Abstract
Purpose
This study was performed to investigate the changes in clinical findings after switching from ranibizumab or aflibercept to bevacizumab due to the limited number of insured injections in patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration (ARMD).
Methods
The study population consisted of patients who had undergone intravitreal injection of ranibizumab or aflibercept for ≥ 6 months and were then treated with bevacizumab for ≥ 6 consecutive months for exudative ARMD. We evaluated best-corrected visual acuity, central subfield macular thickness, disease activity, and the number of injections for one year at the time of switching the drugs.
Results
Forty patients (26 men and 14 women) were included in the analysis. The mean age was 71.9 (56-89) years old, with typical ARMD in 23 eyes, polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in 15 eyes, and retinal angiomatous proliferation in two eyes. The number of injections for 6 months increased from 2.3 to 2.9 after switching the drugs (p < 0.001). Visual acuity was not significantly different between 6 months before and at the time of switching (LogMAR 0.55 ± 0.34 and 0.52 ± 0.27, respectively) (p = 0.300), but decreased significantly to 0.57 ± 0.34 at 6 months after switching (p = 0.018). There were no significant differences in central subfield macular thickness or disease activity.
Figures and Tables
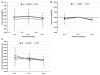 | Figure 1Visual acuity and central subfield macular thickness (CSMT) before and after 6 months from switching to bevacizumab from ranibizumab/aflibercept for treating exudative age-related macular degeneration. (A) Visual acuity. (B) Visual acuity changes comparing to when the drug was switched. (C) CSMT measured using optical coherence tomography. ARMD = age-related macular degeneration; PCV = polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy; m = month. *p<0.05, comparing to the previous visit. |
Table 1
Patients' characteristics of exudative age-related macular degeneration when switching anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents to bevacizumab from ranibizumab/aflibercept

References
1. Augood C, Fletcher A, Bentham G, et al. Methods for a population-based study of the prevalence of and risk factors for age-related maculopathy and macular degeneration in elderly European populations: the EUREYE study. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2004; 11:117–129.


2. Friedman DS, O'Colmain BJ, Muñoz B, et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:564–572.


3. Park SJ, Lee JH, Woo SJ, et al. Age-related macular degeneration: prevalence and risk factors from Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008 through 2011. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:1756–1765.

4. Rosenfeld PJ, Brown DM, Heier JS, et al. Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1419–1431.


5. Brown DM, Kaiser PK, Michels M, et al. Ranibizumab versus verteporfin for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1432–1444.


6. Avery RL, Pieramici DJ, Rabena MD, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:363–372.


7. Folk JC, Stone EM. Ranibizumab therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1648–1655.


8. Lanzetta P, Mitchell P, Wolf S, Veritti D. Different antivascular endothelial growth factor treatments and regimens and their outcomes in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a literature review. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013; 97:1497–1507.


9. Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials Research Group. Martin DF, Maguire MG, et al. Ranibizumab and bevacizumab for treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration: two-year results. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1388–1398.


10. Heier JS, Brown DM, Chong V, et al. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2537–2548.


11. Ehlken C, Jungmann S, Böhringer D, et al. Switch of anti-VEGF agents is an option for nonresponders in the treatment of AMD. Eye (Lond). 2014; 28:538–545.



12. Bakri SJ, Snyder MR, Reid JM, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravitreal ranibizumab (Lucentis). Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:2179–2182.

13. Moisseiev E, Katz G, Moisseiev J, et al. Switching treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration from bevacizumab to ranibizumab: who is likely to benefit from the switch? Retina. 2015; 35:1323–1330.

14. Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004; 25:581–611.


15. Ferrara N, Damico L, Shams N, et al. Development of ranibizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antigen binding fragment, as therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 2006; 26:859–870.

16. Gaudreault J, Fei D, Rusit J, et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetics of ranibizumab (rhuFabV2) after a single intravitreal administration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:726–733.


17. Binder S. Loss of reactivity in intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy: tachyphylaxis or tolerance? Br J Ophthalmol. 2012; 96:1–2.


18. Gasperini JL, Fawzi AA, Khondkaryan A, et al. Bevacizumab and ranibizumab tachyphylaxis in the treatment of choroidal neovascularisation. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012; 96:14–20.


19. Rosenfeld PJ, Moshfeghi AA, Puliafito CA. Optical coherence tomography findings after an intravitreal injection of bevacizumab (avastin) for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2005; 36:331–335.


20. Kim JH, Cho NC, Kim WJ. Intravitreal aflibercept for neovascular age-related macular degeneration resistant to bevacizumab and ranibizumab. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:1359–1364.

21. Singh RP, Srivastava S, Ehlers JP, et al. A single-arm, investigator-initiated study of the efficacy, safety and tolerability of intravitreal aflibercept injection in subjects with exudative age-related macular degeneration previously treated with ranibizumab or bevacizumab: 6-month interim analysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014; 98:Suppl 1. i22–i27.
22. Moon DR, Lee DK, Kim SH, et al. Aflibercept treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy refractory to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2015; 29:226–232.







 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download