1. Park SB, Kim J, Jeong JH, Lee JK, Chin DK, Chung CK, et al. Prevalence and incidence of osteoporosis and osteoporotic vertebral fracture in Korea: nationwide epidemiological study focusing on differences in socioeconomic status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016; 41(4):328–336.
2. Eastell R, Cedel SL, Wahner HW, Riggs BL, Melton LJ 3rd. Classification of vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 1991; 6(3):207–215.

3. Odén A, McCloskey EV, Kanis JA, Harvey NC, Johansson H. Burden of high fracture probability worldwide: secular increases 2010–2040. Osteoporos Int. 2015; 26(9):2243–2248.

4. Angevine PD, O'Leary PT, Bridwell KH. Fixed sagittal imbalance. In : Herkowitz H, Garfin S, Eismont F, Bell G, Balderston R, editors. Rothman-Simeone The Spine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier;2011. p. 1285–1296.
5. Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A(3):454–463.

6. Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Rinella A, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A:Suppl 1. 44–50.
7. Kado DM, Huang MH, Karlamangla AS, Barrett-Connor E, Greendale GA. Hyperkyphotic posture predicts mortality in older community-dwelling men and women: a prospective study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004; 52(10):1662–1667.

8. O'Brein MF, Kuklo TR, Blanke KM, Lenke LG. Spinal Deformity Study Group. Radiographic Measurement Manual. Memphis, TN: Medtronic Sofamor Danek USA, Inc.;2004.
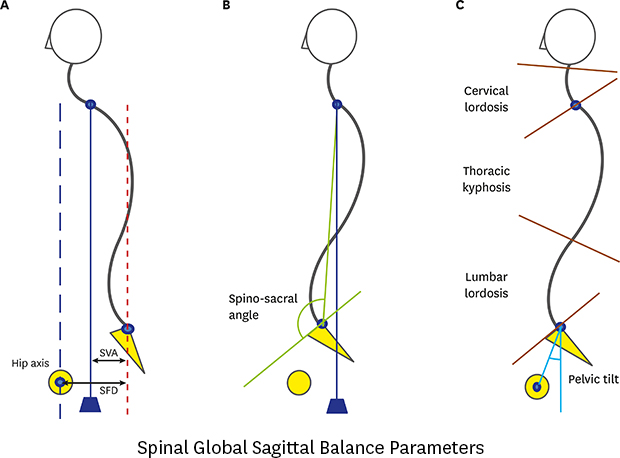
9. Barrey C, Roussouly P, Le Huec JC, D'Acunzi G, Perrin G. Compensatory mechanisms contributing to keep the sagittal balance of the spine. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:Suppl 6. S834–S841.

10. Imagama S, Matsuyama Y, Hasegawa Y, Sakai Y, Ito Z, Ishiguro N, et al. Back muscle strength and spinal mobility are predictors of quality of life in middle-aged and elderly males. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(6):954–961.

11. Hwang H, Bae J, Hwang S, Park H, Kim I. Effects of breath-hold diving on bone mineral density of women divers. Joint Bone Spine. 2006; 73(4):419–423.
12. Elixhauser A, Steiner C, Harris DR, Coffey RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. 1998; 36(1):8–27.

13. Booth KC, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Baldus CR, Blanke KM. Complications and predictive factors for the successful treatment of flatback deformity (fixed sagittal imbalance). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24(16):1712–1720.

14. Karlsson MK, Nordqvist A, Karlsson C. Physical activity increases bone mass during growth. Food Nutr Res. 2008; 52.

15. Stengel SV, Kemmler W, Pintag R, Beeskow C, Weineck J, Lauber D, et al. Power training is more effective than strength training for maintaining bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005; 99(1):181–188.

16. Wesolowska K, Czarkowska-Paczek B, Przedlacki J, Przybylski J. Scuba diving does not affect bone mineral density or bone mineral content. Joint Bone Spine. 2011; 78(6):616–618.

17. Pereira Silva JA, Costa Dias F, Fonseca JE, Canhao H, Resende C, Viana Queiroz M. Low bone mineral density in professional scuba divers. Clin Rheumatol. 2004; 23(1):19–20.
18. Burr DB, Robling AG, Turner CH. Effects of biomechanical stress on bones in animals. Bone. 2002; 30(5):781–786.

19. Robling AG, Turner CH. Mechanical signaling for bone modeling and remodeling. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009; 19(4):319–338.

20. Scofield KL, Hecht S. Bone health in endurance athletes: runners, cyclists, and swimmers. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2012; 11(6):328–334.
21. Gomez-Bruton A, Montero-Marín J, González-Agüero A, García-Campayo J, Moreno LA, Casajús JA, et al. The effect of swimming during childhood and adolescence on bone mineral density: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2016; 46(3):365–379.

23. Sinaki M, Itoi E, Rogers JW, Bergstralh EJ, Wahner HW. Correlation of back extensor strength with thoracic kyphosis and lumbar lordosis in estrogen-deficient women. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1996; 75(5):370–374.
24. Mika A, Unnithan VB, Mika P. Differences in thoracic kyphosis and in back muscle strength in women with bone loss due to osteoporosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(2):241–246.

25. Iki M, Saito Y, Dohi Y, Kajita E, Nishino H, Yonemasu K, et al. Greater trunk muscle torque reduces postmenopausal bone loss at the spine independently of age, body size, and vitamin D receptor genotype in Japanese women. Calcif Tissue Int. 2002; 71(4):300–307.

26. Meghji S, Morrison MS, Henderson B, Arnett TR. pH dependence of bone resorption: mouse calvarial osteoclasts are activated by acidosis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 280(1):E112–E119.

27. Bushinsky DA, Parker WR, Alexander KM, Krieger NS. Metabolic, but not respiratory, acidosis increases bone PGE2 levels and calcium release. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001; 281(6):F1058–F1066.







 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download