Abstract
Wrist arthroscopy has been used as an important adjunct procedure to distal radius fracture management. This procedure allows minimal surgical intervention and provides excellent visualization of the joint for anatomical restoration of articular fracture of the distal radius and early management of associated injuries. To many, it is still technically challenging to adequately perform arthroscopy in the distal radius fractures. With this review, we aimed to provide an updated arthroscopic technique in the management of distal radius fractures and potential pitfalls of this technique.
Go to : 
References
1. Chen AC, Chan YS, Yuan LJ, Ye WL, Lee MS, Chao EK. Arthroscopically assisted osteosynthesis of complex intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. J Trauma. 2002; 53:354–9.

2. Cooney WP, Berger RA. Treatment of complex fractures of the distal radius: combined use of internal and external fixation and arthroscopic reduction. Hand Clin. 1993; 9:603–12.
3. Baratz ME, Des Jardins J, Anderson DD, Imbriglia JE. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: the effect of fracture displacement on contact stresses in a cadaver model. J Hand Surg Am. 1996; 21:183–8.
4. Knirk JL, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:647–59.

5. Bradway JK, Amadio PC, Cooney WP. Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced, comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:839–47.

6. Trumble TE, Schmitt SR, Vedder NB. Factors affecting functional outcome of displaced intra-articular distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1994; 19:325–40.

7. Mehta JA, Bain GI, Heptinstall RJ. Anatomical reduction of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. An arthroscopically-assisted approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000; 82:79–86.
8. Auge WK 2nd, Velazquez PA. The application of indirect reduction techniques in the distal radius: the role of adjuvant arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2000; 16:830–5.
9. Ruch DS, Vallee J, Poehling GG, Smith BP, Kuzma GR. Arthroscopic reduction versus fluoroscopic reduction in the management of intra-articular distal radius fractures. Arthroscopy. 2004; 20:225–30.

10. Lutsky K, Boyer MI, Steffen JA, Goldfarb CA. Arthroscopic assessment of intra-articular distal radius fractures after open reduction and internal fixation from a volar approach. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33:476–84.

11. Varitimidis SE, Basdekis GK, Dailiana ZH, Hantes ME, Bargiotas K, Malizos K. Treatment of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: fluoroscopic or arthro-scopic reduction? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:778–85.
12. Geissler WB, Freeland AE. Arthroscopically assisted reduction of intraarticular distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (327):125–34.

13. Whipple TL. The role of arthroscopy in the treatment of intra-articular wrist fractures. Hand Clin. 1995; 11:13–8.

14. Wiesler ER, Chloros GD, Mahirogullari M, Kuzma GR. Arthroscopic management of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:1516–26.

15. Geissler WB, Freeland AE. Arthroscopic management of intra-articular distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 1999; 15:455–65.

16. Lindau T, Arner M, Hagberg L. Intraarticular lesions in distal fractures of the radius in young adults. A descriptive arthroscopic study in 50 patients. J Hand Surg Br. 1997; 22:638–43.
17. del Pinal F, Garcia-Bernal FJ, Pisani D, Regalado J, Ayala H, Studer A. Dry arthroscopy of the wrist: surgical technique. J Hand Surg Am. 2007; 32:119–23.
19. Doi K, Hattori Y, Otsuka K, Abe Y, Yamamoto H. Intra-articular fractures of the distal aspect of the radius: arthroscopically assisted reduction compared with open reduction and internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:1093–110.
20. Geissler WB. Intra-articular distal radius fractures: the role of arthroscopy? Hand Clin. 2005; 21:407–16.

21. Park MJ, Yao J. Advances in hand and wrist arthroscopy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014; 134:758e–765e.

22. Abe Y, Tsubone T, Tominaga Y. Plate presetting arthroscopic reduction technique for the distal radius fractures. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2008; 12:136–43.

23. Richards RS, Bennett JD, Roth JH, Milne K Jr. Arthroscopic diagnosis of intra-articular soft tissue injuries associated with distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1997; 22:772–6.

25. Geissler WB, Freeland AE, Savoie FH, McIntyre LW, Whipple TL. Intracarpal soft-tissue lesions associated with an intra-articular fracture of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:357–65.

26. Lindau T, Adlercreutz C, Aspenberg P. Peripheral tears of the triangular fibrocartilage complex cause distal radioulnar joint instability after distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2000; 25:464–8.

27. Ruch DS, Yang CC, Smith BP. Results of acute arthroscopically repaired triangular fibrocartilage complex injuries associated with intra-articular distal radius fractures. Arthroscopy. 2003; 19:511–6.

28. Park MJ. The role of arthroscophy in management of distal radius fractures. J Korean Hand Soc. 2001; 6:101–7.
29. Scheer JH, Adolfsson LE. Patterns of triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) injury associated with severely dorsally displaced extra-articular distal radius fractures. Injury. 2012; 43:926–32.

30. Watson HK, Ballet FL. The SLAC wrist: scapholunate advanced collapse pattern of degenerative arthritis. J Hand Surg Am. 1984; 9:358–65.

