Abstract
Aortoesophageal fistula (AEF) is an extremely rare but lethal cause of massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Characteristic symptoms are mid-thoracic pain, sentinel minor hemorrhage, and massive hemorrhage after a symptom-free interval. Prompt diagnosis and immediate treatments are necessary to reduce mortality. However, AEF is difficult to diagnose because it is uncommon and often leads to death with massive bleeding before proper evaluation. We report a case of endoscopic diagnosis of AEF that did not present with hematemesis; it was treated with thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) and surgery. A 71-year-old female presented to the emergency department with epigastric discomfort. Endoscopy demonstrated a submucosal tumor-like protrusion and pulsating mass with blood clots. Contrast-enhanced chest CT confirmed AEF due to descending thoracic aortic aneurysm. The patient immediately underwent TEVAR to prevent massive bleeding and subsequently underwent surgery. Endoscopists should consider AEF if they see a submucosal tumor-like mass with a central ulcerative lesion or a pulsating protrusion covered with blood clots in mid-esophagus during an endoscopy.
Figures and Tables
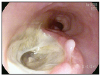
Fig. 1
Endoscopic finding. Submucosal mass-like protrusion and pulsating mass with blood clots is found at 30 cm below the incisors.
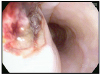
Fig. 2
Contrast-enhanced chest CT. (A) Esophageal lumen is narrow and esophageal wall is thickening (arrow). (B) Peripheral enhancing loculated cavity filled with fluid and multiple air-bubbles in posterior mediastinum (arrow).
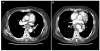
Fig. 3
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR). (A) Saccular aneurysm is visible. (B) TEVAR was performed in thoracic descending aorta.
References
1. Bergqvist D. Arterioenteric fistula. Review of a vascular emergency. Acta Chir Scand. 1987; 153:81–86.
2. Prokakis C, Koletsis E, Apostolakis E, Dedeilias P, Dougenis D. Aortoesophageal fistulas due to thoracic aorta aneurysm: surgical versus endovascular repair. Is there a role for combined aortic management? Med Sci Monit. 2008; 14:RA48–RA54.
3. Chiari H. Ueber Fremdkorpeverletzung des Oesophagus mit Aortenperforation. Ber Klin Wochenschr. 1914; 51:7–9.
4. Ikeda Y, Morita N, Kurihara H, Niimi M, Okinaga K. A primary aortoesophageal fistula due to esophageal carcinoma successfully treated with endoluminal aortic stent grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006; 131:486–487.


5. Shiraishi S, Watarida S, Matsubayashi K, Motoishi M, Satsu T. Successful management of an aortoesophageal fistula resulting from an aneurysm of the thoracic aorta with a covered stent. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2002; 43:95–98.

6. Contini S, Corrente V, Nervi G, Franzè A, Scarpignato C. Dysphagia aortica: a neglected symptom of aortoesophageal fistula. Dig Liver Dis. 2006; 38:51–54.


8. Cutler JA, Mendeloff AI. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Nature and magnitude of the problem in the U.S. Dig Dis Sci. 1981; 26:7 Suppl. 90S–96S.

9. Hollander JE, Quick G. Aortoesophageal fistula: a comprehensive review of the literature. Am J Med. 1991; 91:279–287.


10. Canaud L, Ozdemir BA, Bee WW, Bahia S, Holt P, Thompson M. Thoracic endovascular aortic repair in management of aortoesophageal fistulas. J Vasc Surg. 2014; 59:248–254.


11. Lee JT, Saroyan RM, Belzberg G, Pianim NA, Bongard FS. Primary aortoenteric fistula: computed tomographic diagnosis of an atypical presentation. Ann Vasc Surg. 2001; 15:251–254.


12. Yang Y, Hu D, Peng D. Primary aortoesophageal fistula: a fatal outcome. Am J Emerg Med. 2018; 36:343.e1–343.e3.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download