Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the effects of preoperative corneal asphericity on the refractive outcomes of multifocal intraocular lens implantation by correlating Q-values on anterior corneal surfaces and the prediction errors after surgery.
Methods
Fifty-six eyes of 39 patients who underwent phacoemulsification, and multifocal intraocular lens implantation were included in this retrospective study. Intraocular lens power was calculated using the SRK/T, Hoffer Q, and Haigis formulas. The Q-values were measured at 6 mm, 7 mm, 8 mm, 9 mm, and 10 mm with a rotating Sheimpflug camera (Pentacam®, Oculus, Wetzlar, Germany). The relationship between the prediction errors and the Q-values at 6 mm, 7 mm, 8 mm, 9 mm, and 10 mm were assessed by linear regression.
Results
Two different multifocal intraocular lens models (Acrysof IQ RESTOR +2.5D SV25T0 [Alcon Laboratories Inc., Fort Worth, TX, USA] and ZEISS AT LISA tri 839MP [Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Inc., Jena, Germany]) were implanted in 56 eyes. In both groups, regression analyses showed statistically significant relationships between the prediction errors and the Q-values at 6 mm, 7 mm, and 8 mm using the SRK/T formula. The correlation coefficient between the Q-values and the prediction errors were higher using the SRK/T formula than using the Hoffer-Q and Haigis formulas.
Figures and Tables
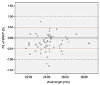 | Figure 1Scatter spot of axial length and the PE of the SRK/T formula. PE = prediction error; D = diopter. |
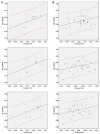 | Figure 2Regression line showing the relationship between the PE of the SRK/T formula and corneal asphericity (Q-value 6 mm, 7 mm, 8 mm) in the (A) Acrysof group (left) and (B) ZEISS group (right). Straight line represent regression line, and two curved lines represent the 95% prediction interval. Scatter spot means patient distribution. PE = prediction error. |
Table 2
Demographic data and ocular charateristics of Acrysof IQ Restor (Alcon Laboratories Inc., Fort Worth, TX, USA) group and Zeiss AT LISA (Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Inc., Jena, Germany) tri group

Table 3
Refractive outcomes of IOL power calculation with the formulas evaluated after multifocal IOL implantation

References
1. Haigis W, Lege B, Miller N, Schneider B. Comparison of immersion ultrasound biometry and partial coherence interferometry for intraocular lens calculation according to Haigis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238:765–773.


2. Hoffer KJ. The Hoffer Q formula: a comparison of theoretic and regression formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:700–712.


3. Holladay JT, Prager TC, Chandler TY, et al. A three-part system for refining intraocular lens power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1988; 14:17–24.


4. Retzlaff JA, Sanders DR, Kraff MC. Development of the SRK/T intraocular lens implant power calculation formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:333–340.


5. Savini G, Hoffer KJ, Barboni P. Influence of corneal asphericity on the refractive outcome of intraocular lens implantation in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:785–789.


6. Kang SI, Moon K, Jun JH. Accuracy of three intraocular lens-power formulas in predicting refractive outcomes in different intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:1891–1896.

7. Norrby S. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:368–376.


8. Xiong Y, Li J, Wang N, et al. The analysis of corneal asphericity (Q value) and its related factors of 1,683 Chinese eyes older than 30 years. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0176913.

9. Fuller DG, Alperin D. Variations in corneal asphericity (Q value) between African-Americans and whites. Optom Vis Sci. 2013; 90:667–673.


10. Savini G, Hoffer KJ, Barboni P, et al. Corneal asphericity and IOL power calculation in eyes with aspherical IOLs. J Refract Surg. 2017; 33:476–481.


11. Holladay JT. Effect of corneal asphericity and spherical aberration on intraocular lens power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:1553–1554.


12. Shammas HJ, Chan S. Precision of biometry, keratometry, and refractive measurements with a partial coherence interferometry-keratometry device. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1474–1478.


13. Eom Y, Kang SY, Song JS, Kim HM. Use of corneal power-specific constants to improve the accuracy of the SRK/T formula. Ophthalmology. 2013; 120:477–481.


14. Olsen T, Corydon L, Gimbel H. Intraocular lens power calculation with an improved anterior chamber depth prediction algorithm. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995; 21:313–319.






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download