1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65(1):5–29.

2. Jung KW, Won YJ, Oh CM, Kong HJ, Lee DH, Lee KH, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2014. Cancer Res Treat. 2017; 49(2):292–305.

3. Robinson JW, Moritz S, Fung T. Meta-analysis of rates of erectile function after treatment of localized prostate carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 54(4):1063–1068.

4. D’Souza WD, Thames HD. Is the alpha/beta ratio for prostate cancer low? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001; 51(1):1–3.
5. King CR, Fowler JF. A simple analytic derivation suggests that prostate cancer alpha/beta ratio is low. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001; 51(1):213–214.
6. Miralbell R, Roberts SA, Zubizarreta E, Hendry JH. Dose-fractionation sensitivity of prostate cancer deduced from radiotherapy outcomes of 5,969 patients in seven international institutional datasets: alpha/beta= 1.4 (0.9-2.2) Gy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 82(1):e17–24.
7. Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Fractionation and protraction for radiotherapy of prostate carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43(5):1095–1101.

8. Kim H, Kim JW, Hong SJ, Rha KH, Lee CG, Yang SC, et al. Treatment outcome of localized prostate cancer by 70 Gy hypofractionated intensity-modulated radiotherapy with a customized rectal balloon. Radiat Oncol J. 2014; 32(3):187–197.

9. Roeske JC, Forman JD, Mesina CF, He T, Pelizzari CA, Fontenla E, et al. Evaluation of changes in the size and location of the prostate, seminal vesicles, bladder, and rectum during a course of external beam radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995; 33(5):1321–1329.

10. Beltran C, Herman MG, Davis BJ. Planning target margin calculations for prostate radiotherapy based on intrafraction and interfraction motion using four localization methods. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 70(1):289–295.

11. Létourneau D, Martinez AA, Lockman D, Yan D, Vargas C, Ivaldi G, et al. Assessment of residual error for online cone-beam CT-guided treatment of prostate cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 62(4):1239–1246.

12. Smitsmans MH, de Bois J, Sonke JJ, Betgen A, Zijp LJ, Jaffray DA, et al. Automatic prostate localization on cone-beam CT scans for high precision image-guided radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 63(4):975–984.

13. Alonso-Arrizabalaga S, Brualla Gonzalez L, Rosello Ferrando JV, Pastor Peidro J, Lopez Torrecilla J, Planes Meseguer D, et al. Prostate planning treatment volume margin calculation based on the ExacTrac X-Ray 6D image-guided system: margins for various clinical implementations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 69(3):936–943.

14. Lee SS, Min CK, Cho GS, Han S, Kim KB, Jung H, et al. Quantitative evaluation of patient positioning error using CBCT 3D gamma density analysis in radiotherapy. Prog Med Phys. 2017; 28(4):149–155.

15. Chung H, Cho S, Cho B. Feasibility study of robotics-based patient immobilization device for real-time motion compensation. Prog Med Phys. 2016; 27(2):117–124.

16. Xie Y, Djajaputra D, King CR, Hossain S, Ma L, Xing L. Intrafractional motion of the prostate during hypofractionated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 72(1):236–246.

17. Polat B, Guenther I, Wilbert J, Goebel J, Sweeney RA, Flentje M, et al. Intra-fractional uncertainties in image-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) of prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol. 2008; 184(12):668–673.

18. Lei S, Piel N, Oermann EK, Chen V, Ju AW, Dahal KN, et al. Six-dimensional correction of intra-fractional prostate motion with cyberknife stereotactic body radiation therapy. Front Oncol. 2011; 1:48.

19. Freeman DE, King CR. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for low-risk prostate cancer: five-year outcomes. Radiat Oncol. 2011; 6:3.

20. van Herk M, Remeijer P, Rasch C, Lebesque JV. The probability of correct target dosage: dose-population histograms for deriving treatment margins in radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 47(4):1121–1135.

21. Abramowitz MC, Li T, Buyyounouski MK, Ross E, Uzzo RG, Pollack A, et al. The Phoenix definition of biochemical failure predicts for overall survival in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer. 2008; 112(1):55–60.

22. Litzenberg DW, Balter JM, Hadley SW, Sandler HM, Willoughby TR, Kupelian PA, et al. Influence of intrafraction motion on margins for prostate radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 65(2):548–553.

23. Nederveen AJ, van der Heide UA, Dehnad H, van Moorselaar RJ, Hofman P, Lagendijk JJ. Measurements and clinical consequences of prostate motion during a radiotherapy fraction. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 53(1):206–214.

24. Huang E, Dong L, Chandra A, Kuban DA, Rosen II, Evans A, et al. Intrafraction prostate motion during IMRT for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 53(2):261–268.

25. Mah D, Freedman G, Milestone B, Hanlon A, Palacio E, Richardson T, et al. Measurement of intrafractional prostate motion using magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 54(2):568–575.

26. Jeong BK, Jeong H, Ha IB, Choi HS, Kam SC, Hwa JS, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for low- to intermediate-risk prostate adenocarcinoma. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30(6):710–715.

27. Murphy MJ, Cox RS. The accuracy of dose localization for an image-guided frameless radiosurgery system. Med Phys. 1996; 23(12):2043–2049.

28. Chang SD, Main W, Martin DP, Gibbs IC, Heilbrun MP. An analysis of the accuracy of the CyberKnife: a robotic frameless stereotactic radiosurgical system. Neurosurgery. 2003; 52(1):140–146.

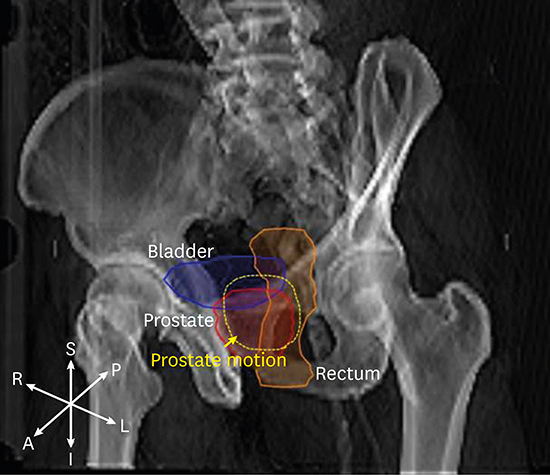
 , with δx representing a magnitude of prostate motion along x axis.
, with δx representing a magnitude of prostate motion along x axis.







 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download