flow events in patients with rumination and supragastric belching. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:379–384.


14. Greenhill C. Motility: baclofen effective for rumination and supragastric belching in a pilot study. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 9:3.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download