Abstract
The natural course of lateral epicondylitis is widely regarded to be self-limiting within 1 year of symptom duration in 90% of all patients. The spectrum of treatments include simple ‘wait and see’, bracing, physical therapy, corticosteroid injection, and recently some biologic injection such as autologous blood and platelet rich plasma. However, recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis which are not responding to conservative treatments can be treated with surgical treatment although much remains unclear regarding the ideal treatment. Debates surrounding open procedures are the management for the defect after resection of pathologic tissue, necessity of decortication, selective denervation procedure, etc. Since the trend is changing to minimal invasive surgery and ar-throscopic release of extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon are becoming more popular these days, surgical tips and pitfall to obtain good results and avoid complications have been reported recently. Bipolar radiofrequency (RF)-based microtenotomy or percutaneous tendon release is another surgical procedures reported to be effective in lateral epicondylitis. However, there are some patients who present with persistent pain after surgical treatment. Thus, selection of ideal candidates for surgery, thorough evaluation of all pathologies prior to surgery, and adequate surgical procedures would be essential in the surgical treatment of lateral epicondylitis.
Go to : 
References
1. Walker-Bone K, Palmer KT, Reading I, Coggon D, Cooper C. Prevalence and impact of musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb in the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 51:642–51.

2. Solheim E, Hegna J, Oyen J. Extensor tendon release in tennis elbow: results and prognostic factors in 80 elbows. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:1023–7.

3. Ahmad Z, Siddiqui N, Malik SS, Abdus-Samee M, Tyther-leigh-Strong G, Rushton N. Lateral epicondylitis: a review of pathology and management. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95:1158–64.
4. Karkhanis S, Frost A, Maffulli N. Operative management of tennis elbow: a quantitative review. Br Med Bull. 2008; 88:171–88.

5. Goldie I. Epicondylitis lateralis humeri (epicondylalgia or tennis elbow): a pathogenetical study. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1964; 57(Suppl 339):1+.
6. Riek S, Chapman AE, Milner T. A simulation of muscle force and internal kinematics of extensor carpi radialis brevis during backhand tennis stroke: implications for injury. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1999; 14:477–83.

7. Matache BA, Berdusco R, Momoli F, Lapner PL, Pollock JW. A randomized double-blind sham-controlled trial on the efficacy of arthroscopic tennis elbow release for the management of chronic lateral epicondylitis. BMC Mus-culoskelet Disord. 2016; 17:239.

8. Bowen RE, Dorey FJ, Shapiro MS. Efficacy of nonoperative treatment for lateral epicondylitis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2001; 30:642–6.
9. Boyer MI, Hastings H 2nd. Lateral tennis elbow: “Is there any science out there?”. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999; 8:481–91.

10. Greenbaum B, Itamura J, Vangsness CT, Tibone J, Atkinson R. Extensor carpi radialis brevis: an anatomical analysis of its origin. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81:926–9.
11. Doyle JR, Botte MJ. Surgical anatomy of the hand and upper extremity. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;. 2003.
12. Cohen MS, Romeo AA, Hennigan SP, Gordon M. Lateral epicondylitis: anatomic relationships of the extensor tendon origins and implications for arthroscopic treatment. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008; 17:954–60.

13. Diliberti T, Botte MJ, Abrams RA. Anatomical considerations regarding the posterior interosseous nerve during posterolateral approaches to the proximal part of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82:809–13.

14. Field LD, Altchek DW, Warren RF, O’Brien SJ, Skyhar MJ, Wickiewicz TL. Arthroscopic anatomy of the lateral elbow: a comparison of three portals. Arthroscopy. 1994; 10:602–7.

15. Omid R, Hamid N, Keener JD, Galatz LM, Yamaguchi K. Relation of the radial nerve to the anterior capsule of the elbow: anatomy with correlation to arthroscopy. Arthros-copy. 2012; 28:1800–4.

17. Bot SD, van der Waal JM, Terwee CB, van der Windt DA, Bouter LM, Dekker J. Course and prognosis of elbow complaints: a cohort study in general practice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:1331–6.
18. Nilsson P, Baigi A, Sward L, Moller M, Mansson J. Lateral epicondylalgia: a structured programme better than corticosteroids and NSAID. Scand J Occup Ther. 2012; 19:404–10.

