INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
LCMVs
Infection and tissue harvest
Plaque assay
Antibody specific for LCMV NP and fluorescent conjugation
Antibody staining for SFQF
RESULTS
Vero cells were more frequently infected with LCMV than BHK21 cells
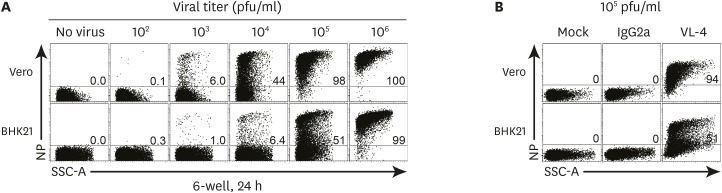 | Figure 1Vero cells were more susceptible than BHK21 cells to LCMV ARM infection. A total of 3.0×105 Vero and BHK21 cells were plated in a 6-well plate with 3 ml of DMEM complete medium for 15 h before use. After the removal of the culture medium, cells were treated with 200 µl of serial dilutions (106 to 102 pfu/ml) of LCMV ARM for 1 h. A total of 2 ml of the medium was dispensed and cells were stained with VL-4 after 24 h of incubation, followed by flow cytometry analysis. (A) NP expression in Vero and BHK21 cells infected with serial dilutions of LCMV ARM. (B) The expression of isotype control of VL-4 antibody (IgG2a) in Vero and BHK21 cells infected with LCMV ARM (105 pfu/ml). The number in the plot indicates the percentage of NP+ cell population in Vero and BHK21 cells. Data are representative of 5 independent experiments.
SSC-A, side scatter area.
|
Optimization of cell confluence excluding cell overgrowth
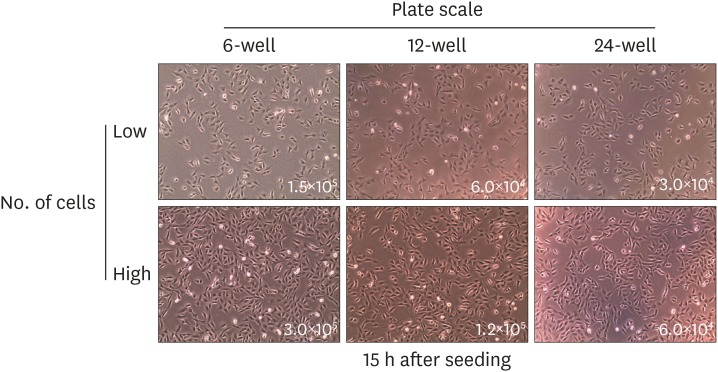 | Figure 2Initial cell seeding number was set to high and low for each plate scale. Cell numbers for each scale were calculated in proportion to the size of 6-, 12-, and 24-well plate. Cells were seeded and incubated for 15 h prior to infection. The number in the image visualized by an optical microscope indicates the cell count of seeded cells as high (top) and low (bottom) confluence in each plate. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. |
Establishment of optimal conditions of SFQF assay
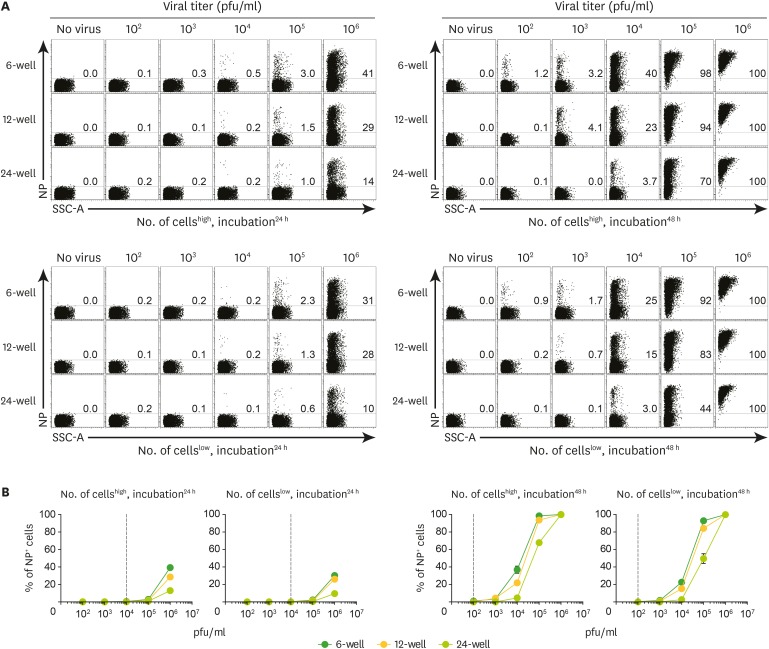 | Figure 3Validation of conditions such as plate scale, cell seeding number, and incubation time to establish an optimal method for SFQF assay. Vero cells were plated on 6-, 12-, and 24-well plates at high and low seeding numbers (as previously determined) and cultured for 15 h. The medium was removed and cells were treated with 200 µl of the serial dilution of LCMV ARM stock (106 pfu/ml) at each incubation time, followed by flow cytometry analysis. (A) The incubation of 48 h in a 6-well plate seeded with a high number of cells was optimal for LCMV detection. Numbers in representative