31. Forward DP, Lindau TR, Melsom DS. Intercarpal ligament injuries associated with fractures of the distal part of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:2334–40.

32. Weiss AP, Akelman E, Lambiase R. Comparison of the findings of triple-injection cinearthrography of the wrist with those of arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:348–56.

33. Cooney WP. Evaluation of chronic wrist pain by arthrography, arthroscopy, and arthrotomy. J Hand Surg Am. 1993; 18:815–22.

34. Abe Y, Yoshida K, Tominaga Y. Less invasive surgery with wrist arthroscopy for distal radius fracture. J Orthop Sci. 2013; 18:398–404.

35. Herzberg G. Intra-articular fracture of the distal radius: arthroscopic-assisted reduction. J Hand Surg Am. 2010; 35:1517–9.

36. Park MJ, Ahn JH. Arthroscopically assisted reduction and percutaneous fixation of dorsal perilunate dislocations and fracture-dislocations. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:1153.

37. Leung F, Tu YK, Chew WY, Chow SP. Comparison of external and percutaneous pin fixation with plate fixation for intra-articular distal radial fractures: a randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:16–22.
38. Roh YH, Lee BK, Baek JR, Noh JH, Gong HS, Baek GH. Ar and omized comparison of volar plate and external fixation for intra-articular distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2015; 40:34–41.
Go to : 
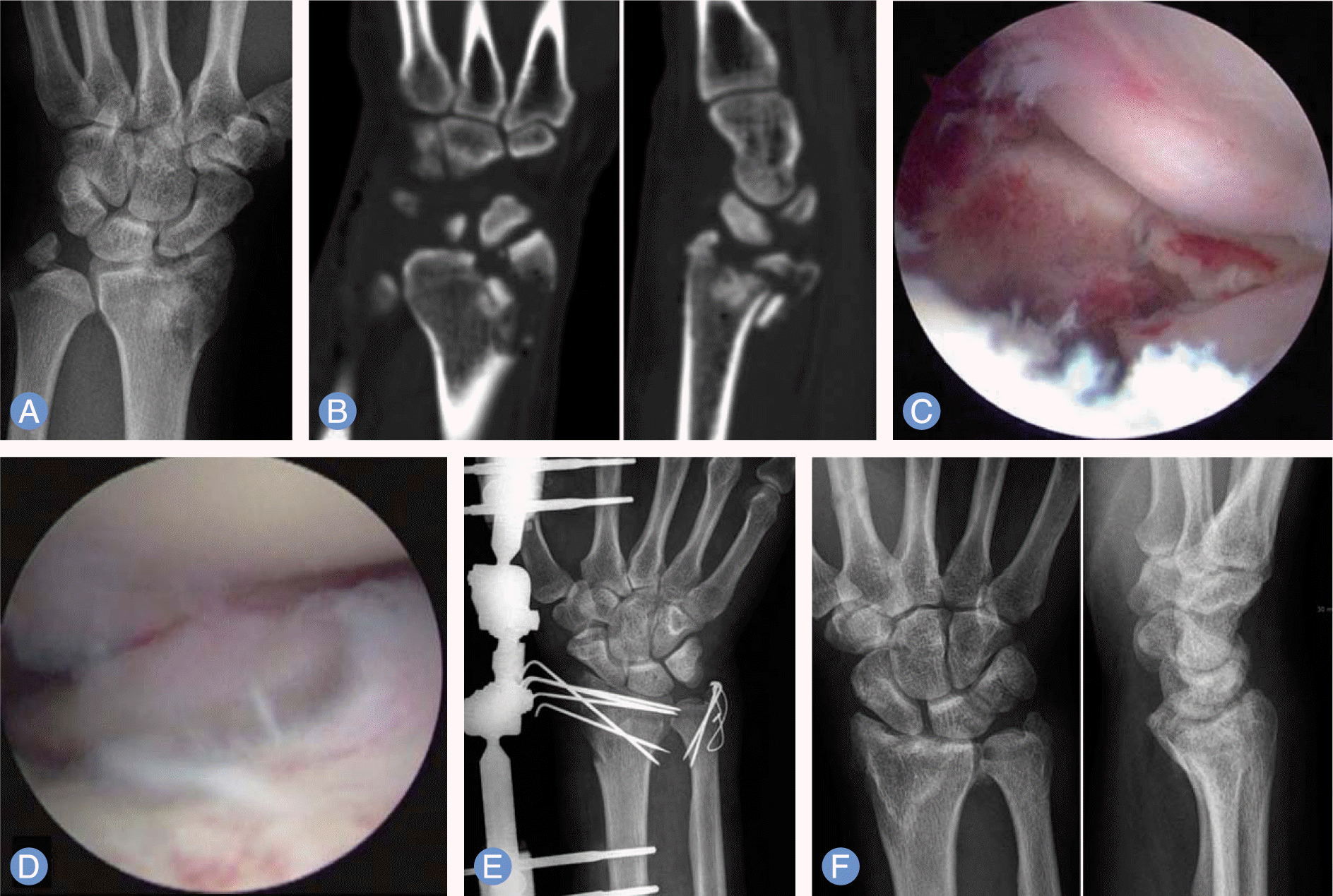 | Fig. 2.
(A-C) Preoperative radiographs and arthroscopic image of 35-year-old male show intraarticular impaction and comminution of right distal radius fracture. (D) Arthroscopic image shows the restoration of the articular surface after reduction and K-wire fixation. (E) Arthroscopically assisted reduction and percutaneous pinning was performed. The ulnar styloid fracture was stabilized with a tension band wiring technique. (F) Postoperative 13-months radiographs show satisfactory healing. |
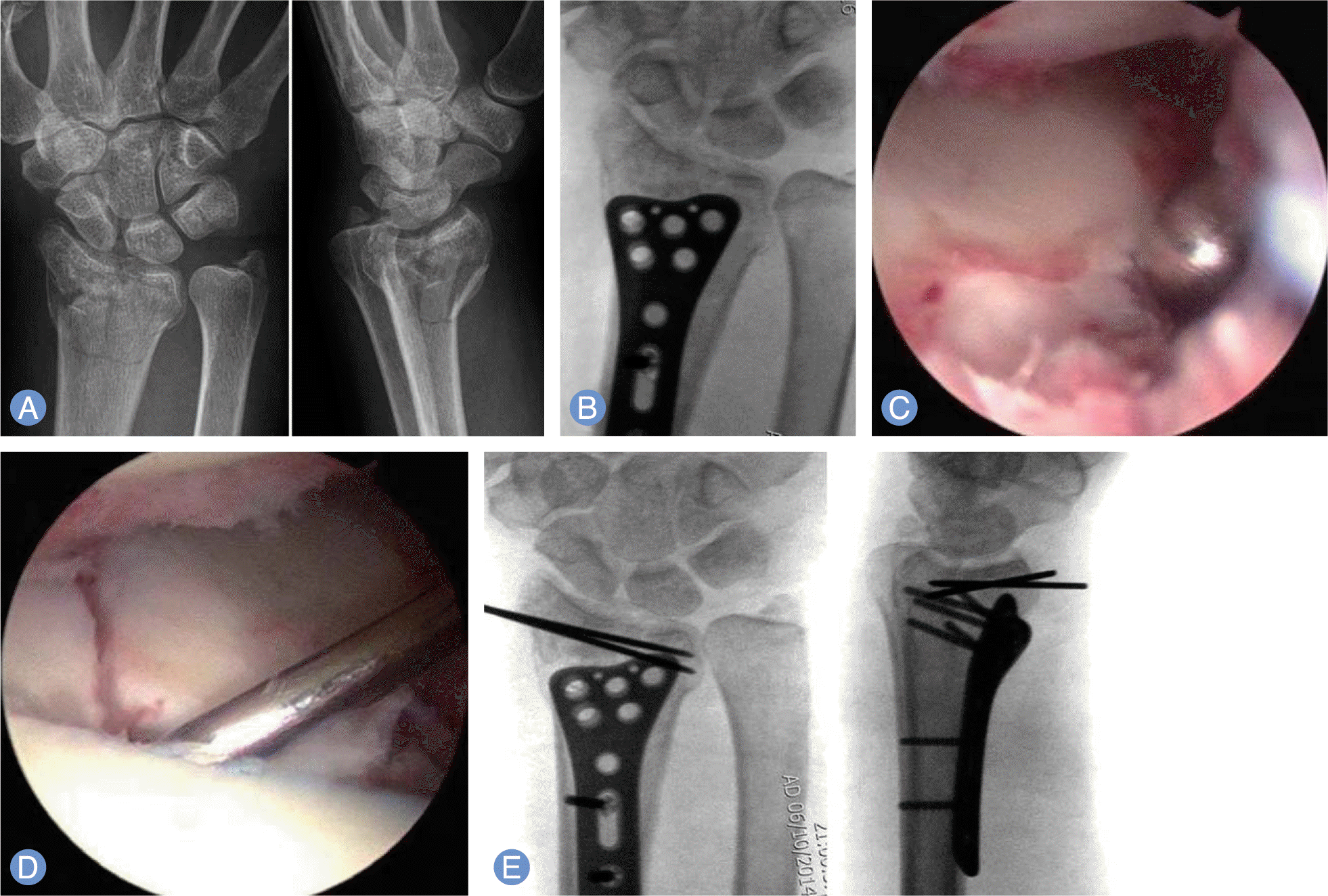 | Fig. 3.
(A) Preoperative radiographs of 54-year-old female show intra-articular comminuted fracture of left distal radius. (B) Intraoperative radiograph shows volar locking plate preset after anatomical alignment was regained under an image intensifier. (C, D) Arthroscopic images show the restoration of the articular surface after reduction. (E) The plate was securely fixed with locking screw after temporary K-wire fixation. |
Table 1.
Arthroscopic classification of interosseous ligament injury




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download