19. Kraushaar BS, Nirschl RP. Tendinosis of the elbow (tennis elbow): clinical features and findings of histological, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopy studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:259–78.
21. Nirschl RP. Tennis elbow tendinosis: pathoanatomy, nonsurgical and surgical management. Gordon SL, Blair SJ, Fine LJ, editors. Repetitive motion disorders of the upper extremity. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons;1995; 467–79.
22. Schneeberger AG, Masquelet AC. Arterial vascularization of the proximal extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; (398):239–44.

23. Bales CP, Placzek JD, Malone KJ, Vaupel Z, Arnoczky SP. Microvascular supply of the lateral epicondyle and common extensor origin. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007; 16:497–501.

24. Calfee RP, Patel A, DaSilva MF, Akelman E. Management of lateral epicondylitis: current concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008; 16:19–29.

25. Gardner RC. Tennis elbow: diagnosis, pathology and treatment: nine severe cases treated by a new reconstructive operation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970; 72:248–53.
26. Cerezal L, Rodriguez-Sammartino M, Canga A, et al. Elbow synovial fold syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:W88–96.

27. Levin D, Nazarian LN, Miller TT, et al. Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow: US findings. Radiology. 2005; 237:230–4.

28. Savnik A, Jensen B, Norregaard J, Egund N, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Bliddal H. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of treatment response of lateral epicondylitis of the elbow. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:964–9.

29. van Leeuwen WF, Janssen SJ, Ring D, Chen N. Incidental magnetic resonance imaging signal changes in the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin are more common with age. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016; 25:1175–81.

30. Dzugan SS, Savoie FH 3rd, Field LD, O’Brien MJ, You Z. Acute radial ulno-humeral ligament injury in patients with chronic lateral epicondylitis: an observational report. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012; 21:1651–5.

31. Chanlalit C, Limsricharoen W. Posterolateral rotatory instability from multiple steroids injections for tennis elbow: a case report. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013; 96(Suppl 1):S104–7.
32. Kalainov DM, Cohen MS. Posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow in association with lateral epicondylitis: a report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:1120–5.
33. Sims SE, Miller K, Elfar JC, Hammert WC. Non-surgical treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Hand (N Y). 2014; 9:419–46.
34. Drake ML, Ring DC. Enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin: effective communication strategies. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016; 24:365–9.
36. Bisset L, Paungmali A, Vicenzino B, Beller E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials on physical interventions for lateral epicondylalgia. Br J Sports Med. 2005; 39:411–22.
37. Labelle H, Guibert R. Efficacy of diclofenac in lateral epicondylitis of the elbow also treated with immobilization: the University of Montreal Orthopaedic Research Group. Arch Fam Med. 1997; 6:257–62.

38. Kjaer M, Langberg H, Skovgaard D, et al. In vivo studies of peritendinous tissue in exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2000; 10:326–31.

39. Mason BS, van der Woude LH, Goosey-Tolfrey VL. The ergonomics of wheelchair configuration for optimal performance in the wheelchair court sports. Sports Med. 2013; 43:23–38.

40. Bandy WD, Irion JM, Briggler M. The effect of time and frequency of static stretching on flexibility of the hamstring muscles. Phys Ther. 1997; 77:1090–6.

41. Fyfe I, Stanish WD. The use of eccentric training and stretching in the treatment and prevention of tendon injuries. Clin Sports Med. 1992; 11:601–24.

43. Cullinane FL, Boocock MG, Trevelyan FC. Is eccentric exercise an effective treatment for lateral epicondylitis? A systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2014; 28:3–19.

44. Han SH, An HJ, Song JY, et al. Effects of corticosteroid on the expressions of neuropeptide and cytokine mRNA and on tenocyte viability in lateral epicondylitis. J Inflamm (Lond). 2012; 9:40.

45. Ljung BO, Alfredson H, Forsgren S. Neurokinin 1-receptors and sensory neuropeptides in tendon insertions at the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus: studies on tennis elbow and medial epicondylalgia. J Orthop Res. 2004; 22:321–7.

