Abstract
Purpose
We report the causes and prognosis of anterior interosseous nerve syndrome (AIN) according to the treatment.
Methods
From March 2009 to December 2015, the 20 patients with the clinical symptom of AIN syndrome were enrolled in the study and electromyography (EMG) of AIN was performed. We retrospectively reviewed hand function test, active range of motion, the disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) score and EMG during the recovery from disease. We further surveyed the time of recovery and residual symptoms.
Results
The patients with unknown cause of the disease (12 cases), heavy work or trauma (6 cases) and infection (2 cases) were investigated in the study. Thirteen out of 15 cases with conservative treatment and 2 out of 5 cases with a surgical treatment at an average of 8 months from disease were recovered. In addition, 8 cases with fine motor disturbance and 3 cases with tingling residual symptom were observed.
Conclusion
Due to the low possibility of entrapment neuropathy, conservative treatment for 7 months is the first choice rather than surgical treatment. If there is no improvement from the conservative treatment, surgical exploration of AIN is the indication of treatment. After recovery, patients may have the symptoms of fine motor disturbance and tingling.
Figures and Tables
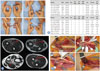 | Fig. 1In 12th case, a 53-year-old man hurt by conveyer belt could not flex interphalangeal joint of thumb and distal interphalangeal joint of index finger in right hand. (A) When he visited the out-patient clinic, he didn't make an ‘O’ sign in the right hand. The power of interphalangeal joint of thumb and distal interphalangeal joint of index finger was decreased. (B) His electromyography test showed weakness of flexor pollicis longus of thumb, flexor digitorum profundus of index finger and pronator quadratus. (C) Magnetic resonance axial images showed high signal intensity of edema in flexor pollicis longus of thumb, flexor digitorum profundus of index finger and pronator quadratus. AIN was also swollen. (D) He took an operation at 3 months. During operation, the finding was swelled anterior interosseous nerve. After operation, he recovered at 9 months. Ins Act., insertional activities; Fibs., fibrillation; Pos. Wave, positive wave; Low Amp., low amplitude; High Amp., high amplitude; Dur, duration; Int. Patt., interference pattern; Flex. Carpi Radialis, flexor carpi radialis; Flex. Carpi Ulnaris, flexor carpi ulnaris; Flex. Digitorum Pro, flexor digitorum profundus; Flex. Pollicis Longus, flexor pollicis longus; Abduc. Digiti Minimi, abductor digiti minimi; Abduc. Pol. Brevis, abductor pollicis brevis; FPL, flexor pollicis longus of thumb; 2nd FDP, flexor digitorum profundus of index finger of index finger; PQ, pronator quadratus; AIN, anterior interosseous nerve syndrome. |
 | Fig. 2In 4th case, a 26-year-old man could not flex interphalangeal joint of thumb and distal interphalangeal joint of index finger in left hand after lifting heavy object. (A) When he visited the out-patient clinic, he didn't make an ‘O’ with the thumb and index finger in the left hand. (B) He started to recovery at 4 months from symptom. After 14 months, when he visited, he could flex the recovered power of thumb interphalangeal joint and index distal interphalangeal joint flexion. |
References
1. Tinel J. Nerve wounds: symptomatology of peripheral nerve lesions caused by war wounds. New York: William Wood;1918. p. 183–185.
2. Parsonage MJ, Turner JW. Neuralgic amyotrophy; the shoulder-girdle syndrome. Lancet. 1948; 1:973–978.

3. Kiloh LG, Nevin S. Isolated neuritis of the anterior interosseous nerve. Br Med J. 1952; 1:850–851.

4. Lipscomb PR. Vascular and neural complications in supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1955; 37:487–492.

5. Fearn CB, Goodfellow JW. Anterior interosseous nerve palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965; 47:91–93.

7. Nigst H, Dick W. Syndromes of compression of the median nerve in the proximal forearm (pronator teres syndrome; anterior interosseous nerve syndrome). Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1979; 93:307–312.

8. Werner CO. The anterior interosseous nerve syndrome. Int Orthop. 1989; 13:193–197.
9. Sood MK, Burke FD. Anterior interosseous nerve palsy: a review of 16 cases. J Hand Surg Br. 1997; 22:64–68.
10. Dunne JW, Prentice DA, Stewart-Wynne EG. Bilateral anterior interosseous nerve syndromes associated with cytomegalovirus infection. Muscle Nerve. 1987; 10:446–448.

11. Wong L, Dellon AL. Brachial neuritis presenting as anterior interosseous nerve compression: implications for diagnosis and treatment: a case report. J Hand Surg Am. 1997; 22:536–539.
12. Miller-Breslow A, Terrono A, Millender LH. Nonoperative treatment of anterior interosseous nerve paralysis. J Hand Surg Am. 1990; 15:493–496.

13. Seror P. Anterior interosseous nerve lesions: clinical and electrophysiological features. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:238–241.
14. Spinner M. Injuries to the major branches of peripheral nerves of the forearm. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders;1978. p. 162–192.
16. Futami T, Kobayashi A, Itoman M, Shilmajiri I, Fujita T. Clinical investigation on the anterior interossous nerve syndrome. J Jpn Soc Surg Hand. 1993; 10:338–341.
17. Park MJ, Lee JY, Kim BJ. Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome: observations for three surgical cases. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 1998; 3:301–308.
18. Kim HM, Jeong C, Lee SU, Roh YT, Park IJ. The anterior interosseous nerve syndrome: clinical investigation of surgically treated 7 cases. J Korean Soc Microsurg. 2009; 18:67–74.
19. Haussmann P. Intratruncal fascicular compression of the anterior interosseous nerve. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 1982; 14:183–185.
20. Pan Y, Wang S, Zheng D, et al. Hourglass-like constrictions of peripheral nerve in the upper extremity: a clinical review and pathological study. Neurosurgery. 2014; 75:10–22.
21. Aranyi Z, Csillik A, Devay K, et al. Ultrasonographic identification of nerve pathology in neuralgic amyotrophy: enlargement, constriction, fascicular entwinement, and torsion. Muscle Nerve. 2015; 52:503–511.

22. Hill NA, Howard FM, Huffer BR. The incomplete anterior interosseous nerve syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:4–16.

23. Vichare NA. Spontaneous paralysis of the anterior interosseous nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1968; 50:806–808.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download