Abbreviations
APC
BV
CTR
CTV
DC
DR
ICI
Lag-3
moDC
RE
Tim-3
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
PBMCs
Reagents and Abs
MLR

Flow cytometry
RESULTS
PD-1 expression is upregulated in allo-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells during MLR
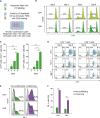 | Figure 1Upregulation of PD-1 expression in allo-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells during MLR. (A) Conventional MLR was performed as described in the section of Materials and Methods. (B) Representative FACS histograms for CTV in the gate of responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are presented. (C) The percentage of CTVlow proliferating cells among responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was analyzed during MLR. (D) Representative FACS plots for PD-1, Tim-3, and Lag-3 with CTV in the gate of responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are presented. (E) Representative FACS histograms for PD-1 in the gate of proliferating (CTVlow) and non-proliferating responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are presented. (F) The percentage of PD-1+ cells among proliferating (CTVlow) and non-proliferating responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was analyzed during MLR. The experiment was performed with responder PBMCs from 3 donors, and triplicate data from a single donor is presented as representative data. Error bars represent SEM.
**p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
|
Conventional MLR is not suitable for evaluation of the functional activities of anti-PD-1
 | Figure 2Effects of anti-PD-1 blocking Abs in conventional MLR. Anti-PD-1 blocking or isotype control Abs were added to conventional MLR cultures when the culture was set-up. (A) Representative FACS histograms for CTV in the gate of responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells with anti-PD-1 blocking or isotype control Abs are presented. Vertical lines indicate the number of cell division. (B) The ratio of the mitotic index with and without anti-PD-1 (mitotic index with anti-PD-1/mitotic index with isotype control Abs) was calculated for responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The experiment was performed with responder PBMCs from 3 donors. |
PD-L1+ or PD-L2+ cells disappear gradually during MLR
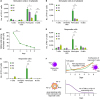 | Figure 3Number of PD-L1+ and PD-L2+ cells during MLR. (A, B) The numbers of PD-L1+ (A) and PD-L2+ (B) stimulator (CFSE+) cells in a well of 96-well round bottom plates were analyzed during MLR. When MLR was set up, 1×105 gamma-irradiated stimulator cells were placed per well. T cells, DCs, monocytes, and B cells were analyzed separately. (C) The percentage of viable cells among stimulator cells was analyzed during MLR. (D, E) The numbers of PD-L1+ (D) and PD-L2+ (E) responder (CTV+) cells in a well of 96-well round bottom plates were analyzed during MLR. When MLR was set up, 1×105 responder cells were placed per well. T cells, DCs, monocytes, and B cells were analyzed separately. The experiment was performed with responder PBMCs from 3 donors, and triplicate data from a single donor is presented as representative data. Error bars represent SEM. (F) Kinetic changes in PD-1 expression on responder T cells and PD-L1 or PD-L2 expression on Ag-presenting cells during conventional MLR are illustrated.
*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
|
Anti-PD-1 increased the proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells during two-round MLR
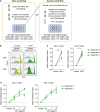 | Figure 4Effects of anti-PD-1 blocking Abs in two-round MLR. (A) two-round MLR was performed as described in the section of Materials and Methods. Anti-PD-1 blocking Abs were added to the MLR culture when the second-round of MLR was set-up. (B) Representative FACS histograms for CTV in the gate of responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells with anti-PD-1 blocking or isotype control Abs are presented. Vertical lines indicate the number of cell division. (C) The ratio of the mitotic index with and without anti-PD-1 (mitotic index with anti-PD-1/mitotic index with isotype control Abs) was calculated for responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The experiment was performed with responder PBMCs from 3 donors in triplicate. (D) Anti-PD-1 blocking Abs were added to the second-round MLR at various doses, and the ratio of the mitotic index with and without anti-PD-1 was calculated for responder CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The experiment was performed with responder PBMCs from 2 donors in triplicate. Error bars represent SEM.
**p<0.01.
|
Two-round MLR could evaluate the effects of immunomodulators in combination with anti-PD-1
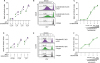 | Figure 5Effects of immunomodulators in combination with anti-PD-1 in two-round MLR. Two-round MLR was performed with immunomodulators, lenalidomide (A-C) or galunisertib (D, F) at various doses in combination with anti-PD-1. Lenalidomode, galunisertib, or anti-PD-1 was added to the MLR culture when the second-round of MLR was set-up. The mitotic index ratio was calculated as the mitotic index in the presence of immunomodulators or anti-PD-1 divided by the mitotic index in the absence of both immunomodulators and anti-PD-1 for responder CD8+ T cells. (B) Representative FACS histograms for CTV in the gate of responder CD8+ T cells with lenalidomide (10 μM) in combination with anti-PD-1 blocking or isotype control Abs are presented. (E) Representative FACS histograms for CTV in the gate of responder CD8+ T cells with galunisertib (1 μM) in combination with anti-PD-1 blocking or isotype control Abs are presented. Vertical lines indicate the number of cell division. The experiment was performed with responder PBMCs from 3 donors (A, D), and triplicate data from a single donor is presented as representative data (C, F). Error bars represent SEM. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download