1. Liu Z, Hu W, He T, Dai Y, Hara H, Bottino R, Cooper DKC, Cai Z, Mou L. Pig-to-Primate Islet Xenotransplantation: Past, Present, and Future. Cell Transplant. 2017; 26(6):925–947. PMID:
28155815.

2. American Diabetes Association. (2) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38(Suppl 1):S8–S16.
3. Basile KJ, Guy VC, Schwartz S, Grant SF. Overlap of genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults. Curr Diab Rep. 2014; 14(11):550. PMID:
25189437.

4. Redondo MJ, Grant SF, Davis A, Greenbaum C. T1D Exchange Biobank. Dissecting heterogeneity in paediatric Type 1 diabetes: association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 TT and low-risk human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes. Diabet Med. 2017; 34(2):286–290. PMID:
27027642.

5. Jin T. Current Understanding on Role of the Wnt Signaling Pathway Effector TCF7L2 in Glucose Homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 2016; 37(3):254–277. PMID:
27159876.

6. van der Kroef S, Noordam R, Deelen J, Akintola AA, Jansen SW, Postmus I, Wijsman CA, Beekman M, Mooijaart SP, Slagboom PE, van Heemst D. Association between the rs7903146 Polymorphism in the TCF7L2 Gene and Parameters Derived with Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Individuals without Diabetes. PLoS One. 2016; 11(2):e0149992. PMID:
26914832.

7. Lin PC, Lin WT, Yeh YH, Wung SF. Transcription Factor 7-Like 2 (TCF7L2) rs7903146 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11(4):e0153044. PMID:
27058589.

8. Koopmans SJ, Schuurman T. Considerations on pig models for appetite, metabolic syndrome and obese type 2 diabetes: From food intake to metabolic disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015; 759:231–239. PMID:
25814261.

9. Hiridis S, Konstantinidis K, Menenakos E, Diamantis T, Papalois A, Zografos G. Preliminary Results of the Influence of Duodenojejunal Bypass in a Porcine Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus. Obes Surg. 2016; 26(4):882–890. PMID:
26843083.

10. Du ZQ, Fan B, Zhao X, Amoako R, Rothschild MF. Association analyses between type 2 diabetes genes and obesity traits in pigs. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009; 17(2):323–329. PMID:
19057525.

11. Fan B, Lkhagvadorj S, Cai W, Young J, Smith RM, Dekkers JC, Huff-Lonergan E, Lonergan SM, Rothschild MF. Identification of genetic markers associated with residual feed intake and meat quality traits in the pig. Meat Sci. 2010; 84(4):645–650. PMID:
20374837.

12. National Research Council. Nutrient requirements of swine. 11th ed. Washington, D.C.: The National Academies Press;2011. p. 208–238.
13. Liu Y, Wang Z, Yin W, Li Q, Cai M, Zhang C, Xiao J, Hou H, Li H, Zu X. Severe insulin resistance and moderate glomerulosclerosis in a minipig model induced by high-fat/high-sucrose/high-cholesterol diet. Exp Anim. 2007; 56(1):11–20. PMID:
17283886.
14. National Research Council. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th ed. Washington, D.C.: The National Academies Press;2011. p. 41–76.
15. Sankari S. A practical method of taking blood samples from the pig. Acta Vet Scand. 1983; 24(1):133–134. PMID:
6869143.

16. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28(7):412–419. PMID:
3899825.
17. Stahl WR. Organ weights in primates and other mammals. Science. 1965; 150(3699):1039–1042. PMID:
5843618.

18. Furman BL. Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Models in Mice and Rats. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2015; 70:5.47.1–5.47.20.

19. King A, Bowe J. Animal models for diabetes: Understanding the pathogenesis and finding new treatments. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016; 99:1–10. PMID:
26432954.

20. Koopmans SJ, Mroz Z, Dekker R, Corbijn H, Ackermans M, Sauerwein H. Association of insulin resistance with hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-diabetic pigs: effects of metformin at isoenergetic feeding in a type 2-like diabetic pig model. Metabolism. 2006; 55(7):960–971. PMID:
16784971.
21. Manell EA, Rydén A, Hedenqvist P, Jacobson M, Jensen-Waern M. Insulin treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetes reestablishes the patterns in carbohydrate, fat and amino acid metabolisms in growing pigs. Lab Anim. 2014; 48(3):261–269. PMID:
24477048.

22. Hara H, Lin YJ, Zhu X, Tai HC, Ezzelarab M, Balamurugan AN, Bottino R, Houser SL, Cooper DK. Safe induction of diabetes by high-dose streptozotocin in pigs. Pancreas. 2008; 36(1):31–38. PMID:
18192878.

23. Huang YH, Lo LL, Liu SH, Yang TS. Age-related changes in semen quality characteristics and expectations of reproductive longevity in Duroc boars. Anim Sci J. 2010; 81(4):432–437. PMID:
20662811.

24. Eskenazi B, Wyrobek AJ, Sloter E, Kidd SA, Moore L, Young S, Moore D. The association of age and semen quality in healthy men. Hum Reprod. 2003; 18(2):447–454. PMID:
12571189.