46. Krogh TP, Bartels EM, Ellingsen T, et al. Comparative effectiveness of injection therapies in lateral epicondylitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:1435–46.
47. Krogh TP, Fredberg U, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Christensen R, Jensen P, Ellingsen T. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with platelet-rich plasma, glucocorticoid, or saline: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:625–35.
48. Peerbooms JC, Sluimer J, Bruijn DJ, Gosens T. Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondylitis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial: platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection with a 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2010; 38:255–62.
49. Smidt N, van der Windt DA, Assendelft WJ, Deville WL, Korthals-de Bos IB, Bouter LM. Corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, or a wait-and-see policy for lateral epicondylitis: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:657–62.

50. Kachooei AR, Talaei-Khoei M, Faghfouri A, Ring D. Factors associated with operative treatment of enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016; 25:666–70.

51. Tosti R, Jennings J, Sewards JM. Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow. Am J Med. 2013; 126:357.e1–6.

52. Tan XX, Ju HY, Yan W, et al. Autologous platelet lysate local injections for the treatment of refractory lateral epicondylitis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016; 11:17.

53. Ahmad Z, Brooks R, Kang SN, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on clinical outcomes in lateral epicondylitis. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:1851–62.
54. Sirico F, Ricca F, DI Meglio F, et al. Local corticosteroid versus autologous blood injections in lateral epicondylitis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2016; Sep1 [Epub].

55. Rompe JD, Hope C, Kullmer K, Heine J, Burger R. Analgesic effect of extracorporeal shock-wave therapy on chronic tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:233–7.

56. Speed CA, Nichols D, Richards C. . Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for lateral epicondylitis: a double blind randomised controlled trial. J Orthop Res. 2002; 20:895–8.
57. Haake M, Konig IR, Decker T, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a randomized multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84:1982–91.
58. Buchbinder R, Green SE, Youd JM, Assendelft WJ, Barnsley L, Smidt N. Shock wave therapy for lateral elbow pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; (4):CD003524.

59. Park JW, Hwang JH, Choi YS, Kim SJ. Correction: comparison of therapeutic effect of extracorporeal shock wave in calcific versus noncalcific lateral epicondylopathy. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016; 40:294–300.

60. Yoon JP, Chung SW, Yi JH, et al. Prognostic factors of arthroscopic extensor carpi radialis brevis release for lateral epicondylitis. Arthroscopy. 2015; 31:1232–7.

61. Knutsen EJ, Calfee RP, Chen RE, Goldfarb CA, Park KW, Osei DA. Factors associated with failure of nonoperative treatment in lateral epicondylitis. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43:2133–7.

62. Nirschl RP, Pettrone FA. Tennis elbow: the surgical treatment of lateral epicondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61:832–9.

63. Carroll RE, Jorgensen EC. Evaluation of the Garden procedure for lateral epicondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1968; 60:201–4.

64. Boyd HB. McLeod AC Jr. Tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973; 55:1183–7.
65. Khashaba A. Nirschl tennis elbow release with or without drilling. Br J Sports Med. 2001; 35:200–1.

66. Almquist EE, Necking L, Bach AW. Epicondylar resection with anconeus muscle transfer for chronic lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Am. 1998; 23:723–31.

67. Ruch DS, Orr SB, Richard MJ, Leversedge FJ, Mithani SK, Laino DK. A comparison of debridement with and without anconeus muscle flap for treatment of refractory lateral epicondylitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015; 24:236–41.
68. Thornton SJ, Rogers JR, Prickett WD, Dunn WR, Allen AA, Hannafin JA. Treatment of recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis with suture anchor repair. Am J Sports Med. 2005; 33:1558–64.

69. Rose NE, Forman SK, Dellon AL. Denervation of the lateral humeral epicondyle for treatment of chronic lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Am. 2013; 38:344–9.

