INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Patients and tissue samples
Table 1
Clinicopathologic characteristics of ALK-rearranged adenocarcinoma with combined neuroendocrine component tumor in this study
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
EGFR mutation and ALK gene status
Ethics statement
RESULTS
Histologic features, ALK and EGFR status of each cases
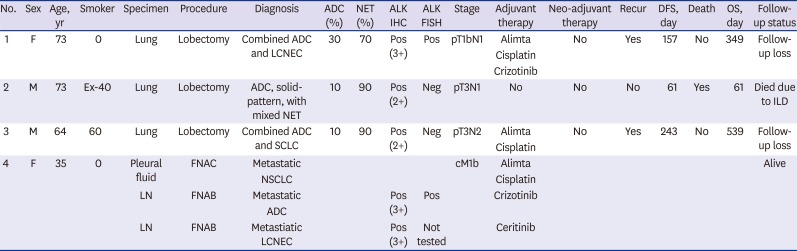
 | Fig. 1Histologic finding, immunohistochemical results and ALK FISH study of case 1. The tumor shows acinar-pattern adenocarcinoma (A, ×100, right lower) with combined large cell neuroendocrine component (A, left upper; B, ×200). Both components are positive for ALK immunohistochemically (C, ×100). However, only large cell neuroendocrine component reveals CD56-positivity (D, ×100). The tumor shows break-apart signal pattern on ALK FISH study (E).
ALK = anaplastic lymphoma kinase, FISH = fluorescence in situ hybridization.
|
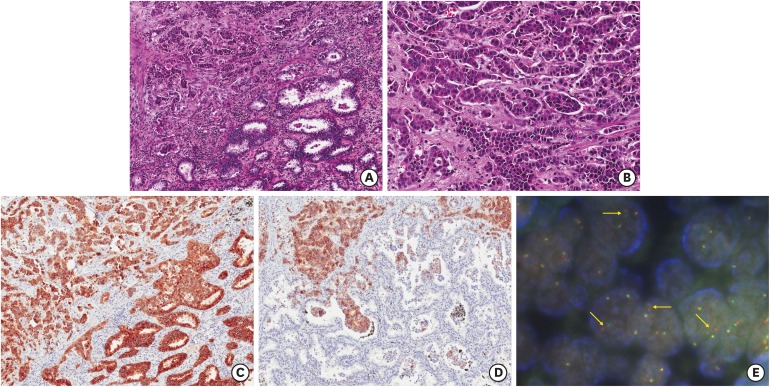
 | Fig. 2Microscopic finding, immunohistochemical results, and ALK FISH study of case 2. The tumor displays poorly differentiated solid-pattern adenocarcinoma (A, ×100, left; B, ×200) with combined large cell neuroendocrine component (A, right; B, ×200). Both components have ALK immunoreactivity (C, ×100). Only large cell neuroendocrine component reveals strong CD56-positivity (D, ×100). However, both components examined with ALK break-apart FISH rearrangement probe kit are negative (E).
ALK = anaplastic lymphoma kinase, FISH = fluorescence in situ hybridization.
|
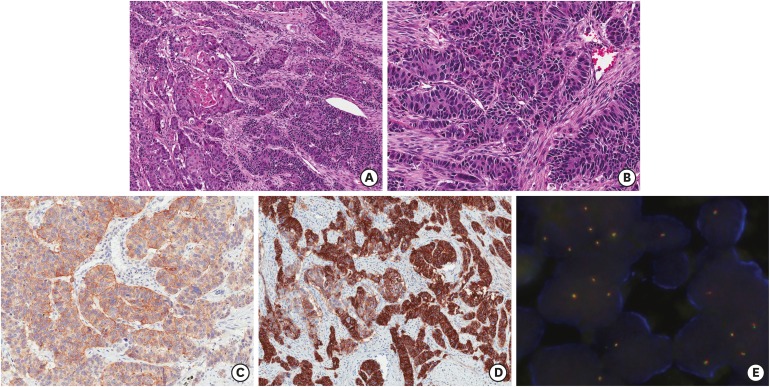
 | Fig. 3Histologic finding and immunohistochemical results of case 3. The tumor reveals acinar-pattern adenocarcinoma (A, ×100, right; B, ×200) with combined small cell neuroendocrine component (A, left; C, ×200). These both components are positive for ALK immunohistochemically (D, ×100). However, only large cell neuroendocrine component shows CD56-positivity (E, ×100). Break-apart signal was not shown on an ALK FISH test (image not included).
ALK = anaplastic lymphoma kinase, FISH = fluorescence in situ hybridization.