25. Kelsey MM, Bjornstad P, McFann K, Nadeau K. Testosterone concentration and insulin sensitivity in young men with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016; 17(3):184–190. PMID:
25611822.

26. Cheung KK, Luk AO, So WY, Ma RC, Kong AP, Chow FC, Chan JC. Testosterone level in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus and related metabolic effects: A review of current evidence. J Diabetes Investig. 2015; 6(2):112–123.
27. Alonso-Magdalena P, Ropero AB, García-Arévalo M, Soriano S, Quesada I, Muhammed SJ, Salehi A, Gustafsson JA, Nadal A. Antidiabetic actions of an estrogen receptor β selective agonist. Diabetes. 2013; 62(6):2015–2025. PMID:
23349481.

28. Kautzky-Willer A, Harreiter J, Pacini G. Sex and Gender Differences in Risk, Pathophysiology and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr Rev. 2016; 37(3):278–316. PMID:
27159875.

29. Reaven EP, Gold G, Reaven GM. Effect of age on glucose-stimulated insulin release by the beta-cell of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979; 64(2):591–599. PMID:
379046.

30. Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Saydah S, Imperatore G, Linder B, Divers J, Bell R, Badaru A, Talton JW, Crume T, Liese AD, Merchant AT, Lawrence JM, Reynolds K, Dolan L, Liu LL, Hamman RF. SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents from 2001 to 2009. JAMA. 2014; 311(17):1778–1786. PMID:
24794371.

31. Mayer-Davis EJ, Lawrence JM, Dabelea D, Divers J, Isom S, Dolan L, Imperatore G, Linder B, Marcovina S, Pettitt DJ, Pihoker C, Saydah S, Wagenknecht L. SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Incidence Trends of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes among Youths, 2002–2012. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376(15):1419–1429. PMID:
28402773.

32. Takamoto I, Kubota N, Nakaya K, Kumagai K, Hashimoto S, Kubota T, Inoue M, Kajiwara E, Katsuyama H, Obata A, Sakurai Y, Iwamoto M, Kitamura T, Ueki K, Kadowaki T. TCF7L2 in mouse pancreatic beta cells plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis by regulating beta cell mass. Diabetologia. 2014; 57(3):542–553. PMID:
24317852.

33. Shu L, Zien K, Gutjahr G, Oberholzer J, Pattou F, Kerr-Conte J, Maedler K. TCF7L2 promotes beta cell regeneration in human and mouse pancreas. Diabetologia. 2012; 55(12):3296–3307. PMID:
22945304.

34. Yang TS, Lin JH. Variation of heart size and its correlation with growth performance and vascular space in domestic pigs. Anim Sci. 1997; 64(3):523–528.

35. Yang TS. Wild to domestic: body and organ size matter fitness in boars. In : Jenkins OP, editor. Advances in Zoology Research. NY: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.;2012. p. 187–200.
36. Cooper DK, Ekser B, Ramsoondar J, Phelps C, Ayares D. The role of genetically engineered pigs in xenotransplantation research. J Pathol. 2016; 238(2):288–299. PMID:
26365762.