70. Milcan A, Ozge A, Sahin G, Saracoglu M, Kuyurtar F. The role of electrophysiologic tests in the early diagnosis of posterior interosseous neuropathy in patients thought to have lateral epicondylitis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2004; 38:326–9.
71. Leppilahti J, Raatikainen T, Pienimaki T, Hanninen A, Jalovaara P. Surgical treatment of resistant tennis elbow: a prospective, randomised study comparing decompression of the posterior interosseous nerve and lengthening of the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001; 121:329–32.
72. Morrey BF. Reoperation for failed surgical treatment of refractory lateral epicondylitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1992; 1:47–55.

73. Jimenez I, Marcos-Garcia A, Muratore-Moreno G, Medina J. Four surgical tips in the treatment of epicondylitis. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2016; 60:38–43.
74. Solheim E, Hegna J, Oyen J. Arthroscopic versus open tennis elbow release: 3- to 6-year results of a case-control series of 305 elbows. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:854–9.

75. Kwon BC, Kim JY, Park KT. The Nirschl procedure versus arthroscopic extensor carpi radialis brevis debridement for lateral epicondylitis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017; 26:118–24.
76. Budoff JE, Hicks JM, Ayala G, Kraushaar BS. The reliability of the “Scratch test”. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2008; 33:166–9.
77. Solheim E, Hegna J, Oyen J, Inderhaug E. Arthroscopic treatment of lateral epicondylitis: tenotomy versus debridement. Arthroscopy. 2016; 32:578–85.

78. Pomerantz ML. Complications of lateral epicondylar release. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016; 47:445–69.

79. Cummins CA. Lateral epicondylitis: in vivo assessment of arthroscopic debridement and correlation with patient outcomes. Am J Sports Med. 2006; 34:1486–91.
80. Chu V, Kuang J, McGinn A, Giaid A, Korkola S, Chiu RC. Angiogenic response induced by mechanical transmyocardial revascularization. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999; 118:849–56.

81. Tasto JP, Cummings J, Medlock V, Hardesty R, Amiel D. Microtenotomy using a radiofrequency probe to treat lateral epicondylitis. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:851–60.

82. Tasto JP, Richmond JM, Cummings JR, Hardesty R, Amiel D. Radiofrequency microtenotomy for elbow epicondylitis: midterm results. Am J Orthop. 2016; 45:29–33.
83. Meknas K, Odden-Miland A, Mercer JB, Castillejo M, Johansen O. Radiofrequency microtenotomy: a promising method for treatment of recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36:1960–5.
84. Takahashi N, Tasto J, Locke J, et al. The use of radiofrequency (RF) for the treatment of chronic tendinosis. Proceedings of 6th Biennial Congress of the International Society of Arthroscopy, Knee Surgery, and Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Congress. 2007 May 2731; Florence, Italy. Abstract 1433.
85. Harwood F, Bowden K, Amiel M, Tasto J, Amiel D. Structural and angiogenic response to bipolar radiofrequency treatment of normal rabbit Achilles tendon: a potential application to the treatment of tendinosis. Trans Orthop Res Soc. 2003; 28:819.
86. Panthi S, Khatri K, Kharel K, et al. Outcome of percutaneous release of tennis elbow: a non-randomized controlled trial study. Cureus. 2017; 9:e952.

87. Dunkow PD, Jatti M, Muddu BN. A comparison of open and percutaneous techniques in the surgical treatment of tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:701–4.