|
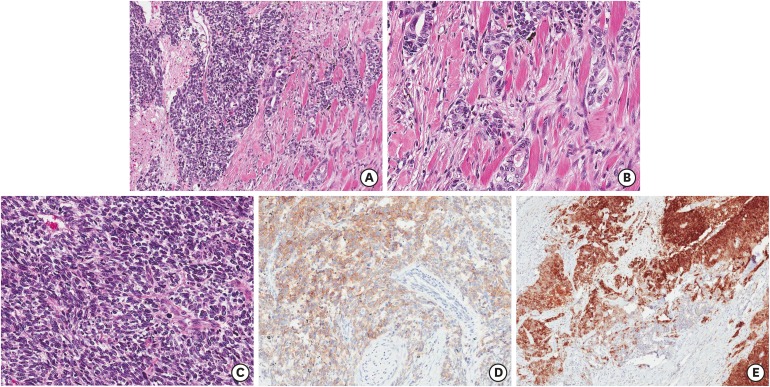
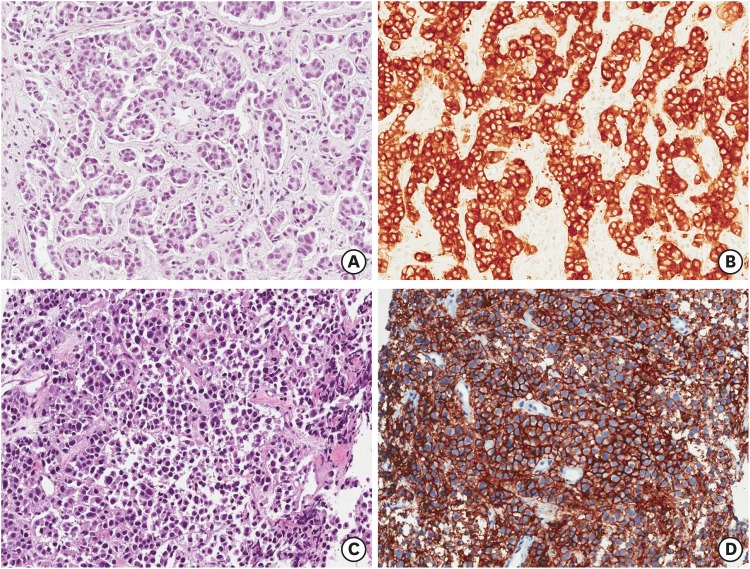 | Fig. 4Microscopic finding and immunohistochemical results of case 4. Second biopsied specimen consists of poorly differentiated solid and acinar-pattern adenocarcinoma (A, ×200) and displays ALK-positivity (B, ×200). The tumor showed break-apart signal pattern on ALK FISH study (image not included). After ALK-TKI (crizotinib) administration, third biopsied tumor reveals solid and sheet pattern tumor with neuroendocrine differentiation (C, ×200). And it reveals also ALK-positivity and CD56-positivity (D, ×200).
ALK = anaplastic lymphoma kinase, FISH = fluorescence in situ hybridization, ALK-TKI = anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
|
DISCUSSION
Table 2
Clinicopathologic features of histologic transformation of ALK-rearranged adenocarcinoma after ALK-TKI administration in the literature
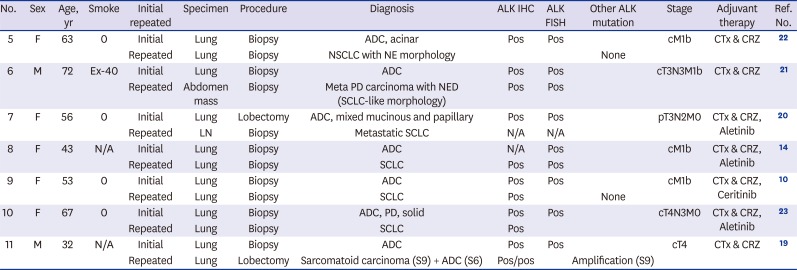
| No. | Sex | Age, yr | Smoke | Initial repeated | Specimen | Procedure | Diagnosis | ALK IHC | ALK FISH | Other ALK mutation | Stage | Adjuvant therapy | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | F | 63 | 0 | Initial | Lung | Biopsy | ADC, acinar | Pos | Pos | cM1b | CTx & CRZ | 22 | |
| Repeated | Lung | Biopsy | NSCLC with NE morphology | None | |||||||||
| 6 | M | 72 | Ex-40 | Initial | Lung | Biopsy | ADC | Pos | Pos | cT3N3M1b | CTx & CRZ | 21 | |
| Repeated | Abdomen mass | Biopsy | Meta PD carcinoma with NED (SCLC-like morphology) | Pos | Pos | ||||||||
| 7 | F | 56 | 0 | Initial | Lung | Lobectomy | ADC, mixed mucinous and papillary | Pos | Pos | pT3N2M0 | CTx & CRZ, Aletinib | 20 | |
| Repeated | LN | Biopsy | Metastatic SCLC | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
| 8 | F | 43 | N/A | Initial | Lung | Biopsy | ADC | N/A | Pos | cM1b | CTx & CRZ, Aletinib | 14 | |
| Repeated | Lung | Biopsy | SCLC | Pos | Pos | ||||||||
| 9 | F | 53 | 0 | Initial | Lung | Biopsy | ADC | Pos | Pos | cM1b | CTx & CRZ, Ceritinib | 10 | |
| Repeated | Lung | Biopsy | SCLC | Pos | None | ||||||||
| 10 | F | 67 | 0 | Initial | Lung | Biopsy | ADC, PD, solid | Pos | Pos | cT4N3M0 | CTx & CRZ, Aletinib | 23 | |
| Repeated | Lung | Biopsy | SCLC | Pos | |||||||||
| 11 | M | 32 | N/A | Initial | Lung | Biopsy | ADC | Pos | Pos | cT4 | CTx & CRZ | 19 | |
| Repeated | Lung | Lobectomy | Sarcomatoid carcinoma (S9) + ADC (S6) | Pos/pos | Amplification (S9) |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download