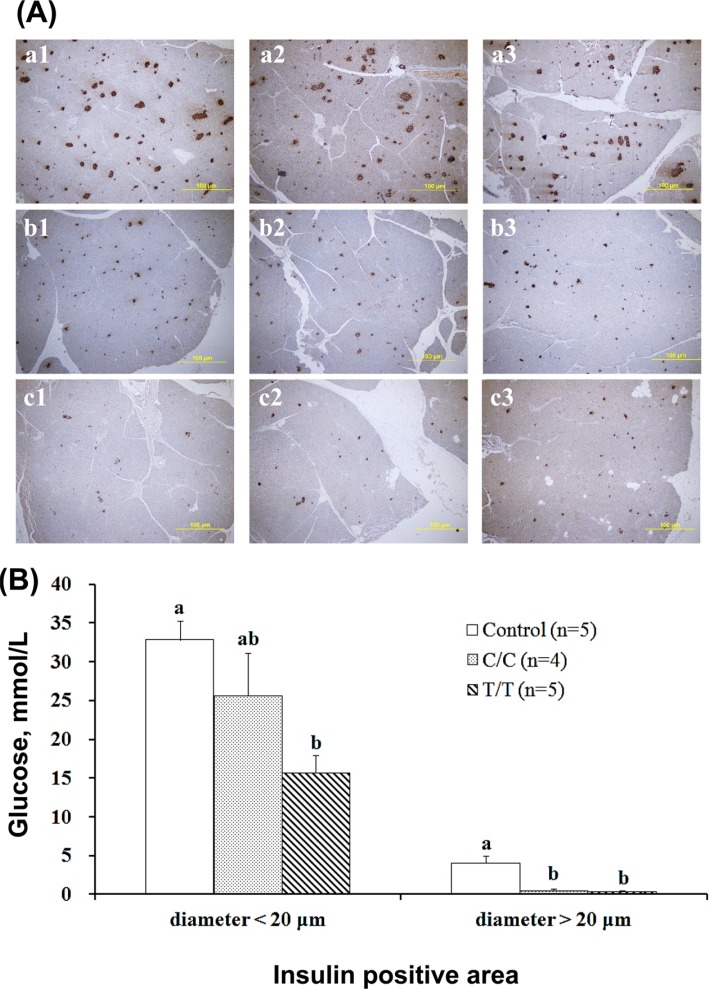
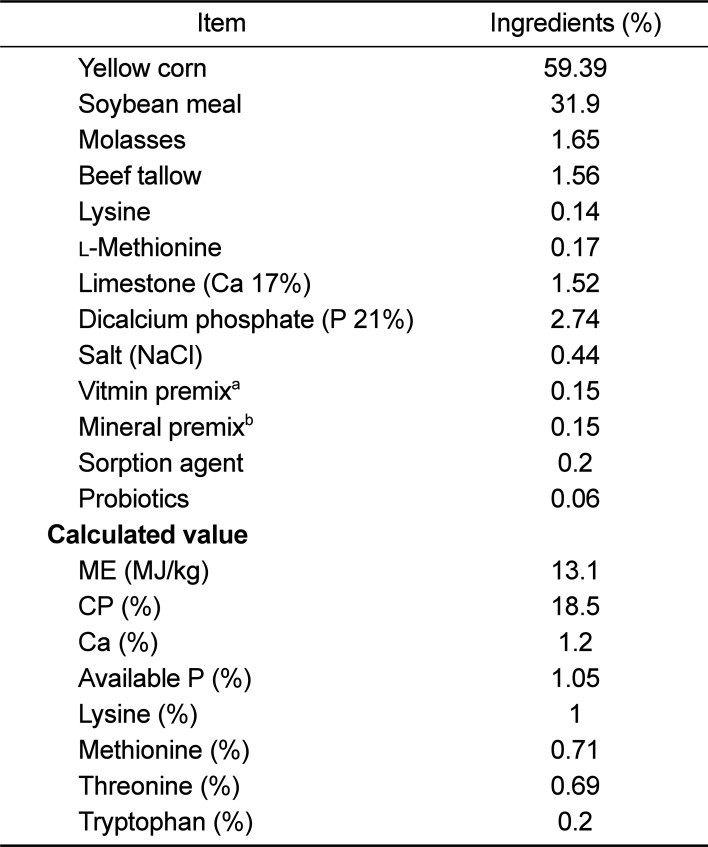
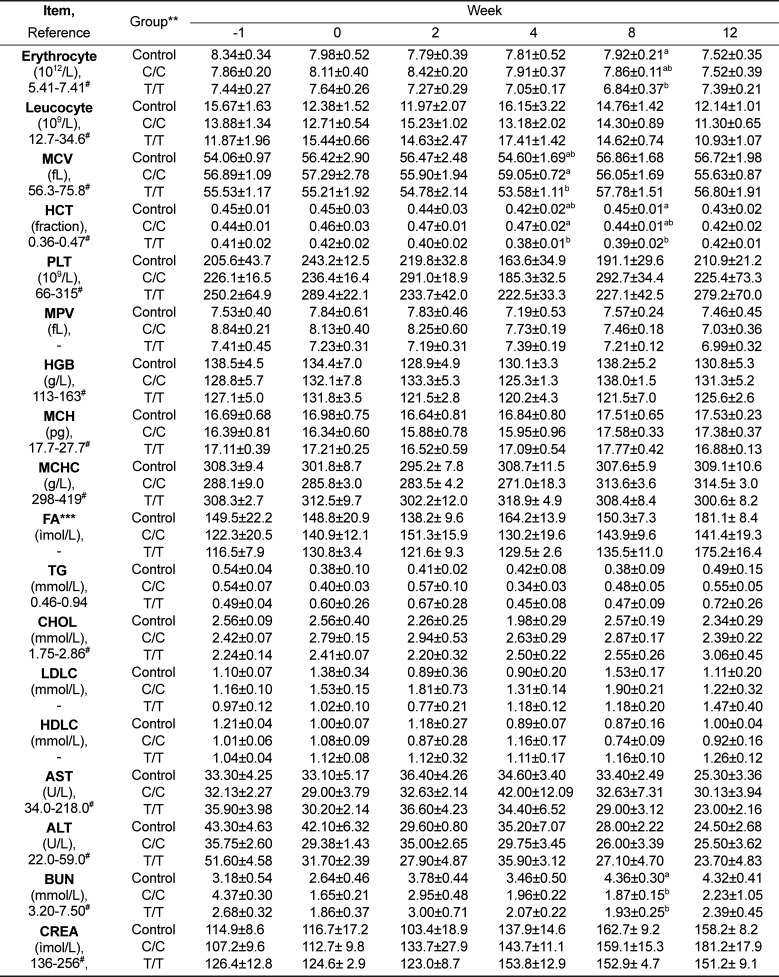




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download