88. MacDermid JC, King GJ. Functional outcome was better after percutaneous surgery than after open formal release for tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:467.
Go to : 
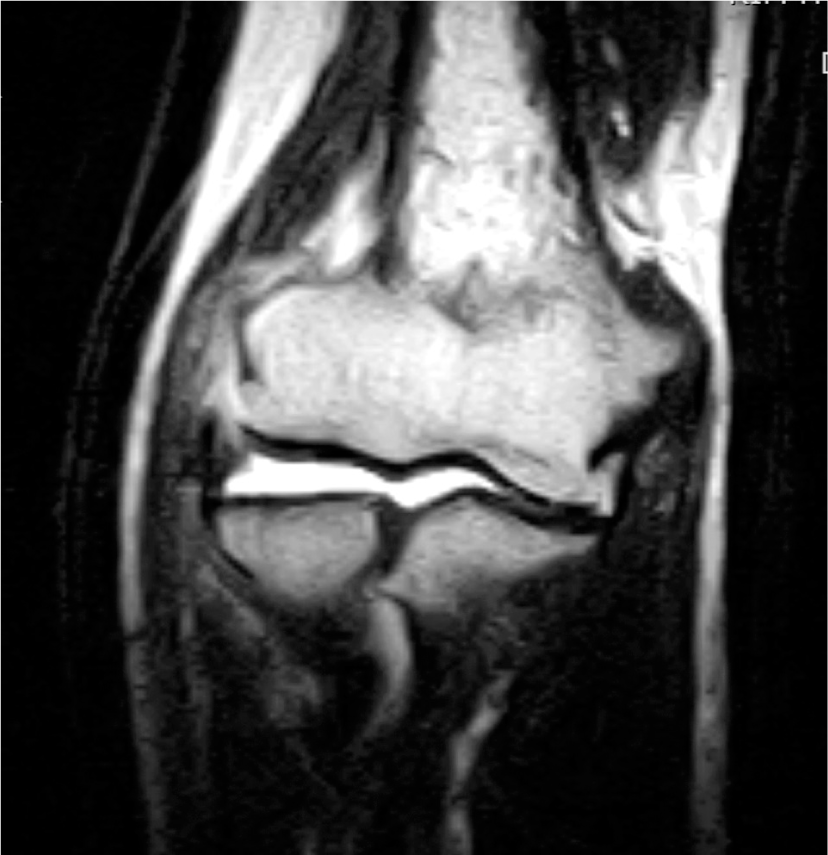 | Fig. 1.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of coronal T2 weighted image showed accompanying lateral ulnar collateral ligament complex insufficiency in a patient with lateral epicondylitis. |
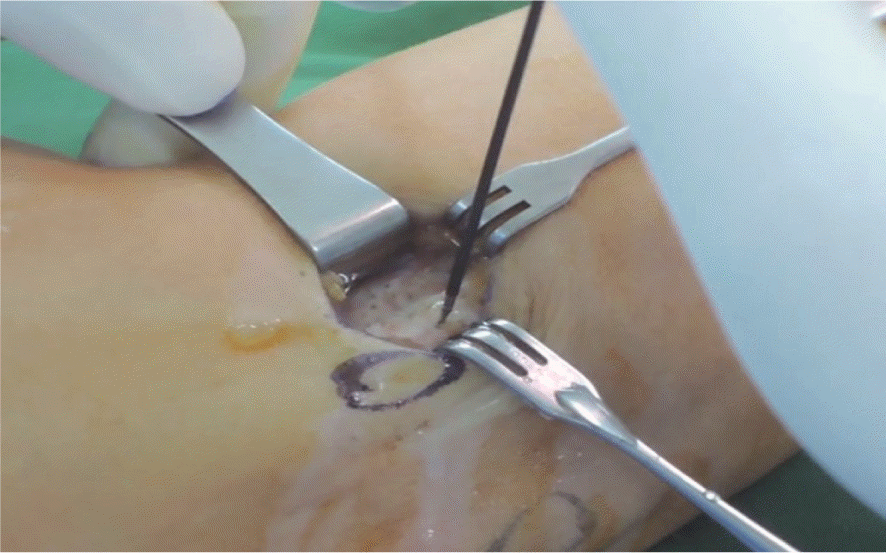
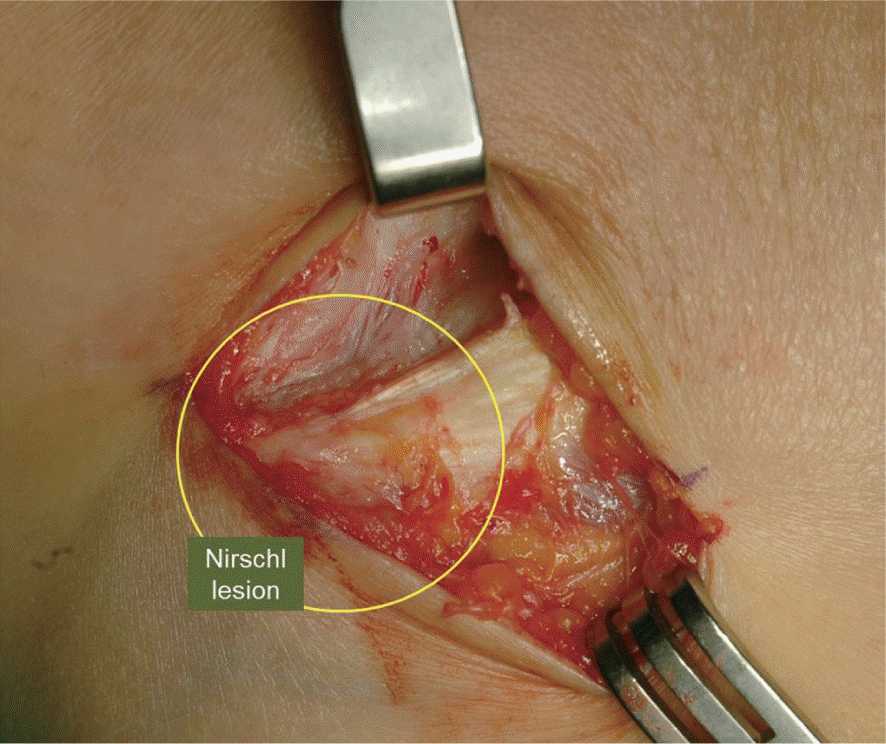 | Fig. 2.Nirschl lesion observed during the open procedure. The