INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
Methods
Data management and statistical analyses
RESULTS
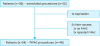 | Fig. 1Flow chart of patient inclusion and PIPAC procedures. 28 patients were eligible for PIPAC with 52 scheduled PIPAC procedures. Because of 1 aspiration and 5 “non-access” abdomens, 24 patients received 46 PIPAC procedures.PIPAC = pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy.
|
Table 1
PIPAC procedures and post-operative in-hospital stay

Table 2
Patient characteristics

Table 3
Previous treatment before PIPAC

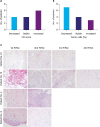 | Fig. 2PCI and tumor cell portion developments in patients with multiple PIPAC procedures. (A) Number of patients with decreased, stable, and increased PCI, (B) Number of patients with decreased, stable, and increased tumor cell portions in PM biopsies, and (C) representative H&E staining of patients with decreased tumor cell portions (patients No. 10 and No. 13) and increased tumor cell portions (patients No. 3 and No. 9). The biopsies for tumor cell evaluation were taken before each PIPAC.PCI = peritoneal carcinomatosis index; PIPAC = pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy; PM = peritoneal metastasis; H&E = hematoxylin and eosin stain.
|
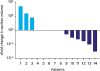 | Fig. 3Relative ascites development in patients with multiple PIPAC procedures. The fold changes of decreased (6), stable (5), and increased (3) ascites volumes during multiple PIPAC procedures are blotted as waterfall blot.PIPAC = pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy.
|
Table 4
Clinical chemistry and hematology

| 1-day post-OP | 3-day post-OP | Reference values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leucocytes (WBC) (×109/L) | 7.15±0.426 | 5.73±0.396 | 3.5–9.8 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 36.9±5.5 | 66.8±11.05 | <5 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 76.8±2.81 | 73.6±2.68 | 45–84 |
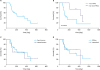 | Fig. 4Survival curves. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of all 24 patients treated by PIPAC, (B) stratification of patients, who received 1 or 2 PIPACs (16) vs. 3 or more PIPACs (8; P=0.0376), (C) metachronous (6) vs. synchronous (18) PM, and (D) diffuse (19) vs. intestinal (5) type of GC according to Laurén's classification (Log-Rank [Mantel-Cox] test).PIPAC = pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy; PM = peritoneal metastasis; GC = gastric cancer.
|
Table 5
EORTC QLQ-C30

DISCUSSION
1) A considerable proportion of patients was included with non-peritoneal metastases for symptomatic control of ascites or according to patients' wishes, although this was generally determined as contraindication.
2) Heterogeneous pre-treatment regimens and responses to systemic therapy, different biology according to Lauren's classification, and various PCI scores at 1st PIPAC, rendering evaluation of the true impact of PIPAC on changes at follow-up more difficult.
3) The relative small cohort and short follow-up of a non-randomized population do not allow any conclusive judgement of this new intervention option for PM in GC. In addition, volume of ascites and QoL are well known to correlate with each other, as QoL increases in the course of ascites control.
4) We were not able to provide associated improvement of the QoL by using validated scores, as provided by the structured interview using the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire, with decreased ascites volumes. This was possibly due to the subjective and the multifactorial nature of the assessment and the lack of reliability in repeated evaluations.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download