INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental animals
Treatments for the experimental animals
Positive control group (n=12)
Negative control group (n=12)
Experimental group (n=12)
Preparation of PRP
Surgical procedures
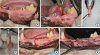 | Figure 2The surgical procedure. (A) The crowns and furcation areas of the premolars were sectioned in the middle and parallel to the long axis of the root with a fissure bur. (B) The extractions were performed as atraumatically as possible. (C) The periodontal ligament and cementum were removed by scaling and root planing in the negative control and experimental groups. (D) The roots were soaked in 1.0 mL of platelet-rich plasma in the experimental group. (E) After replanting, the root canals were filled with calcium hydroxide, and the crowns were removed. (F) The roots were covered using a coronally repositioned flap. |
Histological and histomorphometric evaluation
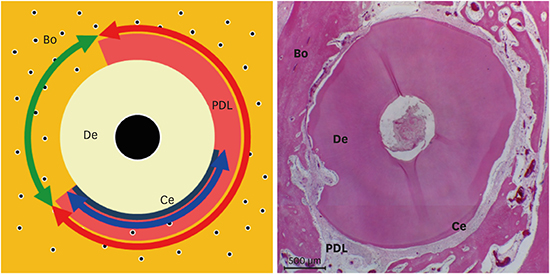
 | Figure 3Schematic illustration representing the horizontal root plane for the histomorphometric analysis. Red, green, and blue arrows shown are periodontal ligament/newly formed periodontal ligament-like tissue, replacement resorption, and cementum/newly formed cementum-like tissue, respectively.Bo: alveolar bone, PDL: periodontal ligament, Ce: cementum, De: dentin.
|
Periodontal ligament/newly formed periodontal ligament-like tissue (PDL/NPDLT): Length of the connective tissue attached to the root surface
Replacement resorption (RR): Length of the part with ankylosis
Cementum/newly formed cementum-like tissue (C/NCeT): Length of the cementum or regenerated cementum on the root surface or the area with cementum-like apposition
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Clinical outcomes
Histological outcomes
At 4 weeks
 | Figure 4Longitudinal sections of periodontal wound healing at 4 weeks after replantation (all samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin). (A, D) PDL and cementum were observed around the dentin (positive control group). (B, E) Alveolar bone was in direct contact with the dentin (negative control group). (C, F) PDL-like tissue and cementum-like tissue were observed around the dentin (experimental group). However, the width of the PDL-like tissue space and cementum-like tissue was irregular in comparison to the positive control group.PDL: periodontal ligament, Bo: alveolar bone, Ce: cementum, De: dentin, NPDLT: newly formed periodontal ligament-like tissue, NCeT: newly formed cementum-like tissue.
|
 | Figure 5Horizontal sections of periodontal wound healing at 4 weeks after replantation (all samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin). (A, D) PDL and cementum were observed almost around the dentin (positive control group). However, ankylosis and surface resorption were occasionally observed around the dentin. (B, E) Alveolar bone was in direct contact with the dentin (negative control group). (C, F) The width of the PDL-like tissue space was regular and PDL-like tissue was denser than in the positive control group (experimental group). However, cementum-like tissue was observed around the dentin.PDL: periodontal ligament, Bo: alveolar bone, Ce: cementum, De: dentin, NPDLT: newly formed periodontal ligament-like tissue, NCeT: newly formed cementum-like tissue.
|
At 8 weeks
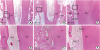 | Figure 6Longitudinal sections of periodontal wound healing at 8 weeks after replantation (all samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin). (A, D) PDL and cementum were observed around the dentin (positive control group). (B, E) Alveolar bone was in direct contact with the dentin (negative control group). Wide and deep inflammatory resorption was observed on the dentin surface. (C, F) PDL-like tissue and cementum-like tissue were observed around the dentin (experimental group). The cementum-like tissue was thinner than the cementum of the positive control group. However, the thickness of the cementum-like tissue was uniform, as in the positive control group.PDL: periodontal ligament, Bo: alveolar bone, PDL: periodontal ligament, Ce: cementum, De: dentin, NPDLT: newly formed periodontal ligament-like tissue, NCeT: newly formed cementum-like tissue.
|
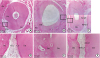 | Figure 7Horizontal sections of periodontal wound healing at 8 weeks after replantation (all samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin). (A, D) PDL and cementum were observed around the dentin (positive control group). (B, E) Alveolar bone was in direct contact with the dentin (negative control group). (C, F) PDL-like tissue and cementum-like tissue were observed around the dentin (experimental group). Cementum-like tissue had formed in the area of surface resorption.PDL: periodontal ligament, Bo: alveolar bone, Ce: cementum, De: dentin, NPDLT: newly formed periodontal ligament-like tissue, NCeT: newly formed cementum-like tissue.
|
Histomorphometric outcomes
Table 1
Histomorphometric results of periodontal wound healing at 4 weeks after replantation

Table 2
Histomorphometric results of periodontal wound healing at 8 weeks after replantation





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download