Abstract
Adverse events such as hemoptysis and gastrointestinal hemorrhage during tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment are relatively rare, but the severity of the bleeding can be higher than other common adverse events. It is necessary to educate patients about its possibility so that they can be found early. In this case report of radioiodine refractory thyroid cancer patient, hemoptysis and gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred following lenvatinib administration. Drug interruption and dose modification and dose interruption were required in addition to management for bleeding itself. It is necessary to confirm the high risk of bleeding before the administration of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and to appropriately control the follow-up interval and drug dosage accordingly.
Figures and Tables
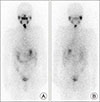 | Fig. 1Anterior (A) and posterior (B) post-radioiodine therapeutic scan showed no significant radioiodine uptake in distant lesion. |
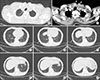 | Fig. 2CT scan revealed multiple lymph node metastases at the surgical site (B, arrows), progressive peritracheal lymph node metastasis (A, arrow) and multiple hematogenous pulmonary metastases (C–H, arrows) after five months of radioiodine therapy. |
References
1. Brose MS, Nutting CM, Jarzab B, Elisei R, Siena S, Bastholt L, et al. Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2014; 384(9940):319–328.

2. Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, Robinson B, Brose MS, Elisei R, et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodinerefractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372(7):621–630.

3. Launay-Vacher V, Deray G. Hypertension and proteinuria: a class-effect of antiangiogenic therapies. Anticancer Drugs. 2009; 20(1):81–82.

4. Blevins DP, Dadu R, Hu M, Baik C, Balachandran D, Ross W, et al. Aerodigestive fistula formation as a rare side effect of antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2014; 24(5):918–922.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download