Abstract
Distal radioulnar dislocation is commonly associated with radius fracture. Most common dislocation pattern is the dorsal dislocation. We present the unique case of volar dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint blocked by displaced dorsal Barton fracture of distal radius and discuss the injury mechanism and anatomic lesions.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Mikic ZD. Galeazzi fracture-dislocations. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975; 57:1jkssh-21-22571–8jkssh-21-225.

2. Macule Beneyto F, Arandes Renu JM, Ferreres Claramunt A, Ramon Soler R. Treatment of Galeazzi fracture-dislocations. J Trauma. 1994; 36:352–5.
3. Itoh Y, Horiuchi Y, Takahashi M, Uchinishi K, Yabe Y. Extensor tendon involvement in Smith's and Galeazzi's fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1987; 12:535–4jkssh-21-225.

4. Magill P, Harrington P. Complex volar dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint in a Galleazi variant associated with interposition of the ulnar neurovascular bundle. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2jkssh-21-225jkssh-21-2259; 19:265–7.

5. Werthel JD, Masmejean E, Silvera J, Boyer P, Schlur C. Acute isolated volar dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint: case report and literature review. Chir Main. 2jkssh-21-22514; 33:364–9.

6. Rose-Innes AP. Anterior dislocation of the ulna at the inferior radio-ulnar joint: case report, with a discussion of the anatomy of rotation of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 196jkssh-21-225; 42:515–21.
Go to : 
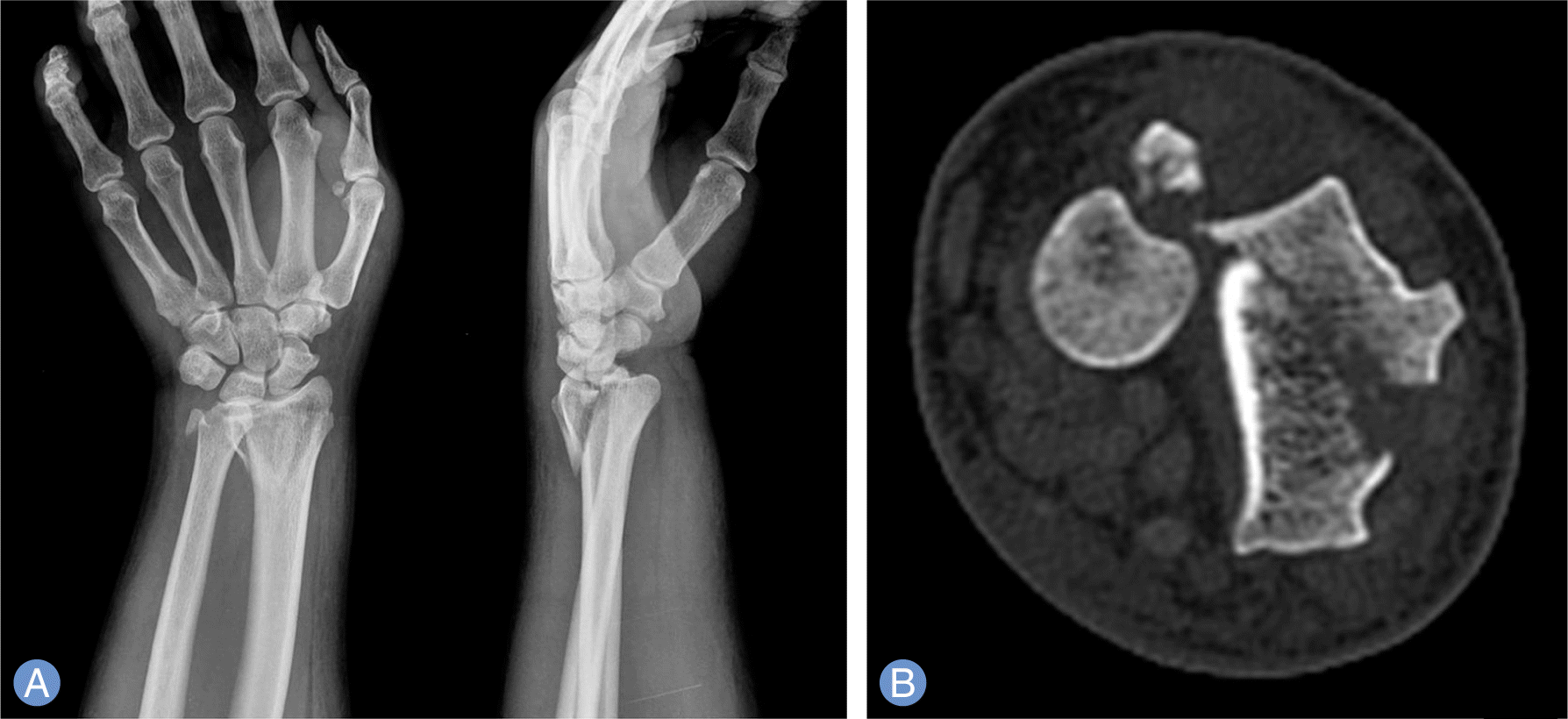 | Fig. 1.Preoperative plain radiographs of left wrist. (A) Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs show displaced dorsal Barton and ulnar styloid process fracture with volar dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). (B) Computed tomography axial view shows that the size of the displaced bone fragment have involved an area ≥1/2 of the sigmoid notch and the fragment is trans-positioned ulnarly to the DRUJ. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download