Abstract
Postoperative maxillary cyst (POMC) is relatively common complication among patients who underwent Caldwell-Luc surgery. Patients with POMC usually have no symptoms, although cyst extension can result in bone destruction or cystic infection with pain. The trigeminal nerve consists of the ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve, and mandibular nerve. Among these branches, the maxillary nerve runs to the lateral and frontal sides of the maxillary sinus wall. POMC can rarely lead to trigeminal neuropathy caused by cyst enlargement that compresses some branches of the trigeminal nerve. Recently, we experienced a case with trigeminal neuralgia due to POMC. The patient was successfully treated with inferior meatal antrostomy. We report this rare case with a literature review.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Jang TY., Lee SJ., Kim KT., Choi YS. Management of Postoperative Mucocele of the Maxillary Sinus through Endoscopic Approach. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2005. 48(3):314–9.
2). Nishioka M., Pittella F., Hamagaki M., Okada N., Takagi M. Prevalence of postoperative maxillary cyst significantly higher in Japan. Oral Medicine & Pathology. 2005. 10(1):9–13.

3). Kubo I. A buccal cyst occurred after the radical operation of the maxillary sinusitis. Dai Nippon Jibi. 1927. 33:896–7.
4). Kubo I. Postoperative wangenzyste. Z Otol Tokyo. 1933. 39:1831–45.
5). Iinuma T., Tanaka M., Oosawa H., Haruyama K., Hirota Y. Postoperative retraction of the maxillary sinus walls. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1983. 86(5):518–30.
6). Suh KS., Lee JG., Kim DY., Koh YW., Yang HD., Kim BH. Inferior Meatal Fenestration Operation of the Postoperative Maxillary Cysts. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1998. 41(1):48–52.
7). Nakamura K., Kitani S., Sato H., Yumoto E., Kawakita S., Aibara R. Endoscopic endonasal surgery for postoperative maxillary cyst. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1995. 98(6):984–8. 1075.

8). Denny C., Jeena Priya K., Ongole R. Trigeminal neuralgia: Current concepts in the medical management. World Journal of Dentistry. 2010. 1(1):43–6.
9). VandeVyver V., Lemmerling M., Van Hecke W., Verstraete K. MRI findings of the normal and diseased trigeminal nerve ganglion and branches: a pictorial review. Clinical Imaging. 2008. 32(2):160.

10). Kouyialis A., Stranjalis G., Boviatsis E., Ziaka D., Bouras T., Sakas D. Recurrence of trigeminal neuralgia due to an acquired arachnoid cyst. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience. 2008. 15(12):1409–11.

11). Park C-S., Park Y-J., Cho J-H., Jung S-H. Infratemporal fossa mucocele with trigeminal nerve compression. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2008. 35(3):455–8.

12). KimJ-Y. Hong SH., Kim Y-D., Na S-J., Lee KO., Yoon B. Compressive Trigeminal Neuropathy after Caldwell-Luc Operation. Journal of the Korean Neurological Association. 2015. 33(3):206–8.

13). Jae Myung Kim, Jae Hoon Cho, Hyo Vin Jung, Jee Min Choi, Jae Seung Kim and Jin Kook Kim. Post-Operative Maxillary Cyst after Maxillary Orthognathic Surgery: Report of an Unusual Case. J Rhi-nol. 2012. 19(1):60–2.
14). Seung Kyu Chung MD. Headache and Facial Pain Related to the Paranasal Sinuses. J Rhinol. 2012. 19(2):83–6.
Go to : 
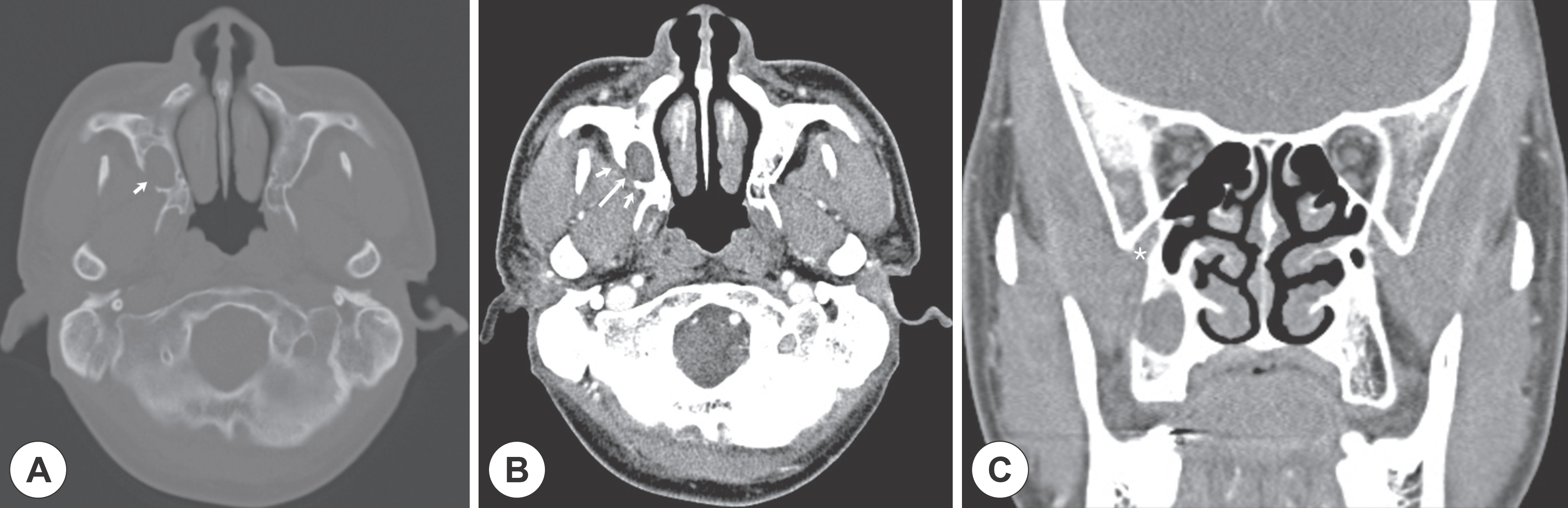 | Fig. 1Images of paranasal sinus CT. A: Bone setting of coronal view shows a 1.8 cm-sized cystic lesion with bone remodeling (arrow) at the postoperative right maxillary sinus. B: Enhanced image shows fat infiltration and inflammatory changes (short arrow) on bony dehiscence side of postoperative maxillary cyst (long arrow). C: Pterygomaxillary fissure (asterisk) is observed upper side of bony dehiscence site at coronal image. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download