INTRODUCTION
CASE DESCRIPTION
Initial presentation, operation, and adjuvant therapy
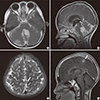 | Fig. 1Initial presentation: medulloblastoma. Axial (A) and sagittal (B) contrast-enhanced MRI show a strongly enhancing lesion in the cerebellum with surrounding leptomeningeal enhancement, suggesting leptomeningeal seeding. Second presentation: meningioma. A 9 × 7 mm round shape mass (arrow) based on the falx cerebri at the high vertex with peripheral enhancement is shown in axial T2 weighted (C), contrast-enhanced sagittal (D).
MRI = magnetic resonance imaging.
|
Second presentation, operation, and adjuvant therapy
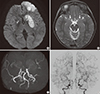 | Fig. 2Acute brain infarction after removal of the radiation-induced tumor. Axial diffusion weighted images (A) show diffusion restriction at the left frontal lobe and both basal ganglia, which indicates acute infarction. Retrospective review of MRI shows bilateral steno-occlusion of the internal carotid artery bifurcation and its branches (arrows) on T2-weighted axial image (B). MRA reveals marked narrowing of the main trunk of both middle cerebral arteries with rather preserved portions of their distal branches (C). Conventional cerebral angiography (D) shows steno-occlusion at the terminal portion of the right internal carotid artery and left internal carotid artery confirming moyamoya syndrome.
MRI = magnetic resonance imaging, MRA = magnetic resonance angiography.
|
Third presentation, operation, and adjuvant therapy
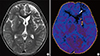 | Fig. 3Third presentation: moyamoya syndrome. T2-weighted axial image shows chronic change of infarction at the left frontal lobe (arrows) and bilateral basal ganglia (A). Perfusion MRI demonstrates delayed time to peak in the both middle cerebral artery territories and aggravated perfusion in the left anterior cerebral artery territory (arrows) (B).
MRI = magnetic resonance imaging.
|
Pathologic findings
DISCUSSION
Table 1
Reported cases of radiation-induced moyamoya syndrome developed after radiation therapy for medulloblastoma

| Author | Year | Age, sex | Dose of radiation | Latency | Occluded vessel | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| al-Amro and Schultz (10) | 1995 | 7, M | 34 Gy whole brain | 4 mon | Bilateral distal ICA and VA | Hemiparesis |
| 20 Gy posterior fossa | ||||||
| 25.5 Gy spine | ||||||
| Ullrich et al. (11) | 2007 | 2, M | 39.6 Gy* | 55 mon | Not described | Hemiparesis |
| Kim et al. (12) | 2011 | 5, F | 36 Gy craniospinal axis | 2 yr | Right supraclinoid ICA and left ICA | Hemiparesis |
| 18 Gy posterior fossa | ||||||
| Present case | 3, M | 30.6 Gy craniospinal axis | 10 yr | Bilateral distal ICA | Hemiparesis | |
| 19.8 Gy posterior fossa |
Table 2
Reported cases of coexistence of radiation-induced tumor and vasculopathy after cranial radiotherapy

| Author | Year | Age, sex | Dose of radiation | Primary tumor (location) | Secondary tumor (location) | Latency, yr* | Vasculopathy; affected vessel | Latency, yr† | Secondary symptom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montanera et al. (13) | 1985 | 9, M | 52.5 Gy brain | Ganglioglioma (left temporal) | Meningioma (left frontoparietal) | 15 | Occlusion of the left ICA | 15 | Seizure |
| 12, F | 45 Gy brain | Astrocytoma (suprasellar) | Meningioma (left temporoparietal) | 20 | Occlusion of the left ICA at ophthalmic branch | 20 | Visual loss | ||
| Foreman et al. (14) | 1995 | 2, M | 20 Gy brain | ALL | Meningioma (right frontal) | 19 | Occlusion of left ACA, PCA (occlusion of right ICA‡) | 19 | Hemiparesis |
| Kamide et al. (15) | 2010 | 5, M | 15 Gy brain | Medulloblastoma (cerebellum) | High grade glioma (cerebellum), probable meningioma without pathology (left frontal, temporal) | 29 | Cavernoma (right temporal) | 7 | 1) Symptomatic hemorrhage (cavernoma) |
| 39 Gy posterior fossa | 2) Truncal ataxia (glioma) | ||||||||
| Baheti et al. (17) | 2010 | 9, M | 18 Gy brain | ALL | Meningioma (right frontal) | 21 | Cavernoma (pons) | 21 | Seizure |
| Paramanathan et al. (18) | 2010 | 5, F | 54 Gy brain | Ependymoma (left frontoparietal) | Meningioma (orbital) | 16 | Cavernoma (left cerebellar and bilateral basal ganglia) | 16 | Ptosis |
| Chourmouzi et al. (16) | 2013 | 10, M | ND | Medulloblastoma (cerebellum) | Meningioma (right frontal) | 19 | Cavernoma (left centrum semiovale and right temporal) | 19 | Seizure |
| Present case | 3, M | 30.6 Gy craniospinal axis | Medulloblastoma (cerebellum) | Meningioma (falx) | 10 | Moyamoya syndrome; bilateral occlusion of distal ICA | 10 | Hemiparesis | |
| 19.8 Gy posterior fossa |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download