Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related ophthalmic disease associated with adult xanthogranulomatous disease.
Case summary
A 38-year-old male with a history of cholecystectomy visited our clinic for bilateral periorbital swelling. Histopathology of the orbital biopsy showed diffuse infiltration of foamy histiocytes with Touton giant cells and lymphoid follicles, with a diagnosis of adult-onset xanthogranuloma. After excisional biopsy, he was treated with azathioprine and prednisolone. Four years after treatment, he again visited the clinic due to bilateral, yellowish eyelid masses. Serological examinations were all nonspecific findings, except for elevation of IgG and IgG4 levels. Magnetic resonance imaging showed bilateral symmetric soft tissue enlargement with slightly heterogeneous T1/T2 isosignal intensity, with contrast enhancement at the superolateral aspect of extraconal spaces. Excisional biopsy and blepharoplasty were performed. Immunohistochemical sections showed that the IgG4+/IgG plasma cell ratio was 10–20% and the IgG4 plasma cell count was 22/high power field (HPF). His past sections of 2013 from the pathology department were again stained and showed that the IgG4+/IgG plasma cell ratio was 40–50% and the IgG4 plasma cell count was 59/HPF. Thus, he was definitely diagnosed with IgG4-related ophthalmic disease.
Figures and Tables
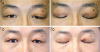 | Figure 1Clinical photographs of the patient's eyelid with the diagnosis of adult xanthogranulomatous disease. The patient visited clinic with bilateral eyelid swelling and yellowish mass (A, B). Four years later, he was re-visited with the same symptoms (C, D). |
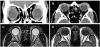 | Figure 2Orbital computed tomography on the first visit demonstrated bilateral soft tissue swelling with no bone invasions (A, B). Coronal image (A), Axial image (B), magnetic resonance imaging on 4 years later demonstrated bilateral soft tissue swelling with no bone invasions (C, D). T2 axial image show diffuse swelling with heterogenous signal intensities at bilateral lacrimal glands (C). T1 axial image show heterogenous soft tissue swelling at bilateral eyelids and preseptal areas (D). |
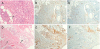 | Figure 3Histologic findings of orbital mass on the first excisional biopsy. (A) Variable germinal centers and nodular lymphoid infiltrates in the lacrimal gland and the touton giant cells (arrow) and many foamy histiocytes in the subcutaneous layer (Hematoxylin and eosin [H&E] stain, ×200). (B, C) Immunohistochemical stain of orbital mass 4 years later, immunoglobulin G4 [IgG4]+/IgG+ plasma cell ratio of 40–50% and 59 IgG4+ plasma cells per high power field (HPF). IgG plasma cells (×100) (B), IgG4 plasma cells (×100) (C). Histologic findings of orbital mass on relapse (D). Diffuse infiltration of foamy histiocytes (arrow) and a few lymphoplasma cells (dash arrow) (H&E stain, ×100). (E, F) Immunohistochemical stain of orbital mass on relapse, IgG4+/IgG+plasma cell ratio of 10–20%and 22 IgG4+ plasma cells per HPF. IgG plasma cells (×100) (E), IgG4 plasma cells (×100) (F). |
References
2. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:21–30.
3. Goto H, Takahira M, Azumi A. Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2015; 59:1–7.

4. Guo J, Wang J. Adult orbital xanthogranulomatous disease: review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009; 133:1994–1997.

5. Burris CK, Rodriguez ME, Raven ML, et al. Adult-onset asthma and periocular xanthogranulomas associated with systemic IgG4-related disease. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2016; 1:34–37.

6. Honda Y, Nakamizo S, Dainichi T, et al. Adult-onset asthma and periocular xanthogranuloma associated with IgG4-related disease with infiltration of regulatory T cells. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017; 31:e124–e125.

7. Vick VL, Wilson MW, Fleming JC, Haik BG. Orbital and eyelid manifestations of xanthogranulomatous diseases. Orbit. 2006; 25:221–225.

8. Sivak-Callcott JA, Rootman J, Rasmussen SL, et al. Adult xanthogranulomatous disease of the orbit and ocular adnexa: new immunohistochemical findings and clinical review. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006; 90:602–608.

9. Singh K, Rajan KD, Eberhart C. Orbital necrobiotic xanthogranuloma associated with systemic IgG4 disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2010; 18:373–378.

10. McKelvie P, McNab AA, Hardy T, Rathi V. Comparative study of clinical, pathological, radiological, and genetic features of patients with adult ocular adnexal xanthogranulomatous disease, Erdheim-Chester Disease, and IgG4-related disease of the orbit/ocular adnexa. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017; 33:112–119.

11. Mudhar HS, Bhatt R, Sandramouli S. Xanthogranulomatous variant of immunoglobulin G4 sclerosing disease presenting as ptosis, proptosis and eyelid skin plaques. Int Ophthalmol. 2011; 31:245–248.

12. Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Ophthalmic manifestations of IgG4-related disease: single-center experience and literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014; 43:806–817.

13. Kubota T, Katayama M, Moritani S, Yoshino T. Serologic factors in early relapse of IgG4-related orbital inflammation after steroid treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 155:373–379.e1.

14. Chung SR, Lee TE, You IC, et al. A typical case of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease satisfying diagnostic criteria. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017; 58:852–856.

15. Japanese study group of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. A prevalence study of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease in Japan. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2013; 57:573–579.
16. Kim K, Lee MJ, Kim NJ, et al. Three cases of hyper-IgG4 syndrome involving ocular adnexa. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:1133–1138.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download