INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data selection
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
 | Fig. 1The graph shows that the procedural number of total hip arthroplasties from 2000 to 2014 increased consistently. |
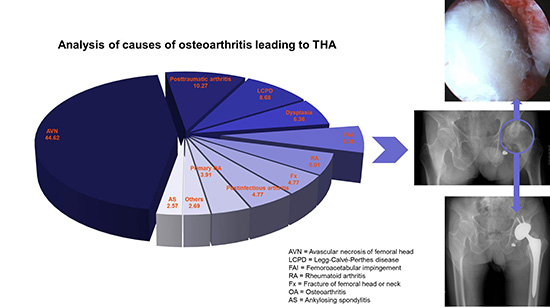
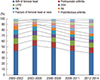 | Fig. 2The graph shows the changes of causes leading to THA.
THA = total hip arthroplasty, AVN = avascular necrosis, LCPD = Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, DDH = developmental dysplasia of the hip, FAI = femoroacetabular impingement, RA = rheumatoid arthritis.
|
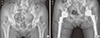 | Fig. 3Anteroposterior radiographs illustrate the case of a 62-year-old female patient who had primary OA of both hips. (A) The radiograph was taken before THA. Lateral center-edge angle, sharp angle, and acetabular roof obliquity of right hip was 37.2°, 35.8°, and 8.6°, respectively. Left hip was 43.5°, 35.2°, and 7.0°, respectively. (B) The radiograph was taken after THA to treat primary OA.
THA = total hip arthroplasty, OA = osteoarthritis.
|
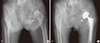 | Fig. 4Anteroposterior radiographs illustrate the case of an 85-year-old female patient who had secondary OA caused by Cam type FAI of left hip. (A) Preoperative radiograph shows typical pistol grip deformity on left hip. (B) The radiograph was taken after THA.
THA = total hip arthroplasty, FAI = femoroacetabular impingement, OA = osteoarthritis.
|
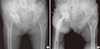 | Fig. 5Anteroposterior radiographs illustrate the case of a 76-year-old female patient who had secondary OA caused by Pincer type FAI of left hip. (A) Preoperative radiograph shows typical acetabular protrusion on right hip. (B) The radiograph was taken after THA.
THA = total hip arthroplasty, FAI = femoroacetabular impingement, OA = osteoarthritis.
|
Table 1
Causes leading to primary THA
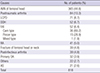
Table 2
Intraclass intraobserver and intraobserver reliabilities of radiographic parameters
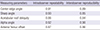
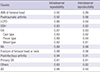
Table 3
Intraobserver and intraobserver reliabilities of the causes leading to primary THA




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download