plots indicate percentages of NP+ cells at indicated conditions such as cell seeding number and incubation time (left top, high and 24 h; left bottom, low and 24 h; right top, high and 48 h; right bottom, low and 48 h). (B) Line graphs summarize the representative data of Fig. 3A obtained from each condition. Data are representatives of 2 independent experiments.
SSC-A, side scatter area.
|
Calibrations of standard curve in SFQF and plaque assay reveal the detection threshold of LCMV NP
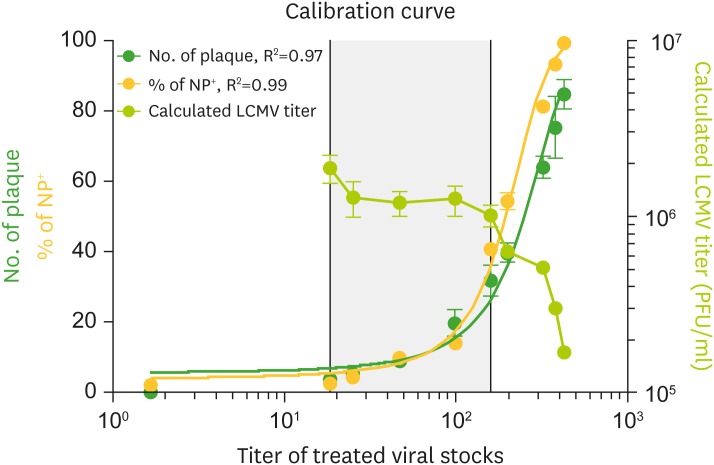 | Figure 4Plaque numbers and NP+ cell frequencies were correlated to obtain a standard curve. Vero cells were plated as per the conditions in Fig. 3 and infected with 200 µl of 2-fold dilution of LCMV ARM (106 pfu/ml) in the amount same as that in the plaque assay. After 48 h of incubation, the frequency of NP+ cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. All of the serial dilutions were analyzed by plaque assay to verify the threshold of the virus detection. Calibration curve of NP+ cell frequency (yellow circle) and plaque number (green circle). Calculation of plaque assay for each serial dilution (yellow green circle). Left Y-axis, right Y-axis, and X-axis indicate plaque number with NP+ cell frequency, calculated LCMV titer of each serial dilution, and titer of each treated serial dilution, respectively. R2 values were obtained using non-linear curve fit analysis. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. |
Frequency of NP+ cells were correlated with the number of plaques
 | Figure 5Validation of LCMV titration in tissues ex vivo. C57BL/6 mice were intravenously infected with LCMV CL13 (2×106 pfu/ml). Spleens and serum were harvested from mice 10 days after infection. Homogenized spleens and bled serum from 10−4 to 10−2 dilution of original stocks were incubated with Vero cells and SFQF and plaque assays were manually performed. (A) Detection of NP+ proportion in serum and spleens of mice infected with LCMV CL13. Numbers in plots indicate the percentage of NP+ population. (B) Bar graphs summarize the titer calculated from the plaque assay (green bar) and frequency of NP+ cells measured by SFQF assay (yellow bar). n=3 mice per group in each experiment. |
DISCUSSION
Table 1
Protocol of SFQF assay

Table 3
Comparisons of LCMV detection methods with various approaches





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download