lesion is involving extensor carpi radialis brevis and some portion of common extensor tendon and distinguished from the relatively healthy-looking distal tendinous portion. |
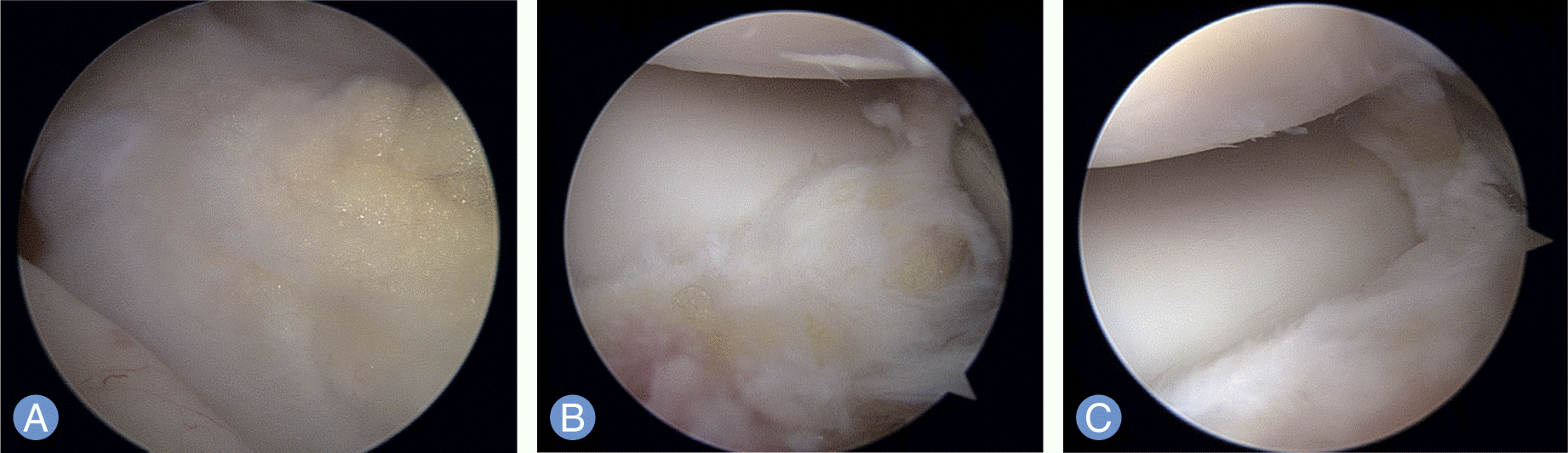 | Fig. 3.Arthroscopic finding of posterior synovial plica during the surgery for lateral epicondylitis. (A) Synovial plica covering radial head prior to removal, (B) partially debrided synovial plica tissue, and (C) completion after removal of impinged synovial plica tissue between the radial head and capitellum. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download